An Offer You Can’t Refuse
How US Federal Prosecutors Force Drug Defendants to Plead Guilty
Summary
Darlene Eckles let her drug-dealing brother operate from her house for six months and helped count his money. Federal prosecutors offered to let her plea to a 10-year sentence; she rejected the offer and is now serving an almost 20-year sentence.
Federal prosecutors offered to let Patricio Paladin plead in return for a 20-year sentence for cocaine distribution. He refused to plead and is now serving a sentence of life without parole.
Weldon Angelos was offered a plea of 15 years for marijuana distribution and gun possession. He refused the plea and is now serving a 55-year sentence.
Eckles, Paladin, and Angelos were convicted of federal drug and gun offenses after rejecting plea offers and opting instead to go to trial. Prosecutors sought their remarkably long sentences—at least double the time they would have served had they agreed to plead—not only for their crimes, but for refusing to plead guilty on the prosecutors’ terms.
***
The right to trial lies at the heart of America’s criminal justice system. Yet trials have become all too rare in the United States because nine out of ten federal and state criminal defendants now end their cases by pleading guilty.
There is nothing inherently wrong with resolving cases through guilty pleas—it reduces the many burdens of trial preparation and the trial itself on prosecutors, defendants, judges, and witnesses. But in the US plea bargaining system, many federal prosecutors strong-arm defendants by offering them shorter prison terms if they plead guilty, and threatening them if they go to trial with sentences that, in the words of Judge John Gleeson of the Eastern District of New York, can be “so excessively severe, they take your breath away.”[1] Such coercive plea bargaining tactics abound in state and federal criminal cases, including federal drug cases, the focus of this report.
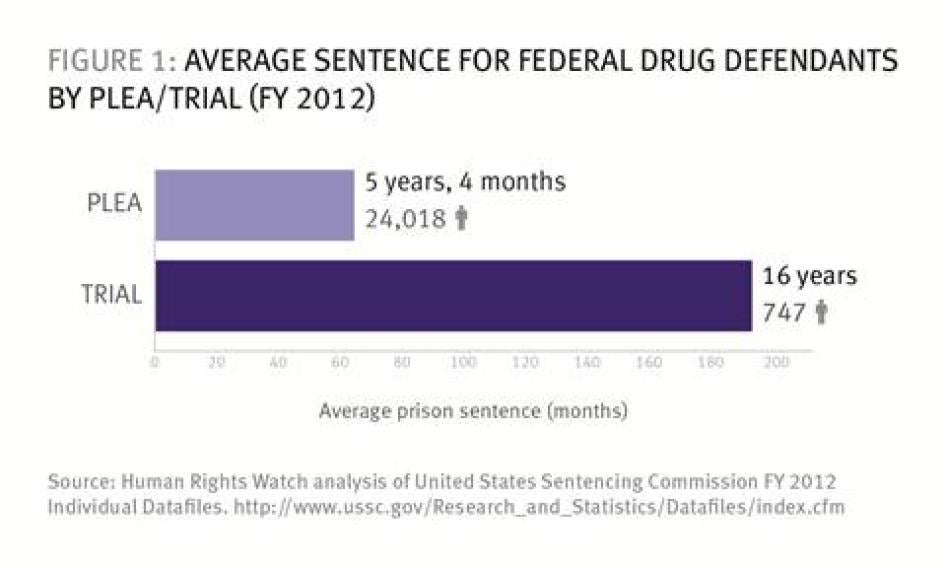
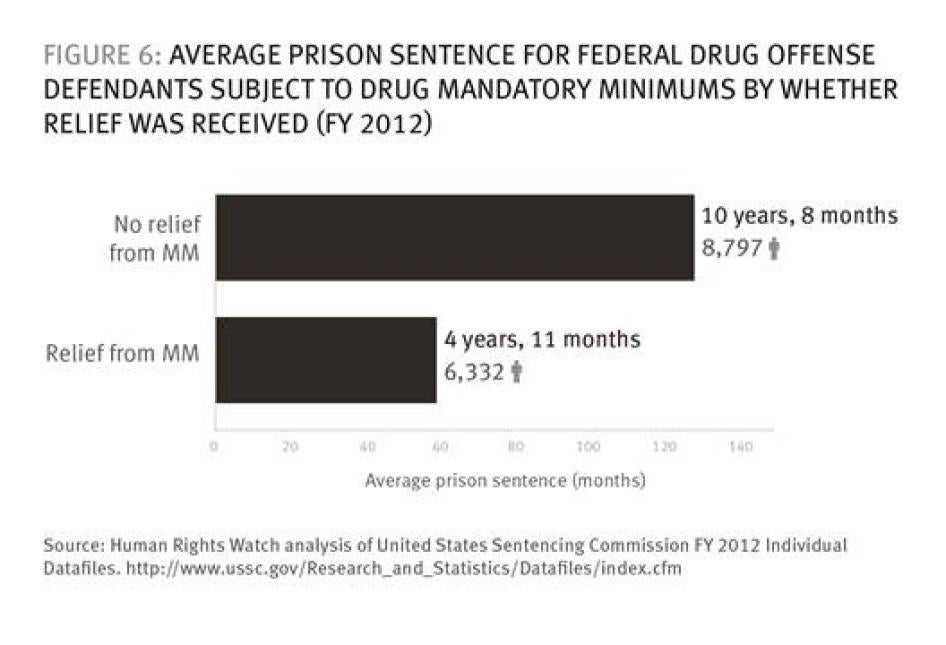
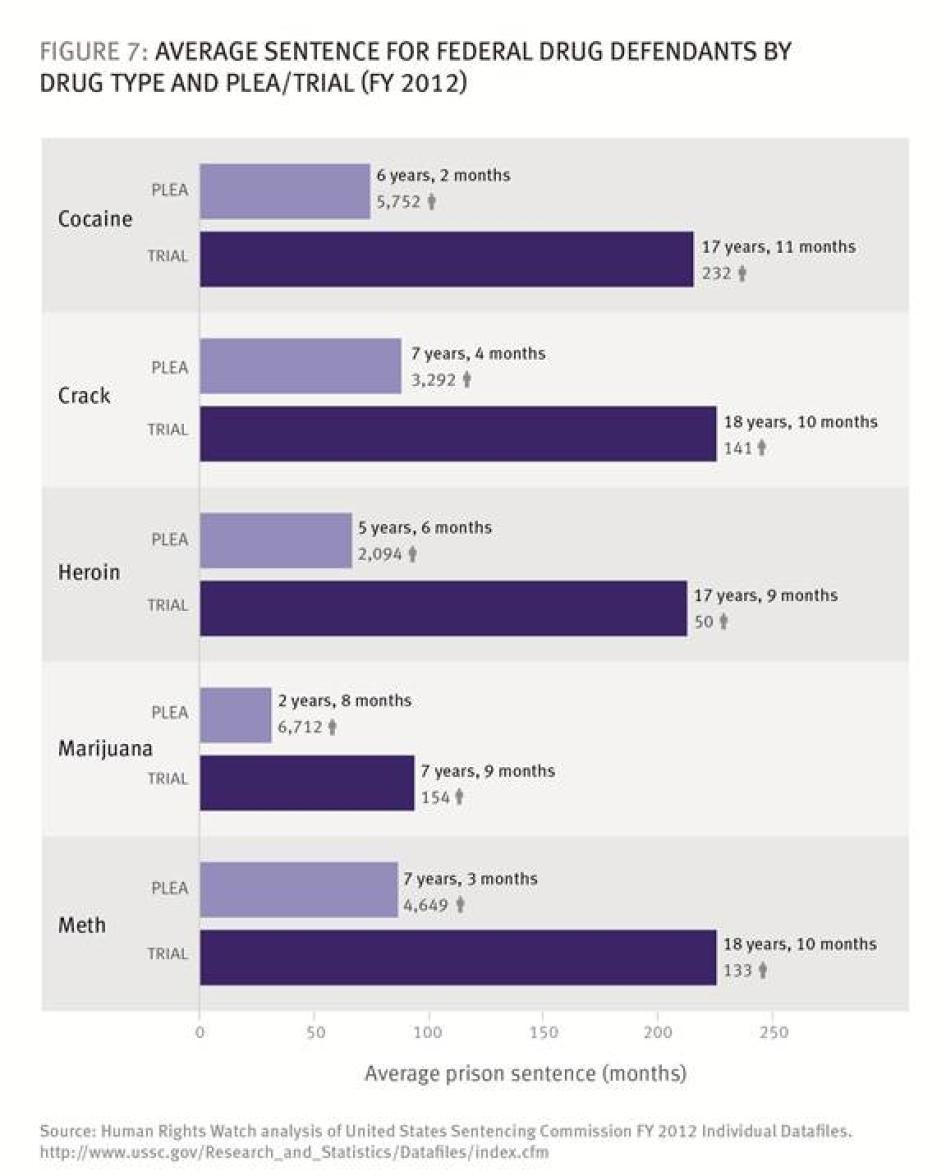
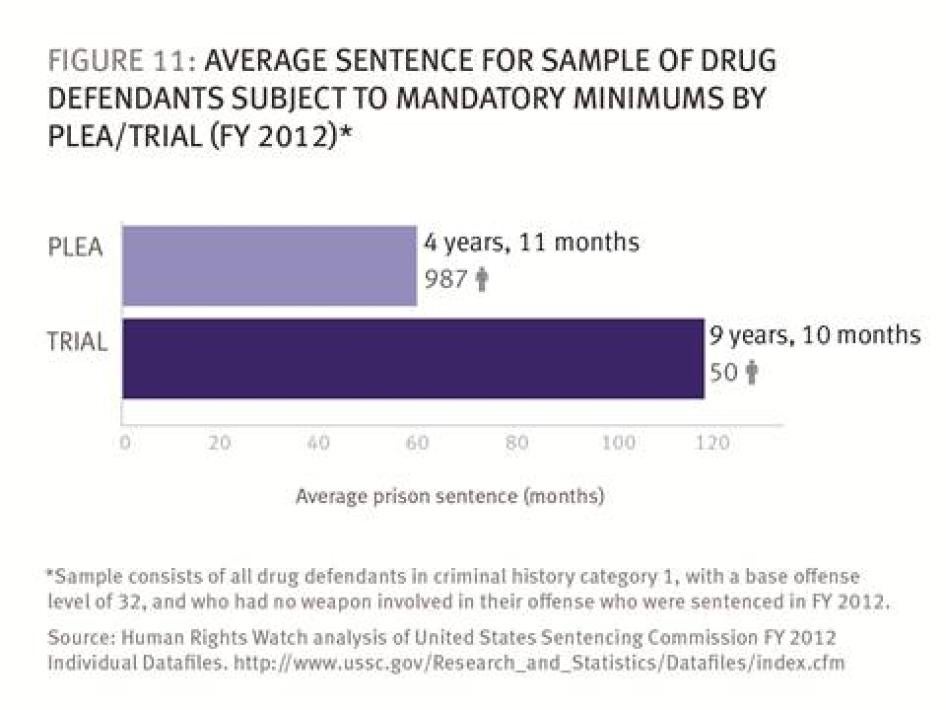
Plea bargaining means higher sentences for defendants who go to trial. In 2012, the average sentence of federal drug offenders convicted after trial was three times higher (16 years) than that received after a guilty plea (5 years and 4 months).
The threat of higher sentences puts “enormous pressure [on defendants] to plead,” Mary Pat Brown, a former federal prosecutor and senior official in the Justice Department told us.[2] So much so that plea agreements, once a choice to consider, have for all intents and purposes become an offer drug defendants cannot afford to refuse. Only three percent of federal drug defendants go to trial. Human Rights Watch believes this historically low rate of trials reflects an unbalanced and unhealthy criminal justice system.
In this report, Human Rights Watch presents cases that illustrate the unjust sentences that result from a dangerous combination of unfettered prosecutorial power and egregiously severe sentencing laws. We also present new data developed for the report that documents the extent of the “trial penalty”— the higher sentences that defendants who go to trial incur compared to what they would receive if they plead guilty. In essence, it is the price prosecutors make defendants pay for exercising their right to trial.
US constitutional jurisprudence offers scant protection from prosecutors who are willing to pressure defendants into pleading and punish those who insist on going to trial. Courts do not view defendants as unconstitutionally coerced to forego their right to a trial if they plead guilty to avoid a staggering sentence. Nor do they consider defendants to have been vindictively—that is, unconstitutionally—punished for exercising their right to trial when prosecutors make good on their threats to seek much higher mandatory penalties for them because they refused to plead. Finally, even when courts agree that prosecutors have sought egregiously long mandatory sentences for drug offenses, they will not rule the sentences so disproportionate as to be unconstitutionally cruel.
Prosecutorial Power and Mandatory Sentences
Prosecutors have discretion, largely unreviewable by judges, as to what charges to bring, what promises or threats to make in plea bargaining, and whether to carry out those threats if the defendant does not plead.
While all prosecutors are in a powerful position vis-a-vis criminal defendants, the power of federal prosecutors in drug cases is strengthened by mandatory sentencing laws that curtail the judiciary’s historic function of ensuring the punishment fits the crime. When prosecutors choose to pursue charges carrying mandatory penalties and the defendant is convicted, judges must impose the sentences. Prosecutors, in effect, sentence convicted defendants by the charges they bring.
Prosecutors typically charge drug defendants with offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences. Mandatory minimum drug sentences are keyed to the weight of the drugs involved in the offense (and the weight of filler substances, like cornstarch, used to dilute the drug). For example, the mandatory minimum sentence for dealing 5 kilograms of cocaine is 10 years and the maximum is life, regardless of the defendant’s role or culpability. The sentence imposed upon conviction will usually be higher than the minimum, as judges—taking their cue from the federal sentencing guidelines—take into account the actual amount of drugs involved in the crime, the defendant’s criminal history, and other aggravating and mitigating factors.
In fiscal year 2012, 60 percent of convicted federal drug defendants were convicted of offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences.[3] They often faced sentences that many observers would consider disproportionate to their crime. An addict who sells drugs to support his habit can get a 10-year sentence. Someone hired to drive a box of drugs across town looks at the same minimum sentence as a major trafficker caught with the box. A defendant involved in a multi-member drug conspiracy can face a sentence based on the amount of drugs handled by all the co-conspirators, even if the defendant had only a minor role and personally distributed only a small amount of drugs or none at all.
Drug defendants have only three ways to avoid mandatory sentences: they can go to trial and hope for an acquittal, even though nine out of ten defendants who take their chances at trial are convicted; they may (if they are a low-level, nonviolent drug offender with scant criminal history) qualify for the limited statutory safety valve that permits judges to sentence them below the applicable mandatory sentences if they are convicted—although most defendants do not qualify; and they can plead guilty.
Most prosecutors will offer drug defendants some sort of plea agreement that reduces their sentence, sometimes substantially. Indeed, they file charges carrying high sentences fully expecting defendants to plead guilty. To secure the plea, prosecutors may then offer to lessen the charges, they may offer to reduce the ones that do not carry mandatory sentences, to stipulate to sentencing factors that lower the sentencing range under the sentencing guidelines or, at the very least, to support a reduced sentence based on the defendant’s willingness to accept responsibility for the offense, i.e., to plead guilty. Prosecutors may also agree to file a motion with the court to permit the judge to sentence below the mandatory sentences when the defendant has provided substantial assistance to the government’s efforts to prosecute others.
But prosecutors also threaten to increase defendants’ sentences if they refuse to plead. Perhaps their most powerful threats are based on two statutory sentencing provisions that can dramatically increase a drug defendant’s sentence. Under 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1) prior felony drug convictions can dramatically increase a mandatory minimum drug sentence. Under 18 U.S.C. §924(c) prosecutors can file charges that dramatically increase a defendant’s sentence if a gun was involved in the drug offense. Prosecutors will threaten to pursue these additional penalties unless the defendant pleads guilty – and they make good on those threats.
Prior Convictions
Sentencing enhancements based on prior drug convictions are triggered only if prosecutors choose to file a prior felony information with the court. If a prosecutor decides to notify the court of one prior conviction, the defendant’s sentence will be doubled. If the prosecutor decides to notify the court of two prior convictions for a defendant facing a 10-year mandatory minimum sentence on the current offense, the sentence increases to life—and there is no parole in the federal system.
Many defendants plead when faced with the threat of such sentences. Early in 2013, for example, Lulzim Kupa refused to plead even though he was looking at a mandatory minimum of 10 years for distributing cocaine. A few weeks before the scheduled trial date, the government filed a prior felony information providing notice of two prior marijuana convictions. It then offered to withdraw the notice (as well as the original 10-year mandatory minimum) if Kupa would plead to a lower charge. He did, and avoided the prospect of life in prison—eventually receiving a sentence of 11 years.[4]
Involvement of Weapons
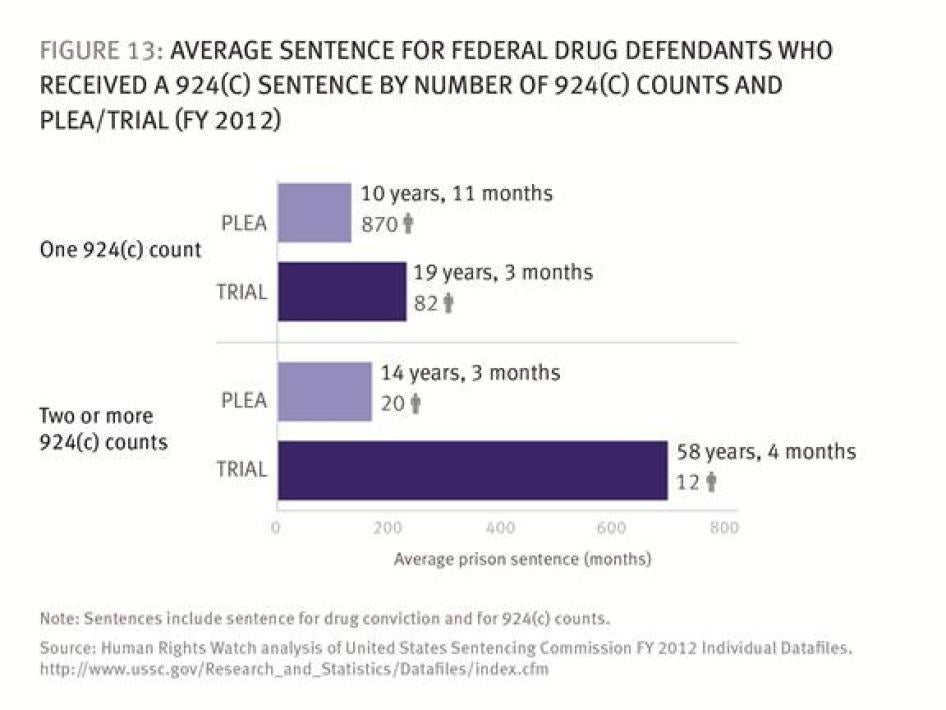
If a weapon was involved in a drug offense, prosecutors will press the defendant to plead by raising the specter of consecutive sentences under 18 U.S.C §924(c). The first §924(c) conviction imposes a mandatory five-year sentence consecutive to the sentence imposed for the underlying drug crime; second and subsequent convictions each carry 25-year consecutive sentences—resulting in grotesquely long sentences for drug defendants. In 2004 for example, Marnail Washington, a 22-year-old with no criminal history, was sentenced to 40 years after conviction of possession with intent to distribute crack cocaine and two §924(c) counts based on possessing, but not using, guns in connection with his drug offenses. That is, 30 years of his 40-year sentence were on gun counts.
It is entirely up to prosecutors whether to pursue these increased penalties against an eligible defendant. If they do and the defendant is convicted, the penalties are mandatory and judges must impose them. In one case in 2002, Judge Paul Cassell was so distressed at his powerlessness to avoid imposing an unduly harsh sentence on a young marijuana dealer (55 years for convictions on three §924(c) counts) that in his sentencing memorandum he called on President George W. Bush to commute the sentence. The president did not do so. And in a 2010 case, Judge Kiyo Masumoto said that she thought a 20-year sentence was “quite more than necessary” in the case of Tyquan Midyett, a low-level drug dealer who refused a 10-year plea and the prosecutors then doubled his sentence by filing a prior felony §851 information. Still, the judge said she did “not have discretion under the law to consider a lesser sentence.”[5]
Punishment to Fit the Crime?
Under well-established criminal justice principles, reflected in US and international human rights law, convicted criminal offenders should receive a punishment commensurate with their crime and culpability and no longer than necessary to serve the legitimate purposes of punishment. Those purposes include holding offenders accountable for their wrongdoing, protecting the public by keeping them in prison, deterring crime, and rehabilitating the offenders. They do not include penalizing defendants for going to trial or discouraging future defendants from doing so.
Prosecutors nonetheless believe a defendant’s insistence on going to trial is a perfectly legitimate reason to pursue an increased sentence—even one that is wholly disproportionate to the underlying offense. As a former US Attorney told us: “We weren’t trained to think about the lowest sentence that serves the goals of punishment.” [6]
Even prosecutors who try to achieve fair sentences through plea bargains acknowledge that the quest for fairness ends if the defendant refuses to plead. Prosecutors also insist they are not "punishing" defendants with higher sentences when they refuse to plead guilty, but rather “rewarding” defendants who, by pleading, spare them the expenditure of time and resources needed for a trial. From the perspective of the defendant looking at a significant trial penalty, this is no distinction.
Once they have made a threat during plea negotiations, prosecutors believe they must follow through with it if the defendant goes to trial, both because a defendant who refuses to plead deserves “no mercy,” and because they want to be sure future defendants take their threats seriously. They think they will lose credibility if they permit defendants to reap the same sentencing "concessions" after a trial as they had been offered if they pled. Asked if they thought these much higher post-trial sentences are just, prosecutors dodged the question.
In 2012, 26,560 federal drug defendants were prosecuted by 93 US Attorneys and over 5,400 assistant US attorneys in 94 federal districts.[7] Determining prosecutorial practices and policies in each district is beyond the scope of this report. Our research shows that prosecutorial charging and plea bargaining practices vary dramatically from district to district. It also shows that the trial penalty is widespread across the country.
Key Findings
Using sentencing data from individual cases collected nationwide by the United States Sentencing Commission (the Sentencing Commission), most of it from 2012, Human Rights Watch has developed statistics that shed light on the size of the trial penalty. Each case contains a unique mix of factors that results in the final sentence, but our findings nonetheless provide deeply troubling evidence of the price defendants pay if they refuse to plead.
Among our findings:
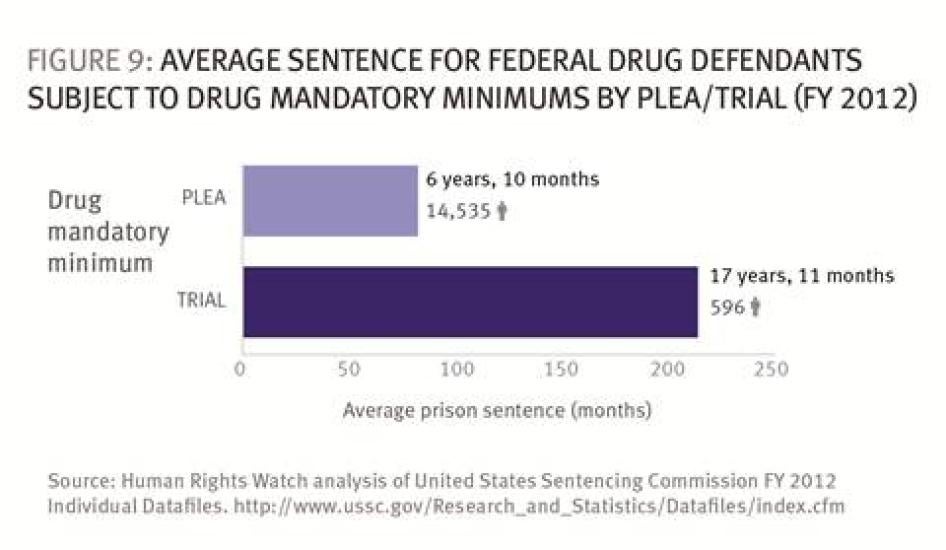
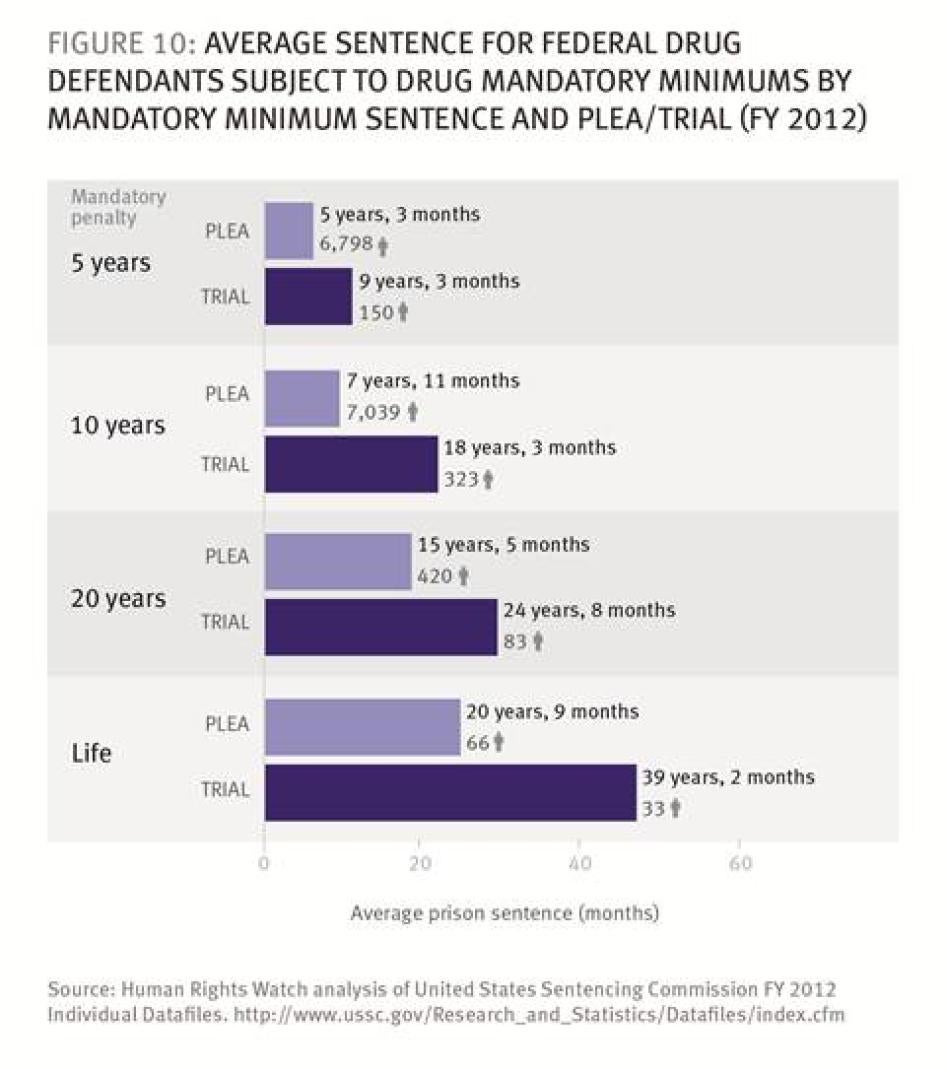
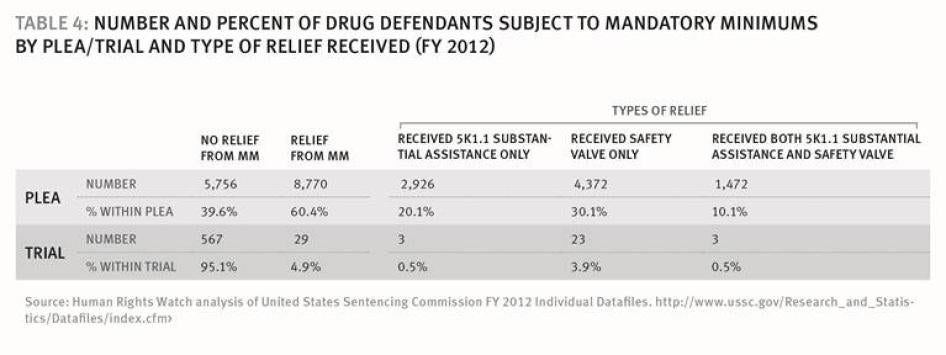
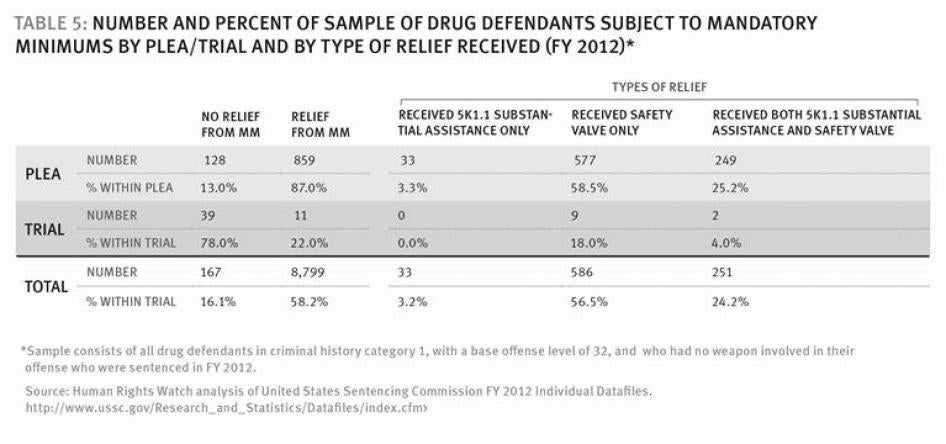
- Defendants convicted of drug offenses with mandatory minimum sentences who went to trial received sentences on average 11 years longer than those who pled guilty (215 versus 82.5 months).
- Among first-time drug defendants facing mandatory minimum sentences who had the same offense level and no weapon involved in their offense, those who went to trial had almost twice the sentence length of those who pled guilty (117.6 months versus 59.5 months).
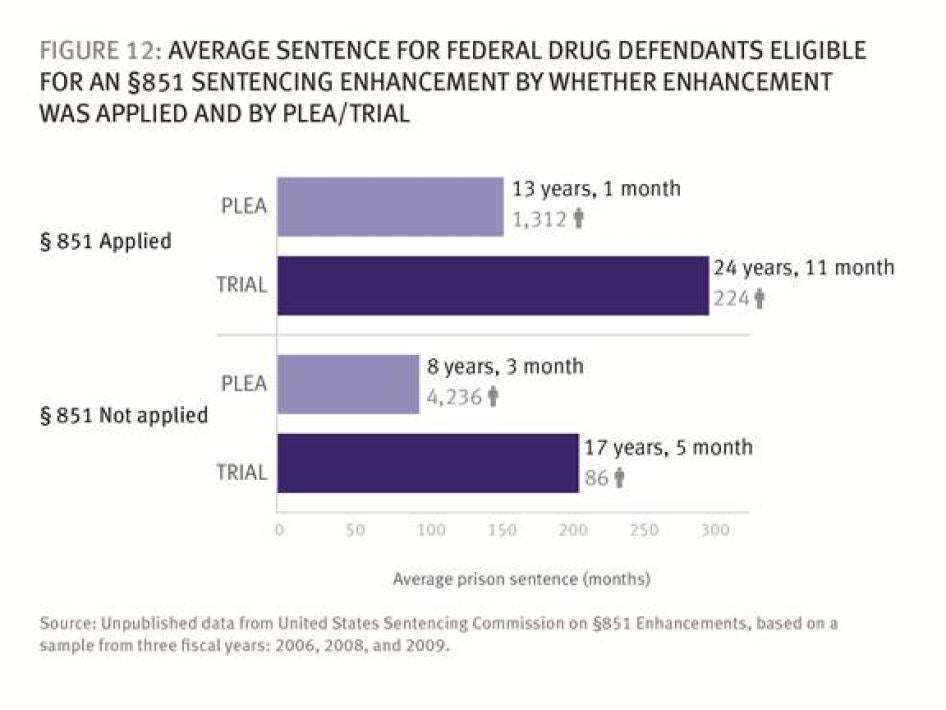
- Among defendants who were eligible for a sentencing enhancement because of prior convictions, those who went to trial were 8.4 times more likely to have the enhancement applied than those who plead guilty.
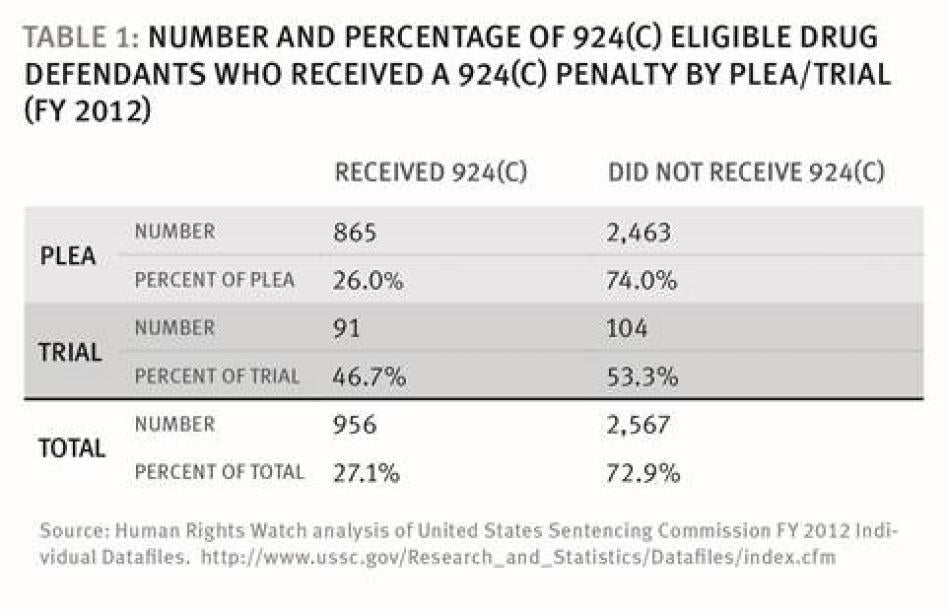
- Among drug defendants with a weapon involved in their offense, those who went to trial were 2.5 times more likely to receive consecutive sentences for §924(c) charges than those who pled guilty.
These statistics cannot fully capture the leverage that prosecutors exert over individual defendants during plea bargaining. If a prosecutor’s threats are made orally, there may be no written record of them. During hearings, when the judge makes a decision whether to accept a plea agreement, it is rare for prosecutors, defense counsel, or defendants to mention the sentencing risk defendants faced if they did not plead.
The following case exemplifies the dire consequences that result when prosecutors made good on their threats to pursue increased sentences for a defendant who refuses to plead. A prosecutor who was willing to accept a plea that gave the defendant a 10-year sentence, was willing to have her sentenced to life without parole because she insisted on going to trial.
Sandra Avery[8]Sandra Avery was a survivor of childhood sexual abuse who served in the army and the army reserves, earned a college degree, overcame an addiction to crack, became a born-again Christian, and worked as an accountant. But in her early forties, her life spun out of control: she became addicted to crack cocaine again, lost her job, and started delivering and selling small amounts of crack for her husband, a crack dealer. In 2005, Avery was arrested and indicted by a federal grand jury for possessing 50 grams of crack with intent to deliver, an offense then carrying a mandatory minimum sentence of 10 years. Avery refused to enter into a plea agreement with the government because it did not offer anything less than 10 years and because, as she says, “I simply was not in my right mind at the time.” She was convicted after trial, and sentenced to life. Because there is no parole in the federal system, she will remain in prison until she dies. The life sentence resulted from the government’s choice to trigger a sentencing enhancement based on Avery’s previous drug convictions. During the early 1990s, she had been convicted three times under Florida law for possessing small amounts of crack for her personal use; she told Human Rights Watch that the value of drugs in those three cases amounted to less than $100 and she was sentenced to community supervision. When Human Rights Watch asked Avery’s prosecutor why he sought the enhancement in her case, he said “because it applied.” He said the policy in his office is to seek such enhancements whenever they are applicable, although there is “room to negotiate” if a defendant pleads guilty and agrees to cooperate with the government. His office policy also permits prosecutors to seek approval from their superiors not to file for the enhancement, which did not happen in Avery’s case. Asked whether he thought Avery’s life sentence was just, he refused to comment. |
A Call for Federal Reform
In an August speech to the American Bar Association, Attorney General Eric Holder endorsed the need to reform federal sentencing laws and practices to reduce the number of people sent to prison and the length of their sentences.
Identifying “just sentences” for low-level, nonviolent drug defendants as a Department of Justice priority, Holder issued a memorandum to federal prosecutors instructing them to avoid charging offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences for certain low-level, nonviolent offenders. He also directed prosecutors to avoid seeking mandatory drug sentencing enhancements based on prior convictions when such severe sentences are not warranted.
It is too soon to tell how prosecutors will carry out the new policies: they contain easily-exploited loopholes and do not prohibit prosecutors from pursuing harsh sentences against a defendant who refuses to plead. Moreover, there is no remedy if prosecutors ignore the letter or spirit of Holder’s policies. If a defendant is convicted, the judge must impose the applicable mandatory minimum sentence or sentencing enhancement sought by the prosecutor.
A recent case in which the defendant was sentenced after Holder issued his memorandum suggests some prosecutors may continue to seek egregiously long sentences for drug defendants who refuse to plead.
Roy Lee Clay[9]On August 27, 2013, a federal court sentenced part-time house remodeler, Roy Lee Clay, 48, to life behind bars without possibility of parole. He was convicted after trial of one count of conspiring to distribute one kilogram or more of heroin—a crime that normally carries a 10-year sentence. Prosecutors asserted he was part of a 14-person heroin trafficking group centered in Baltimore, Maryland, and that for two-and-a-half years, Clay distributed heroin to other dealers and to users as well. There was no evidence in his case that he used violence to further his drug activities. Clay had two prior drug convictions: a 1993 federal conviction for possession with intent to distribute 100 grams of a mixture containing heroin for which he was sentenced to 87 months in prison, and a 2004 state conviction for possession with intent to distribute controlled substances. The government offered to let Clay plead to 10 years on the drug charges. It also threatened to file an information with the court seeking a penalty enhancement to life based on the two prior convictions if Clay insisted on going to trial. He rejected the plea offer and went to trial, which ended with a hung jury. The government renewed the 10-year plea offer, but Clay again refused. After the second trial, Clay was convicted. The government made good on its threat and sought the mandatory enhancement based on the two prior convictions. Previously willing to accept a 10-year sentence, prosecutors ensured Clay would spend the rest of his life behind bars. At his sentencing, Judge Catherine Blake called the life without parole sentence “extremely severe and harsh.” [10] One prosecutor in the case told Human Rights Watch he thought the life sentence was consistent with the Attorney General’s August 2013 memorandum instructing prosecutors to seek prior conviction enhancements only in cases in which such severe sanctions are appropriate. Still, he refused to explain why he thought Clay deserved a life sentence. |
Looking Ahead
As an organization dedicated to enhancing respect for and protection of human rights, Human Rights Watch insists that individuals who violate the rights of others be held accountable for their crimes. We also insist that all people accused of crimes have fair legal proceedings to determine their guilt.
Plea agreements do not necessarily violate human rights; defendants may choose to give up their right to trial in return for a sentencing concession. Nevertheless, plea bargaining as practiced in US federal drug cases raises significant human rights concerns. It is one thing for prosecutors to offer a modest reduction of otherwise proportionate sentences for defendants who plead guilty and accept responsibility for their offense. Such a discount does not offend human rights.
But the threat of a large trial penalty is unavoidably coercive and contrary to the right to liberty and to a fair trial. In some cases, the sentences imposed on drug defendants who refused to plead are so disproportionately long they qualify as cruel and inhuman.
Momentum is growing to end nearly three decades of harsh sentences for federal drug offenders amid growing realization that the US cannot incarcerate its way out of drug use and abuse, and that long sentences neither ensure public safety nor strengthen communities. There is also growing and welcome national recognition that meaningful reform of federal drug laws must include restoring sentencing discretion to federal judges.
We believe Congress should eliminate mandatory minimum drug sentences: the one-size-fits-all approach of the mandatory minimum statutes prevents sentences tailored to the individual case. Congress should also eliminate mandatory penalties based on prior convictions or guns. With sentencing guidelines and appellate review to keep judicial sentencing discretion within appropriate bounds, there is no need for mandatory punishments that primarily serve to coerce defendants into pleading guilty, an unacceptable exercise of government power.
A sound criminal justice system, like all forms of good government, needs checks and balances. Prosecutors should have charging discretion and be encouraged to exercise it carefully and fairly. But the final say over sentences defendants receive must come from independent federal judges who have no personal or institutional stake in the outcome of a case other than to ensure justice is done and rights are respected. Judges with sentencing discretion could end the disgraceful trial penalty in federal drug cases and ensure defendants receive sentences reflecting their crimes, not their willingness to plead.[11]
Recommendations
Human Rights Watch offers the recommendations below to end the prosecutorial practice of coercing drug defendants into guilty pleas with threats of draconian sentences. Our recommendations address both the need for reform of the federal sentencing regime and the need for constraints on prosecutorial plea bargaining practices.
Our most important recommendation is for Congress to restore sentencing discretion to the federal judiciary. While mandatory punishment is not the only factor that convinces defendants to plead guilty, there is no question prosecutors coerce many pleas because they can threaten exorbitant mandatory sentences for defendants who go to trial. If federal judges had authority to review and revise drug sentences to ensure they satisfy the requirements of justice, it would diminish the power of prosecutorial threats.
Our recommendations would not eliminate plea bargaining. Prosecutors could offer modest sentence reductions to reward defendants who choose to plead guilty. But prosecutors would no longer be able to force defendants to plead to avoid grotesquely long sentences. They would be required to charge offenses carrying sentences proportionate to the defendant’s crime and culpability, they would be limited in the extent of the discount from those sentences that could be offered in exchange for the defendant’s willingness to plead guilty, they would be prohibited from threatening superseding indictments with higher charges in order to secure a plea and, finally, they would be prohibited from filing such indictments to punish defendants who refuse to plead.
To Congress
- End mandatory minimum drug sentences and
restore to judges the ability to calculate proportionate sentences in all drug
cases, taking into account the sentencing guidelines for federal drug
defendants. Congress should enact legislation to:
- Abolish federal mandatory minimums for drug offenders based upon the quantity of the drug involved.
- Abolish mandatory sentence increases based on the number and nature of prior convictions.
- Abolish mandatory consecutive sentences for drug defendants who use, carry, or possess firearms in connection with their drug crime.
To the Attorney General
- Establish just sentences as a Department of Justice goal for all drug offenders regardless of whether they plead guilty or go to trial. Define just sentences as those which are proportionate to the defendant’s individual conduct and culpability and which are no longer than necessary to further the purposes of punishment in each individual case.
- Direct prosecutors to seek indictments only for charges that would yield a fair and proportionate sentence for each individual defendant in light of the facts known about that defendant. If an offense carrying a fair sentence has been charged, prosecutors may offer a modest sentencing benefit to reward a defendant for pleading guilty, but should not offer to reduce the defendant’s sentence to such an extent as to coerce the defendant into waiving the right to trial. We urge the Department of Justice to establish parameters for what such a modest reward might be. In addition, the Department of Justice should explicitly prohibit prosecutors from: 1) threatening higher sentences to secure pleas from drug defendants and 2) filing superseding indictments that raise the sentence faced by a defendant solely because the defendant refused to plead guilty.
Methodology
This report is based on the following sources of information: interviews; federal cases, legal articles, and other literature on drug cases and plea bargaining; and sentencing statistics.
Human Rights Watch interviewed scores of individuals with deep knowledge of federal sentencing practices, including 7 federal district judges, 4 current or former US Attorneys, 18 current or former assistant US attorneys, and 40 federal public defenders and defense counsel in private practice (not including former prosecutors now in private practice). We also talked with academics and public policy advocates and corresponded with a handful of federal prisoners serving sentences for drugs. The names of most current and former prosecutors and private attorneys have been kept confidential at their request.
We reviewed court decisions and documents filed in hundreds of cases. The documents filed in individual court cases were available through PACER (Public Access to Court Electronic Records). Unfortunately, plea bargains were often not available to view on PACER. Similarly, documents that refer to or reflect cooperation with the government by a defendant are often sealed and not available to view. Presentencing reports filed by probation officials are also confidential and not available for public viewing on PACER.
All statistics in this report regarding the sentencing of federal drug defendants originated in sentencing data maintained or published by the United States Sentencing Commission (the Sentencing Commission). Where possible, we relied on relevant data published by the Sentencing Commission in various reports and documents. We used data available from the Sentencing Commission’s publically accessible Monitoring Datafile for Fiscal Year 2012 to develop findings regarding the sentencing consequences for federal drug offenders of pleading guilty versus going to trial. Analysis was limited to federal drug defendants for whom the Sentencing Commission received full documentation from the courts. Of the 26,560 drug offenders in the Sentencing Commission’s files for fiscal year 2012, there was enough data to analyze 24,765 or 93 percent of them.
We also used unpublished data, developed by the Sentencing Commission, on the proportion in each federal district of drug defendants eligible for prior drug conviction enhancements and the rate at which such enhancements were applied to eligible defendants. We also used commission data on the average sentences for defendants based on whether they were convicted by plea or after trial and by whether the sentencing enhancement was applied. The Sentencing Commission developed this data by analyzing samples of 3,050 cases from fiscal year 2006, 5,434 cases from fiscal year 2008, and 5,451 cases from fiscal year 2009.[12] The Sentencing Commission provided the data to Judge Mark Bennett, who used them in a recent decision and shared it with us.[13]
I. Federal Drug Sentencing and Swollen Federal Prison Populations
Since the modern day anti-drug effort began in the mid-1980s, vigorous federal drug law enforcement and harsh sentences have fueled the soaring federal prison population and resulted in large numbers of prisoners serving long drug sentences in federal prisons.[14]
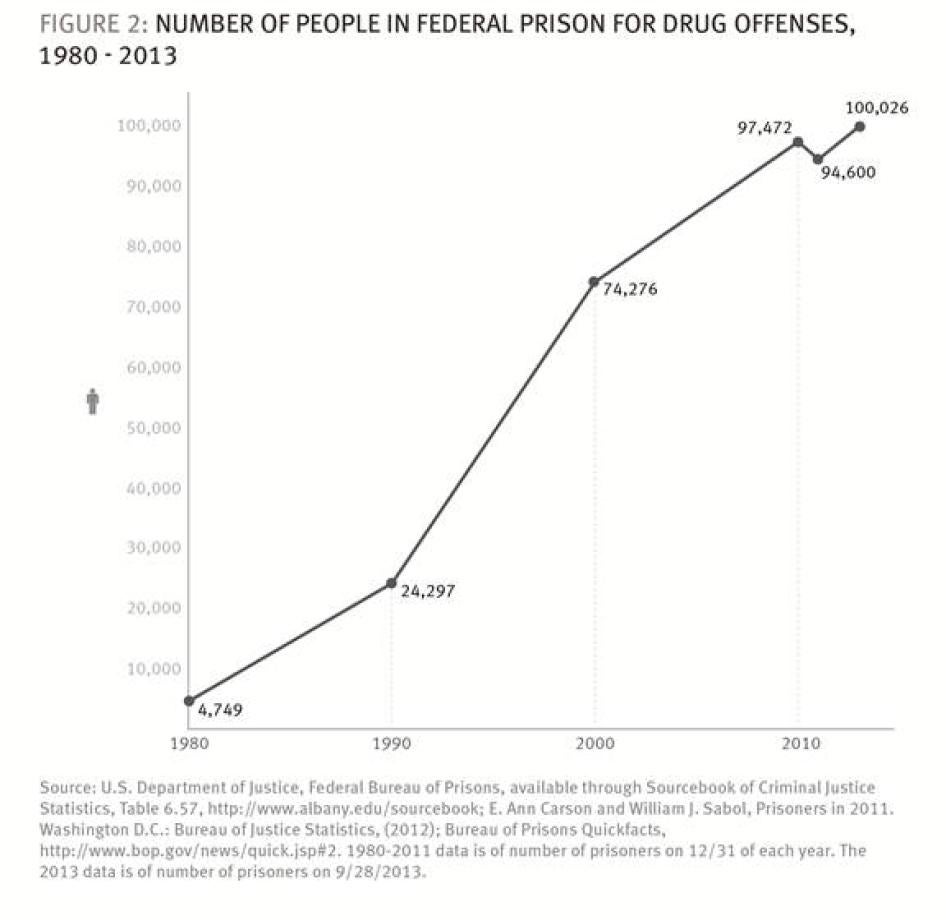
Between 1980 and 2013, the number of incarcerated federal drug defendants soared from 4,749 to 100,026—an astonishing 2,006 percent. As of September 28, 2013, half—50.1 percent—of all federal prisoners were serving time for drug offenses.[15] In fiscal year 2012 alone, 26,560 men and women were convicted of federal drug crimes.[16]
Counter to popular belief, most drug offenders are not kingpins or the most serious drug offenders. As one former US Attorney told Human Rights Watch,
The public simply does not realize how many low-level guys are in [federal] prison.… We lock up the lowest fruit in drug conspiracies. I once asked another US Attorney with 30 years as a prosecutor how many times he’d put a major drug player in prison. He said he could count them on one hand.[17]
In fact, the most common functions of convicted federal drug defendants were courier (23 percent), followed by wholesaler (21.2 percent) and street-level dealer (17.2 percent), according to an analysis of drug offender function by the Sentencing Commission.[18] The Sentencing Commission has also calculated that 93.4 percent of federal drug defendants were in the lower or middle tiers of the drug business.[19] In 2012, 85 percent of drug defendants had no weapon involved in their offense, a crude proxy for determining whether the defendant’s conduct was violent.[20] Fifty-three percent had either an insignificant or no state or federal criminal history.[21]
The average federal drug sentence has increased 250 percent since 1987 when the Sentencing Commission published its guidelines.[22] In 2012, the average sentence length for all defendants sentenced for federal drug trafficking offenses was 68 months.[23] The Urban Institute, a private research and policy organization, has calculated that the increase in sentence length for federal drug offenders “was the single greatest contributor to growth in the federal prison population between 1998 and 2010.”[24]
The federal government and the states have overlapping laws establishing criminal sanctions for drug-related conduct, and federal law enforcement agents and prosecutors do not have to defer to state prosecutions.[25]
There are 94 districts in the federal criminal justice system. Prosecutors in each district operate under the same federal statutes defining crimes and setting out criminal procedures, and are subject to policies set by the Department of Justice.
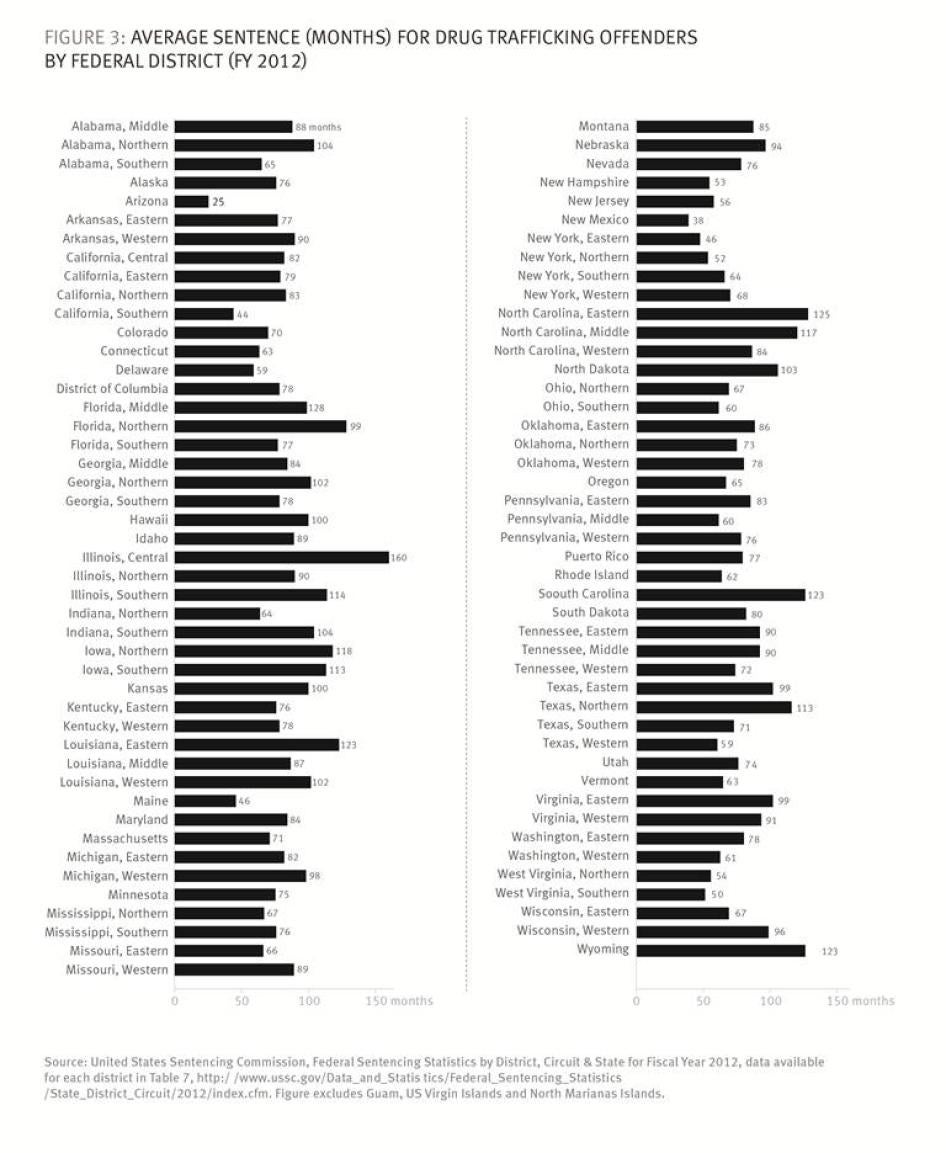
But each district office also has considerable autonomy, its own internal policies and culture, and its own ways of dealing with the local defense bar (which will also have its distinctive characteristics) and the particularities of the federal judges. The data we compiled for this report shows striking variation in the average sentences for federal drug offenders convicted of trafficking offenses across the federal districts (Figure 3).[26]
As seen in Figure 3, the average prison sentence was over 11 years longer in the central district of Illinois—the district with the highest average sentence—than in Arizona, the district with the lowest. The data and our research suggest that the differences to some extent reveal different policies and practices with regard to charging and plea bargaining.[27]
II. Federal Sentencing: Mandatory Sentences and Sentencing Guidelines
Sentencing guidelines and mandatory minimums deny the reality of life; they substitute formulas for reality.
—Judge Jed S. Rakoff, New York, March 18, 2013
In the mid-1980s, Congress dramatically changed sentencing in federal criminal cases. Seeking certainty, uniformity, and severity, Congress stripped the federal judiciary of its ability to determine sentences in federal drug cases by establishing a sentencing regime of mandatory minimum sentences and mandatory sentencing guidelines. Somewhat inconsistently, it also instructed federal judges to impose sentences that were “not greater than necessary” to further punishment: i.e. retribution, incapacitation, deterrence, and rehabilitation.[28]
The new sentencing regime required longer sentences for federal drug offenders.[29] This, coupled with the abolition of federal parole in 1984, resulted in a remarkable increase in the time that federal drug offenders spend behind bars: from 1984 to 1991, their average prison time leaped from less than 30 to nearly 80 months.[30]
Whether a defendant is convicted by plea or after trial, the sentencing judge will impose a sentence based on statutorily mandated sentences and the sentencing guidelines. The guidelines are no longer mandatory, but judges must still take them into consideration when setting a sentence. If a defendant is convicted of an offense carrying a mandatory minimum sentence, the judge cannot sentence below that minimum unless the defendant either qualifies for an exemption under the so-called safety valve, or the government files a motion to waive the minimum because the defendant has provided substantial assistance to the government (see below in Section IV).
Sentences higher than the minimum can be imposed up to the maximum sentence permitted by statute. When a defendant is charged with offenses that do not carry mandatory minimum sentences, or if the defendant qualifies for relief from the minimum, then the judge sets the sentence by looking to the guidelines, and taking into account Congress’ sentencing directives.[31]
This section examines statutory minimum sentences that are keyed to the weight and type of drug, and how they were incorporated into the sentencing guidelines. Section III addresses provisions that trigger higher sentences for drug offenders based on their prior convictions or the use or possession of guns related to the drug offense.
Mandatory Minimum Drug Sentences
[Mandatory minimum sentences] are cruel, unfair, a waste of resources, and bad law enforcement policy. Other than that they are a great idea.[32]
—Former Federal District Judge John S. Martin, Jr. in Notre Dame Journal of Law
The punishment is supposed to fit the crime, but when a legislative body says this is going to be the sentence no matter what other factors there are, that’s draconian in every sense of the word. Mandatory sentences breed injustice.[33]
—Senior United States District Judge Roger Vinson, as quoted in The New York Times, December 12, 2012
With the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986 (ADAA), Congress enacted a mandatory minimum sentencing regime for federal drug crimes keyed to the weight and type of drug involved in the offense.[34] Passed with little deliberation or preparation,[35] the harsh new regime reflected the ascendancy of “tough on crime” policies, concern about drugs, violence, and racial tensions, and the belief severe sentences were needed to restore law and order.[36]
The centerpiece of the new drug sentencing scheme is five- and ten-year mandatory minimum sentences for drug trafficking—a term that encompasses possession with intent to distribute, distribution, or manufacturing.[37] Under current law, for example, a 10-year mandatory minimum sentence with a maximum term of life imprisonment is triggered by drug trafficking offenses involving 5 kilograms of powder cocaine, 280 grams of crack cocaine, or 50 grams of pure methamphetamine. A five-year mandatory minimum sentence with a maximum of forty years is triggered, for example, by 500 grams of powder cocaine, 28 grams of crack, or 5 grams of pure methamphetamine.
When it enacted the ADAA, Congress apparently thought the weight of the drugs involved would be a reasonable proxy for the drug trafficking role.[38] Unfortunately, it got the numbers wrong: even low-level offenders distribute the quantities that garner the five- and ten-year minimum sentences Congress intended for more serious traffickers.[39] According to a 2011 Sentencing Commission analysis, “the quantity of drugs involved in an offense was not closely related to the offender’s function in the offense.”[40] Federal prosecutors do not, however, limit charges carrying mandatory sentences to the drug offenders Congress had in mind. The Department of Justice,
[h]as turned a law that sought to impose enhanced penalties on a select few into a sentencing regime that imposes them on a great many, producing unfairly harsh consequences that Congress did not intend.[41]
Sixty percent of federal drug offenders sentenced in fiscal year 2012 were convicted of charges carrying a mandatory minimum sentence for their drug offense.[42] We do not know how many of the remaining 40 percent of defendants were originally charged with offenses that carried a minimum sentence reduced to non-mandatory minimum offense due to a plea bargain. From 1995 to 2010, the proportion of drug offenders in federal prison convicted of offenses carrying mandatory minimum penalties rose from 78.2 to 84.6 percent.[43]
In 2010, Jamel Dossie, a 20-year-old, small-time street-level drug dealer’s assistant earned about $140 acting as a go-between in four hand-to-hand sales totaling 88.1 grams or 3.1 ounces of crack. He was a “mope”—a person occupying the lowest rungs in the drug business. Prosecutors could have charged him under a statute that carried a sentencing range of 0 to 20 years.[44] Instead, they charged him with an offense carrying the five-year mandatory minimum sentence intended for mid-level offenders.[45] Judge John Gleeson felt a five-year sentence was “too severe” for a low-level addict selling drugs on the street, but was nevertheless required by the sentencing law to impose it.[46]
Conspiracy Laws: Ratcheting up the Drug Quantity
Conspiracy to commit a drug crime carries the same mandatory sentence as the underlying substantive crime.[47] Conspiracy law is complicated, but the bottom line is that prosecutors may charge defendants who are members of a drug conspiracy with a much greater quantity of drugs than they individually possessed or distributed, thereby ratcheting up the sentences they face and increasing the pressure on them to plead guilty.
A drug defendant can be treated as a co-conspirator if he knowingly and willingly entered into an agreement with one or more people to commit a narcotics related crime. As a co-conspirator, a defendant can be sentenced based on the amount of drugs possessed or distributed by the other members within the scope of the defendant’s agreement, as long as he knew or could reasonably have foreseen the amount. He does not have to be a leader or major player in the conspiracy; a minor role suffices to establish his responsibility.[48] Not surprisingly, as many cases in this report illustrate, prosecutors often charge drug defendants with conspiring to distribute drugs. They may then offer plea agreements that eliminate the conspiracy charge or otherwise reduce the quantity for which the defendant is held legally responsible.
Natacha Jihad Pizarro-Campos[49]Natacha Jihad Pizarro-Campos grew up in Puerto Rico and at the age of 20 moved to Florida. She was the mother of a young boy and had a history of mental illness and drug addiction. When Pizarro-Campos turned 21, she began working in a bar where she met Rafael Hernandez, a successful drug dealer. When Pizarro-Campos gave birth to a baby who died in a tragic accident, Hernandez paid for the funeral expenses. He also paid for Pizarro-Campos’ living expenses and supplied her with unlimited quantities of drugs for her personal use. In turn, he expected her to help him with his drug operation. One of the customers to whom she sold drugs on his behalf turned out to be a confidential informant. In June 2010, federal prosecutors in the Middle District of Florida secured an indictment against Pizarro-Campos and other defendants, charging them with conspiracy to distribute and possession with intent to distribute 500 grams or more of a substance containing methamphetamine. Pizarro-Campos pled guilty. In her plea agreement, Pizarro-Campos stipulated that she and others conspired to distribute between 1.5 and 5 kilograms of a mixture containing methamphetamine. She personally sold a total of 406.7 grams of methamphetamine in 5 transactions in 2009 and 2010. Under the guidelines, her sentence range for selling that amount would have been 70 to 87 months. But she had pled guilty to conspiracy to distribute 500 grams or more, which was punishable by a minimum prison term of 10 years and a maximum of life. She was sentenced to 10 years. |
Anthony Bowens[50]Anthony Bowens was one of 43 people indicted in 2005 for alleged participation in a multi-year crack conspiracy operating in a New York City public housing project. Bowens worked as a “pitcher,” collecting money from customers and providing them with the purchased cocaine in transactions arranged by his bosses. He had no managerial or supervisory role in the conspiracy. Bowens apparently joined the conspiracy in December 2003, at the tail end of the conspiracy’s 11-year history. The indictment set forth a single overt act involving Bowens, the sale of approximately 63 vials of crack on or about May 11, 2004.[51]As a member of a conspiracy that allegedly distributed 50 grams or more of crack, Bowens faced a 10-year mandatory minimum sentence and a guidelines range of 19.6 to 24.4 years (235 to 293 months).[52]Prosecutors gave Bowens a plea offer under which he would be permitted to plead guilty to a single count to distribute and possess with intent to distribute crack, an offense carrying a 5-year mandatory minimum sentence and a stipulated guidelines range of 70 to 87 months.[53]Owens chose to go to trial. The prosecutors could have filed a superseding indictment taking Bowens out of the conspiracy and simply charging him with possession with intent to distribute, but they did not. Bowens was convicted after a jury trial on the original conspiracy charge carrying a 10-year mandatory minimum. The government sought a sentence for Bowens within the guidelines range of about 19 to 24 years (235-293 months), a range predicated on a drug quantity of 1.5 kilograms of crack. Such a sentence would have greatly exceeded the sentences secured by defendants with similar roles in the conspiracy who pled guilty.[54] The judge sentenced him to 15 years, a sentence subsequently reduced to 12 years following the retroactive changes in 2010 to the guidelines for crack cocaine offenses. |
Mandatory Minimums: A Bad Idea at Best
When judges with lifetime tenure quit over the unfairness of [mandatory minimum] sentences, when dozen[s] of former federal prosecutors petition Congress to change such sentences, and when defense lawyers inundate the Executive Branch with complaints and pleas for clemency, it is clear that the downside of such sentences eclipses their usefulness in our federal sentencing scheme.[55]
—Professor Laurie L. Levenson, Loyola Law School, May 27, 2010
Mandatory minimums are one of the most significant obstacles to fair sentencing in the criminal justice system.Justice Anthony Kennedy has stated, “I can accept neither the necessity nor the wisdom of federal mandatory minimum sentences. In too many cases, mandatory minimum sentences are unwise and unjust.”[56] Many members of the judiciary agree.[57] Prosecutors also recognize the problems with mandatory minimums.[58] Scott Lassar, a former US Attorney, bluntly told Human Rights Watch, “Mandatory minimums lead to unfair sentences.”[59] In testimony before the Sentencing Commission, Federal Public Defender Michael Nachmanoff stated, there is “overwhelming evidence that mandatory minimums require excessive sentences for tens of thousands of less serious offenders who are not dangerous.”[60]
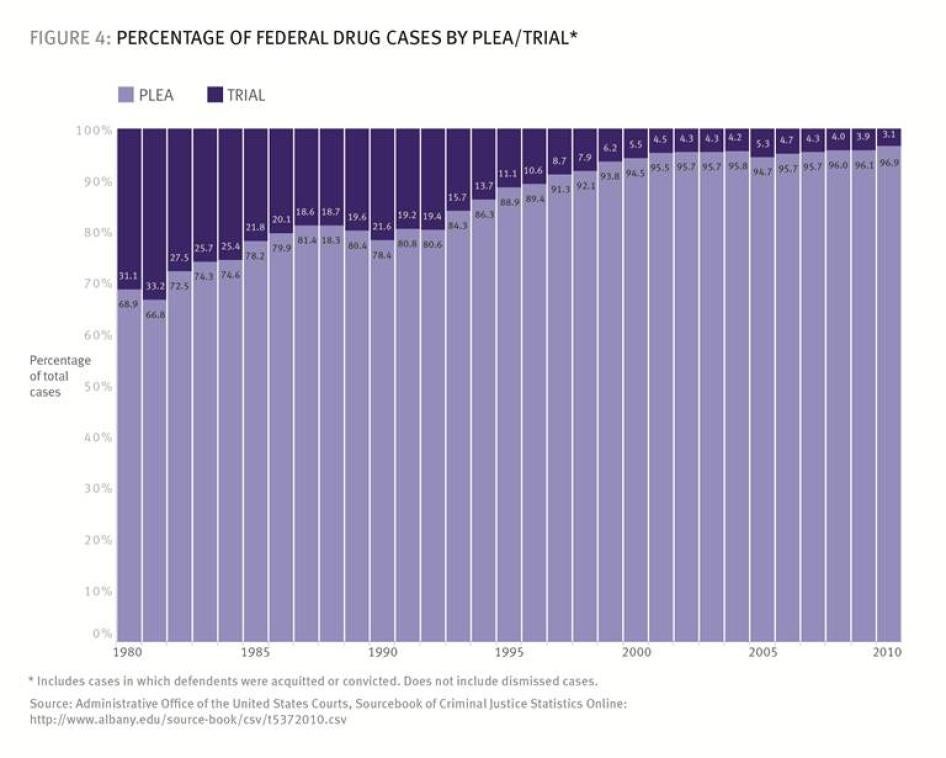
Mandatory minimum sentencing laws increased prosecutorial power, transferring sentencing power from judges to prosecutors.[61] Previously, federal prosecutors “played no role in sentencing.”[62] But with judges’ sentencing discretion curtailed, prosecutors could determine the sentences defendants would face through the charges they pressed and the facts they brought forward at sentencing.[63] Unfortunately, prosecutors often charge or threaten to charge mandatory minimums not because they result in appropriate punishment, even in the view of the prosecutor, but to pressure defendants to plead guilty and to punish them if they do not. The pressure they could bring to bear on defendants led to soaring numbers of guilty pleas in drug cases: from 1980 to 2010, the percentage of federal drug cases resolved by a plea increased from 68.9 to 96.9 percent, where it remained in 2012 (Figure 4).[64]
Supporters of mandatory minimum sentences believe they ensure uniformity and certainty—offenders who commit similar crimes receive similar punishment; transparency—offenders and the public know what the punishment for the crime is; crime prevention—the certainty and harshness of the punishment deters future crime; and encourage pleas and cooperation with the government. The problem with all but the last of these justifications is that they are belied by the facts.[65]
The only indisputable effect of mandatory minimums is that they help pressure defendants into pleading guilty and cooperating with the government.[66] A former assistant US attorney described mandatory minimums as “a hammer to convince people to cooperate…. They provide a practical benefit for prosecutors but can create unfair consequences for defendants.”[67] A current assistant US attorney made a similar point: “Mandatory minimums really help get defendants to cooperate.”[68]
The Department of Justice has traditionally supported high mandatory sentences because “the threat of the higher sentence provides a greater inducement for defendant cooperation.”[69] According to Lanny Breuer, a former assistant attorney general, the Department of Justice favors mandatory minimum sentences because they “remove dangerous offenders from society, ensure just punishment, and are an essential tool in gaining cooperation from members of violent street gangs and drug distribution networks.”[70]
In the words of Justice Kennedy, this “transfer of sentencing discretion from a judge to an Assistant U.S. Attorney, often not much older than the defendant, is misguided.” It “gives the decision to an assistant prosecutor not trained in the exercise of discretion and takes discretion from the trial judge…, the one actor in the system most experienced with exercising discretion in a transparent, open, and reasoned way.”[71]
Sentencing Guidelines
Over twenty-five years of application experience have demonstrated that the drug trafficking offense guideline is unnecessarily severe and produces unjust outcomes.[72]
—Judge John Gleeson, United States v. Diaz, 2013
For the government, the guidelines are sacrosanct. Prosecutors insist they must be followed – except they will bend them whenever it suits their purposes.[73]
—Gerald McMahon, New York, July 1, 2013
Congress created the United States Sentencing Commission (the Sentencing Commission) in 1984, charging it with promulgating sentencing guidelines for all federal crimes.[74] The guidelines were to further the purposes of sentencing (just punishment, deterrence, incapacitation, and rehabilitation) set forth in 18 U.S.C. §3553(a)(2), while avoiding unwarranted disparities among similar defendants.[75]
The Sentencing Commission has created detailed and complicated guidelines that culminate in a prescribed sentencing range (calculated in months) for every federal crime using a Sentencing Table that combines offense seriousness with the defendant’s criminal history.[76] The seriousness of the offenses are measured by 43 offense levels on the vertical axis of the Sentencing Table and six criminal history categories on the horizontal axis. The base offense level for drug offenses is initially set by the type and weight of the drug involved, pegged to the mandatory minimum sentences established under the ADAA.[77] Numerous aggravating factors can increase the base offense level and a few mitigating factors can reduce it.[78] After adjusting the base offense level to reflect aggravating and mitigating factors, a final offense severity level is determined. The sentencing range for the defendant is ultimately determined by the cell in the Sentencing Table that lies at the intersection of final offense severity level and his criminal history category.[79]
Given that the drug guidelines were established to be proportionate to the statutory mandatory minimum sentences, now widely recognized as excessively severe, it is no surprise that the guidelines also yield egregiously long sentences.[80] For example, street-level dealers who sell to retail customers can easily distribute 300 grams of crack or 500 grams of methamphetamine in a month, with a retail value of $20,000 to $50,000.[81] Yet the guidelines sentencing range for a nonviolent, first-time offender distributing this quantity of those drugs to an adult is 10 to 12 years—greater than for forcible rape of an adult, killing a person in voluntary manslaughter, disclosing top secret national defense information, or violent extortion of more than $5 million involving serious bodily injury.[82] Someone who has one prior drug felony conviction, who runs a small drug operation of three people including himself, and who is convicted of possession with intent to distribute 20 kilograms of cocaine faces a guidelines sentencing range of 210 to 262 months (approximately 17 to 21 years).[83]
On February 28, 2012, a federal judge imposed a 12-year guidelines sentence on Dwayne Ingram for selling less than 1 gram of crack (about the equivalent of a sweetener packet) within 1,000 feet of public housing property, following 2 earlier convictions for selling small crack quantities. As federal appellate Judge Guido Calabresi said in a concurring opinion upholding the sentence, “[T]here is nothing ‘reasonable’ about sending a man to prison for twelve years to punish him for a nonviolent, $80 drug sale.”[84]
From Mandatory to Advisory
From 1987 to 2005, the sentencing guidelines dictated federal sentences unless trumped by mandatory minimum statutes.[85] Except in extraordinary and unusual circumstances, federal district judges were not able to impose sentences lower than the guidelines mandated.
In the 2005 decision of United States v. Booker, the Supreme Court held that mandatory sentencing guidelines ran afoul of the Sixth Amendment.[86] Under Booker and its progeny, the guidelines remain “the starting point and initial benchmark” for sentencing calculations.[87] Judges should not, however, presume that a sentence within the guidelines range is reasonable.[88] They should impose different sentences than those specified by the guidelines if they decide a non-guidelines sentence would better satisfy congressional sentencing directives, including the requirement to set sentences no greater than necessary to serve the purposes of punishment.[89] Post-Booker, judges can also avoid the false uniformity that results when drug offenders of widely differing culpability face unreasonably similar guidelines sentences because drug quantity overrides other factors.[90]
Corey James[91]On May 2, 2008, Corey James pled guilty to conspiring to distribute 50 grams or more of crack and cocaine during a two-month period in 2008 and to distributing and possessing with intent to distribute 50 grams or more of crack. The charges arose from three drug deals that James brokered, resulting in the sale of 118 grams of crack and 50 grams of powder cocaine. James received $100 for each sale. Because of James’ record of prior convictions, he had a guidelines sentencing range of between 262 and 327 months (that is, between 21 years, 10 months and 27 years, 3 months). Before Booker, Judge Jack B. Weinstein would have had to sentence James to more than 21 years in prison. But he sentenced James instead to 10 years and one day, giving detailed reasons regarding “the nature and circumstances of the offense and the history and characteristics of the defendant” as required by 18 U.S.C. 3553(a)(1) to explain why the lower sentence was justified. [92] According to Judge Weinstein’s decision, the 42-year-old James had a record of serious crimes, including physical violence and was a known street gang member. But James was in poor health, suffered from long-term drug addiction and depression, and he was sincerely remorseful. The judge concluded the 10-year sentence reflected the seriousness of his offense and would send a message that drug trafficking results in lengthy prison sentences. A longer sentence was not necessary to protect the public since James was unlikely to return to serious criminal activity after prison. |
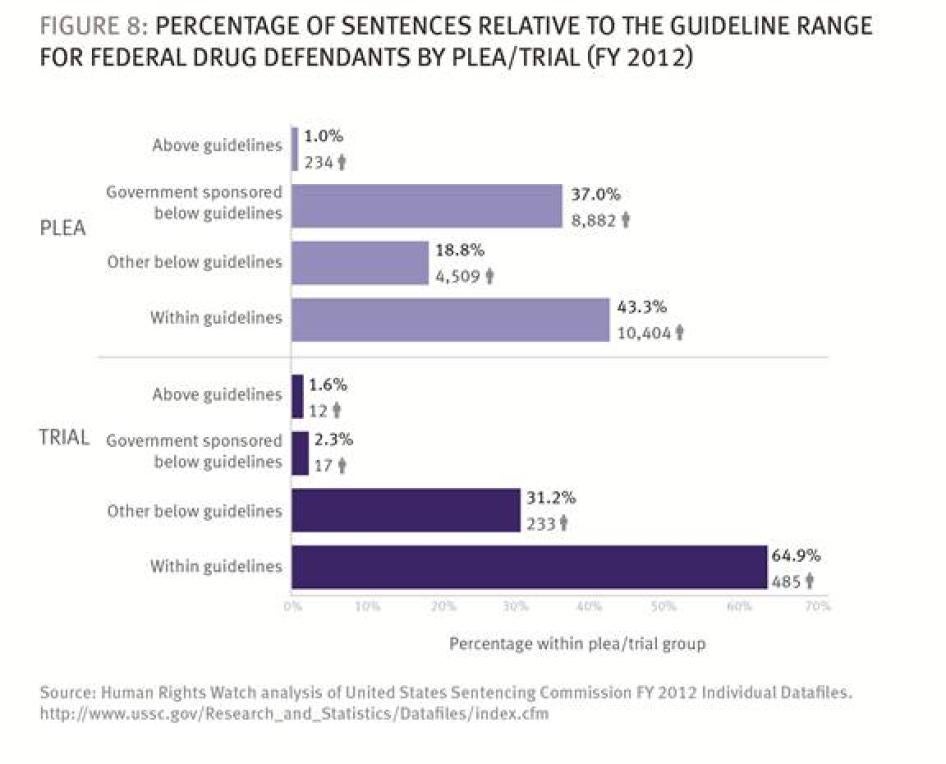
Although the guidelines are no longer binding, most judges still sentence within them unless they have received a government motion for a sentence below the guidelines range, because the defendant has provided substantial assistance or is being prosecuted under a Fast Track program.[93] In fiscal year 2012, 42.9 percent of federal defendants convicted of drug trafficking offenses received sentences within the guidelines range.[94] Judges went below the guidelines without a government motion to do so in only 19.3 percent of drug trafficking cases.[95] The guidelines range is thus the starting and also the ending point for many judges.[96]
Darlene EcklesFor a first time offender, a 19-year sentence; for her drug dealing brother, 12 years[97]Darlene Eckles was arrested on federal narcotics charges in 2006, one of 40 defendants allegedly involved in a drug trafficking business led by her brother, Rick. In late 2003, he needed a place to live after he got out of prison and Darlene permitted him to live with her. Against her wishes, he began operating his drug business out of her home and after a while, she collected and counted money for him. After six months, when her brother would not stop dealing from her house, she kicked him out. He went to live with another sister, and continued his business from her house. A nursing assistant with no criminal record and the mother of a young son, Darlene Eckles’ only involvement with drugs was during the limited time her brother lived with her. The government offered her a plea deal of 10 years for one drug conspiracy count, but she refused to plea, believing she was innocent of drug trafficking. After trial, the jury convicted Darlene of a lesser included drug offense that carried no mandatory minimum. At her sentencing in March 2007, the government argued that she was a “facilitator” of her brother’s drug business, should be held accountable for the full drug weight involved in the conspiracy (1.5 kilograms or more of crack), and should not receive a reduced sentence for her minor role. The judge agreed and calculated her sentencing range under the federal sentencing guidelines as 235 to 293 months. He sentenced her to 235 months— 19 years and seven months—about twice as long as the pre-trial plea offer. Her brother, the conspiracy ring leader, received a sentence of eleven years and eight months after pleading guilty and cooperating with the government, including by testifying against his sister. Darlene’s sister, whose involvement in the conspiracy was the same as Darlene’s, also pled guilty and was a cooperating witness for the government; she received two years’ probation. |
When the guidelines were mandatory, they functioned similarly to mandatory minimum statutes—transferring enormous sentencing authority to federal prosecutors and markedly strengthening their plea bargaining leverage.[98] Prosecutors could charge offenses carrying high guidelines sentences and then use their plea bargaining discretion to circumvent the guidelines in plea agreements.[99]
By making the guidelines advisory, the Supreme Court revived judicial sentencing discretion (subject still to statutory mandatory minimum sentences).[100] Nevertheless, the guidelines remain powerful and prosecutors retain unbridled discretion in deciding what charges to pursue or pleas to accept.
The guidelines themselves encourage defendants to plead guilty by rewarding defendants with a two- or three-level reduction in their offense level for “acceptance of responsibility.” For example, a defendant who has an offense level of 30 and a criminal history category of III faces a sentencing range of 10 to 12-and-a-half years (121 to 151 months). If he pleads, his offense level is automatically reduced to level 28, with a sentencing range of about 8 to 10 years (97 to 121 months). If the government agrees the plea was timely, the offense level will drop one more level, leading to a sentencing range of 7 to 9 years. In other words, by pleading, this defendant would have reduced his sentencing exposure under the guidelines from a possible maximum of 12-and-a-half years to a possible low of 7 years. The guidelines incentive to plead has proven sufficient to maintain high levels of guilty pleas even for offenses that do not carry mandatory minimum sentences.[101]
Efrain Vega[102]Efrain Vega grew up poor in the projects of Hartford, Connecticut with an abusive father, surrounded by violence and alcohol. Nonetheless, he had created a solid life for himself. He had a strong family—a wife and three daughters—and a good full-time job moving and installing office equipment. He was also a recreational cocaine user, who sometimes purchased enough drugs to share with friends, who would pitch in to pay for it. In 2011, federal prosecutors in Connecticut secured a grand jury indictment against Efrain Vega as part of a multi-defendant cocaine distribution conspiracy. The indictment charged Vega with conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute 5 kilograms or more of cocaine and with possession with intent to distribute cocaine. He faced a statutory minimum sentence of 10 years. The prosecutors permitted him to plead guilty to conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute cocaine and agreed that the reasonably foreseeable quantity involved in the conspiracy for which Vega should be held responsible was at least 50 grams but less than 100 grams of cocaine. With the reduced quantity, Vega was no longer subject to a mandatory minimum sentence. Under the sentencing guidelines, with three points off for acceptance of responsibility, his sentencing range would be 12 to 18 months. On its face, this might have seemed like a good plea agreement for Vega. But at the sentencing hearing, Federal Judge Stefan Underhill questioned whether Vega was part of a conspiracy at all. As the judge read the facts, the only evidence the government had to prove conspiracy to distribute was that Vega talked to the dealer on the phone, was arrested after purchasing 35 grams from him, and after he was arrested, asked the dealer for help getting a lawyer. The government subsequently agreed to let Vega plead to possession with intent to distribute an unspecified quantity, but argued he should receive the guidelines sentence. [103] The government’s arguments did not persuade the judge that Vega’s conduct established membership in a conspiracy and warranted prison time. He sentenced Vega to 36 months’ probation. [104] |
III: Upping the Ante: Mandatory Penalties for Prior Convictions and Gun Possession
The sentencing power of prosecutors in drug cases is further strengthened by laws that permit them to seek increased sentences for drug defendants with prior criminal records or who possessed or used guns in connection with their drug offenses. Prosecutors have complete discretion whether or not to seek these additional penalties against defendants eligible for them. Our research indicates that prosecutors use the threat of these sentencing enhancements to obtain pleas and will carry through on those threats for defendants who do not plead.
Increased Sentences for Offenders with Prior Records
We would only invoke the §851 [prior felony enhancement] when a defendant was going to trial. It’s built into the DNA of prosecutors, even well-meaning prosecutors do it. [We] penalize a defendant for the audacity of going to trial.[105]
— Former assistant US attorney, New York, March 21, 2013
Drug offenders with prior convictions for felony drug offenses are eligible for increased mandatory minimum and maximum terms of imprisonment.[106] Judges must impose the recidivist enhancement if the prosecutor files a document known as a prior felony information under 21 U.S.C. §851 (often called an §851 information) that states the government’s intent to obtain a sentencing enhancement and lists prior qualifying convictions.[107]
If the prosecutor lists one prior drug conviction in the §851 information, the defendant’s otherwise applicable mandatory minimum sentence is doubled. If the prosecutor lists two or more prior convictions, the sentence is doubled for defendants charged with offenses carrying five-year mandatory minimum sentences, but for defendants facing ten year mandatory minimum that sentence is increased to life. Because there is no parole in the federal system, a life sentence means the defendant will die behind bars.
The provision was intended originally to ensure that truly hardened, professional drug traffickers with long records received sufficient punishment.[108] Nevertheless, Congress did not require the prior crimes triggering a prior felony enhancement to be particularly serious. State or federal drug convictions punishable by more than one year of imprisonment trigger the enhancement, even if the underlying offense would not qualify as a federal felony and even if the defendant served less than a year or no time at all.[109] Federal prosecutors recently sought a mandatory life sentence via an §851 information for a drug offender in Alabama using, as one of the two predicate offenses, his conviction under state law for possessing marijuana for personal use.[110]
There is also no statutory time bar on the prior convictions that can be used for the mandatory enhancement. The government sought an §851 enhancement for Lawrence Berry, Jr. (who was convicted of cocaine trafficking after a jury trial) based on a marijuana selling conviction that was more than 25 years old. [111] Terence L. Watson, 30, pled guilty in 2011 to being part of a conspiracy to distribute 5 kilograms or more of cocaine.[112] He faced a mandatory minimum sentence of 10 years, but the government filed an §851 notice that Watson had previously been convicted of two prior drug offenses under Florida law. Both convictions were for crimes Watson committed as a young man: one in 2000 for possessing cocaine, and the other in 2002 for distributing marijuana. He served a total of 11 months for both. As a result of the prosecutor’s decision to file the §851 information, Watson was sentenced to life without parole.[113]
Juan Gonzalez[114]In 2010, Juan Gonzalez (pseudonym) was indicted in Pennsylvania on federal charges for conspiracy to distribute and distribution of heroin and cocaine. The minimum sentence on the drug charges was 10 years. Gonzalez was also charged with possession of a gun in furtherance of his drug distribution. Gonzalez bought drugs from his suppliers and in turn sold them to street-level dealers. According to Gonzalez’s attorney, his mother was a drug addict, he stopped school in eighth grade, he can neither read nor write, and he lived on the street for many years. He has an overall IQ score of 61 and a diagnosis of mild mental retardation/intellectual disability. He had no record of violence and while there was a gun in his apartment, there was no evidence he ever carried or used it. Gonzalez had two prior drug convictions from New York: the first, in 1990, when Gonzalez was 19, for which he received probation and another, in 1994, when he was 23. [115] The prosecutor offered a plea under which he would file an information for only one of those convictions, which would double Gonzalez’s sentence on the drug charges from 10 to 20 years. If he refused to plead, the prosecutor said he would file an information listing both prior convictions, which would result in a life sentence if Gonzalez were convicted. Gonzalez nonetheless refused to plead and the prosecutor made good on his threat. [116] After a jury trial, Gonzalez was convicted on the drug and gun charges. Before sentencing, which was scheduled for September 2014, his lawyer ordered a psychologist's report, a copy of which went to the prosecutor. In August 2013, Attorney General Eric Holder issued a memorandum to prosecutors which directed prosecutors to limit filing §851 informations to cases in which severe sanctions were warranted. [117] Shortly before sentencing, the prosecutor filed an amended §851 information, which listed only one prior conviction, reducing Gonzalez’s mandatory minimum drug sentence from life to 20 years. On September 4, 2013, Gonzalez was sentenced to 25 years in prison, 20 for the drugs and a consecutive five years for possessing the gun. |
The legislation authorizing enhanced penalties based on prior convictions does not require prosecutors to consider whether a doubled or life sentence is proportionate to the individual offender’s conduct and criminal record or whether it is necessary to satisfy the purpose of punishment.[118] Prosecutors do not have to explain to the court (much less the defendant or the public) why they sought the enhancements.
Sentencing Commission data analyzed for this report shows marked differences among federal districts in the rate at which §851 enhancements were applied to eligible defendants—from a high of 87 percent in the Northern District of Florida to 1.5 percent in the Southern District of California and the Northern District of Texas; there were also seven districts where the enhancement was not applied to any of the eligible offenders.[119] There were significant variations in application rates within circuits, between neighboring districts and within states.[120]
Judge Mark Bennett has described the “stunningly arbitrary” use of §851 enhancements as the “shocking, dirty little secret of federal sentencing.”[121] Like a “Wheel of Misfortune,” he said, the application of §851 enhancements means that similarly-situated defendants in the same district, same circuit, and nationwide can receive dramatically different sentences solely based on a prosecutor’s decision to seek an enhancement.[122]
Tyquan Midyett[123]Tyquan Midyett sold crack in a housing project in Brooklyn. His life had been similar to many who end up as drug offenders in New York City: he grew up poor and remained poor; lived in a housing project; had spent two years in foster care when he was 13, after his parents separated, and then returned to live with his mother, left school in eleventh grade, and had a long history of substance abuse himself. He worked sporadically as a laborer. Midyett was 26 when arrested in 2007 after selling crack to an undercover police officer. He was indicted with others for conspiring to distribute and possession with the intent to distribute 50 grams or more of crack, a charge which under the still extant crack cocaine sentence laws carried a mandatory minimum term of 10-years imprisonment and a maximum of life. According to government evidence, Midyett was part of group that sold crack at different buildings in a public housing complex; the total amount sold during the conspiracy period was approximately 843 grams of crack. The judge found that Midyett could have foreseen and/or participated personally in the sale of 97 grams of crack. Before trial, the government offered Midyett a 10-year plea, which he refused. [124] To pressure Midyett to accept the plea, the prosecutor said he would file a prior felony §851 information that would double his sentence to 20 years because Midyett had a prior felony drug conviction. [125] That conviction was in 2001 for “criminal possession of a controlled substance in the third degree,” a class B felony under New York law. Midyett nonetheless persisted in going to trial. The government made good on its threat to file the §851 information, and Midyett was convicted and sentenced to 20 years. [126] At sentencing, Judge Kiyo Matsumoto said she thought 20 years was “quite more than necessary, but I do not have discretion under the law to consider a lesser sentence.” [127] |
Brian Moreland[128]In July 2004, Brian Moreland sold 5.93 grams of crack to a West Virginia undercover police officer for $450. When he was arrested, the police found an additional 1.92 grams of crack on him. He was convicted at trial on December 7, 2004, of distributing 5 grams or more of crack, which at the time carried a statutory penalty of a least 5 and not more than 40 years in prison, and of possessing with intent to distribute 1.92 grams of crack, which carried no mandatory minimum but a maximum penalty of 20 years. At the time of sentencing, Moreland was 31 years old. The government chose to file an §851 based on two prior state drug convictions: one in 1992, for delivering a marijuana cigarette to an inmate in prison for which he was sentenced to 60 days in custody and 60 months of probation and the other, in 1996, for possessing 6.92 grams of crack, for which he received a suspended sentence of incarceration and was placed on lifetime probation. Because of the two priors, Moreland’s mandatory minimum sentence was raised from 5 to 10 years and his maximum sentence was raised to life. Without the §851 information, Moreland already faced a high sentencing range of 262 to 327 months (21 to 27 years) because his criminal record qualified him as a “career offender” under the guidelines. But because of the §851 information, Moreland’s sentencing range increased to 30 years to life in prison. When the court sentenced Moreland to 120 months, the government appealed, arguing the sentence was “unreasonably lenient” for a person who qualified as a career offender. [129] The Fourth Circuit remanded for resentencing, directing the district court to impose a sentence of at least 20 years. [130] But before resentencing, the Supreme Court issued additional post-Booker decisions clarifying the ability of district courts to vary substantially from the guidelines and the scope of appellate review of their sentencing decisions. [131] At the resentencing, the government argued that the 20-year minimum should be imposed, but the district court again sentenced Moreland to 10 years, taking into account characteristics of the defendant (broken home, graduated from high school, took college courses); circumstances of the offense (small amounts of drugs and no violence or firearms in his history); and the purposes of sentencing. The court also did not believe Moreland was the sort of repeat drug trafficker or violent offender the career offender guideline was intended to target. [132] It pointed out that Moreland’s prior offenses were over a decade ago, that they involved small, user amounts of drugs—as the court put it, the “amount of drugs involved in [his] entire criminal history would rattle around in a matchbox”—and lacked “temporal proximity to either each other or the present offense,” and hardly constituted the “type and pattern of offenses that would indicate that Moreland has made a career out of drug trafficking” such as to “justify disposal to prison for a period of 30 years to life.” [133] |
Lori Ann Newhouse[134]On April 26, 2012, Lori Ann Newhouse, 33, pled guilty to manufacturing five grams or more of pure methamphetamine. Newhouse was a small time “pill smurfer,” i.e., she purchased legal cold remedies containing pseudoephedrine for small meth cooks and she received home-made methamphetamine in exchange to feed her long-standing addiction. Her actual conduct involved at least 20 but less than 35 grams. Newhouse was brought up in tough circumstances, including parents with mental health issues, and began a life long struggle with drug addiction in her teens. She was the single mother of three children, two of whom were living with her until her arrest. Based on the quantity of drugs to which she pled, Newhouse was subject to a mandatory minimum sentence of five years, which was doubled to 10 years (and the statutory maximum increased from forty years to life) because the prosecution chose to file an §851 information seeking a mandatory sentencing enhancement based on two prior drug convictions for possessing with intent to distribute small amounts of drugs a decade earlier (for which she was sentenced to probation). [135] Under the guidelines, because of her prior offenses, she was considered a “career offender,” with a staggering 262- to 327-month sentencing range. Newhouse was sentenced by Federal District Judge Mark Bennett, who concluded that anything longer than the 120-month mandatory minimum sentence would be “grossly disproportionate to her role and culpability.... [The 120 month sentence] is sufficient in length to reflect the seriousness of the offense, promote respect for the law, provide just punishment, protect the public and reflect the factors embodied in 3553(a)(2).” The government subsequently filed a substantial assistance motion for Newhouse, recommending a 20 percent reduction in her sentence, which enabled the judge to sentence her below the 10-year mandatory minimum. Judge Bennett sentenced Newhouse to 96 months (8 years) which, he noted, “is still exceptionally long, ‘[e]xcept, perhaps, to judges numbed by frequent encounters with the results of the sentencing Guidelines.’” |
Prior Felony Enhancements as a Plea Bargaining Bludgeon
In a recent lengthy opinion, Judge John Gleeson described the way that prosecutors use prior felony sentencing enhancements to coerce defendants into pleading.[136] The willingness of a defendant to plead, he said, is the single most important factor—and an illegitimate one at that—determining whether the government seeks the sentencing enhancement.[137]
The pressure on defendants facing the threat of prior felony sentencing enhancements is enormous. Judge Paul Friedman told Human Rights Watch about three defendants in a current drug case who all faced 10-year mandatory minimums, “except if they go to trial the prosecutor will file §851 enhancements.” One defendant faced a 20-year sentence and the other two, life. All were to be offered pleas of substantially less. “This is a typical situation,” he said. “Huge risks for defendants if they roll the dice and go to trial” rather than pleading guilty.[138]
Sentencing Commission data supports Gleeson’s contention that prosecutors condition their use of §851 informations on whether the defendant pleads guilty to coerce pleas and punish defendants who nonetheless go to trial. From a sample of 5,858 cases of drug defendants who were eligible for the enhancement based on prior convictions, those who went to trial were 8.4 times more likely to receive the §851 enhancement than those who pled.[139]
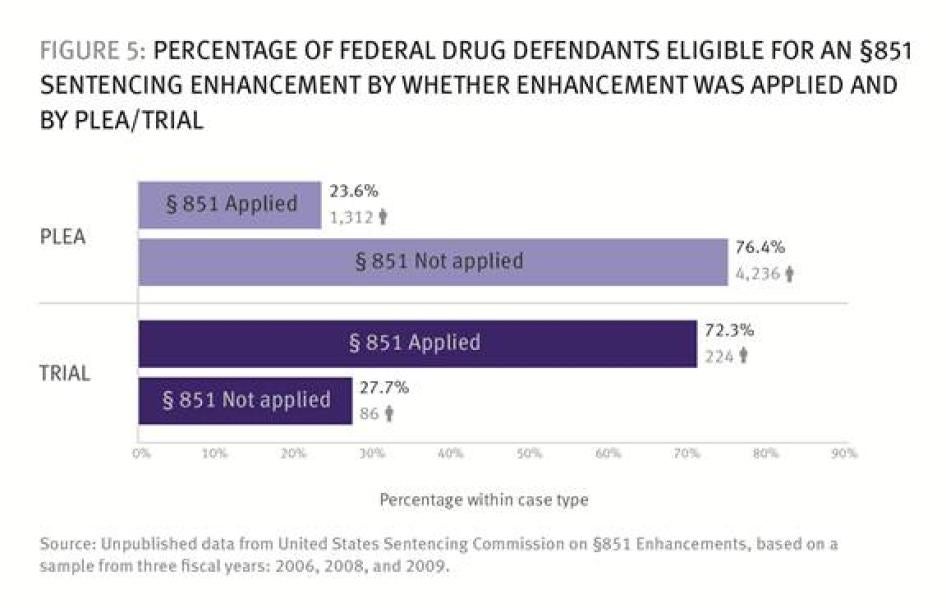
According to our analysis, as shown in Figure 5, only 23.6 percent of eligible defendants who pled guilty had an §851 enhancement. In contrast, 72.2 percent of eligible defendants who went to trial received an §851 enhancement—persuasive evidence that prosecutors withhold pursuing the enhancement if the defendant will plead.[140]
Our interviews, as well as numerous cases, reveal how prosecutors use the threat of prior felony enhancements to coerce drug defendants to plead guilty and to punish those who do not.[141]
A former prosecutor told us that in his district they would only seek prior conviction enhancements if a defendant refused to plead.[142] Similarly, in the Southern District of New York, “absent unusual circumstances we would not file prior felony information if the defendant is willing to plead. But we would charge if we went to trial.”[143]
A federal public defender in Oregon said §851s are typically not in the indictment. “It’s in reserve, to be used as part of a plea negotiation.”[144] A defense attorney in southern Iowa said the US District Attorney there does not like §851 enhancements and rarely files them, even if the defendant will not plead.[145] The US Attorney for the Middle District of Florida said his office considers the nature and date of prior convictions before filing the §851, but will only withdraw it once charged if the defendant pleads and cooperates.[146] A current California federal prosecutor told us his office policy is to seek an enhancement when the indictment is filed and it is part of plea negotiations. “If I think the §851 is too much, I can seek permission not to file the information or to withdraw it,” he said.[147]
In the case of Jumal George Jones, from Chicago, the government obtained a three count indictment charging Jones with possession with intent to distribute 50 grams or more of crack cocaine, with being a felon in possession of a firearm, and with possession of a firearm in furtherance of a drug trafficking crime in violation of §924(c).
Jones had made five trips to sell 91 grams of crack (two-and-a-quarter ounces) of cocaine in Lansing, Michigan. He had a long employment history and was gainfully working at the time of his offense, but sold crack to help finance a home outside the city for his family. He also had prior convictions that made him eligible for an §851 enhancement. Jones pled guilty to the drugs and to the §924(c) violation. In exchange, the government dismissed the second count in the indictment and agreed not to file an §851 information that would have led to a life sentence. He received 15 years (10 for the drugs, 5 for the gun count).[148]
The enhancement for a single prior felony conviction is to double the mandatory drug sentence. Jay Kent, for example, was convicted of distributing 22.7 grams of crack cocaine to an FBI source in 2008. He was arrested and charged with conspiring to possess with intent to distribute and possessing with intent to distribute five grams or more of crack cocaine, which at the time carried a five-year mandatory minimum sentence. The government sought Kent’s cooperation as part of a plea agreement and informed Kent’s lawyer that it would file an §851 information based on a prior conviction if Kent insisted on going to trial. Kent said he would plead guilty, but without an agreement to cooperate. The government immediately filed an §851 information. Kent was sentenced to 10 years, double what he would otherwise have received.
Lulzim Kupa[149]Lulzim Kupa and a number of co-defendants in New York City were indicted in early 2012 on cocaine trafficking charges that carried a 10-year mandatory minimum. Kupa had a substantial criminal history, including two prior marijuana distribution cases. The government made several plea agreement offers to Kupa, including withdrawing the 10-year mandatory minimum and issuing a sentencing recommendation within a 110 to 137 month range. Kupa resisted pleading. On March 15, 2013, the government filed an §851 information against Kupa based on the two prior marijuana convictions. The government knew of the prior convictions long before filing the §851 information, but only filed it when a few weeks before trial, Kupa still refused to plead guilty. As Judge John Gleeson who presided over the case noted in the sentencing memorandum, “Just like that, a defendant for whom the government, only ten days earlier, was willing to recommend an effective sentence of less than eight years was looking at life in prison without the possibility of parole.” [150] The government made another plea offer that it would withdraw both the prior felony information and the 10-year mandatory minimum if Kupa pled guilty. On April 10, 2013 Kupa pled guilty to conspiracy to distribute between 5 to 15 kilograms of cocaine. The government and Kupa agreed to jointly recommend to the court a guidelines sentencing range of a 140 to 175 months. [151] At a sentencing hearing on August 9, 2013, Kupa was sentenced to 11 years in prison. During the hearing, Judge John Gleeson skeptically questioned the prosecutor about whether the government had filed the §851 solely to pressure Kupa into pleading. The prosecutor refused to say why it was filed, but insisted it was acceptable to withdraw the §851 as part of a plea agreement. [152] In response to Judge Gleeson’s concern regarding the apparent use of the §851 information to coerce a plea, the prosecutors wrote to him insisting that the office only files a prior felony information based on “an individualized assessment of numerous facts.” In his statement of reasons supporting Kupa’s sentence, Judge Gleeson noted, “Whatever the result of the ‘individualized assessment’ with regard to Kupa, he was indisputably stuck with a prior felony information—and a life sentence—only if he went to trial, and he was indisputably not stuck with it only if he pled guilty.” [153] He added, “Even though Kupa still had that criminal history when he showed up for sentencing, by then the prior felony information had been withdrawn. Why? Because he buckled under its pressure and agreed to forgo a trial.” [154] |
Patricio Paladin[155]In April 2009, Patricio Paladin, a mid-level drug dealer, was indicted for conspiracy to distribute, possession with intent to distribute and distribution of more than 5 kilograms of cocaine. He was convicted after a jury trial on all counts. Ordinarily, he would have faced a 10-year mandatory minimum sentence for that quantity of cocaine. But Paladin had two prior drug convictions in New Hampshire state court, one from 1997 and one from 2003. During plea negotiations, the prosecutor made clear he would file an §851 including both of them if Paladin did not plea.[156] The prosecutor offered him a plea of 20 years. The judge in his case urged him to carefully consider whether to accept the plea, and the prosecutor laid out to Paladin in detail how he would lose at trial. But Paladin refused to plead. Shortly before trial, when it was clear Paladin was not going to change his mind, the prosecutor filed an §851 information with both prior drug offenses. Paladin was convicted on all counts and on September 4, 2012, was sentenced to life in prison. At the sentencing hearing, Judge Paul J. Barbadoro said he believed a life sentence for the 37-year-old Paladin was excessive, but lawful,[157] and virtually invited the government to dismiss the §851 information.[158] Paladin’s lawyer asked the prosecutor after the conviction but before sentencing if he would drop one of the prior convictions. The prosecutor refused, saying there was no reason to do so.[159] Nevertheless, the judge seemed reluctant to directly fault the prosecutor for insisting on a course of action that required a life sentence. “I’m not condemning the prosecutor here. I understand it is a lawful sentence. It is a charge that the prosecutor was entitled to pursue,” he said. “The prosecutor explained that Paladin was given many opportunities to admit guilt to a charge that involved a lesser sentence but made the decision to reject that.”[160] |
§924(c) Drug Offenders with Firearms: Even More Mandatory Sentences
§924(c) charges are “a powerful weapon that can be abused to force guilty pleas under the threat of an astonishingly long sentence.”[161]
—United States v. Looney, 5th Circuit Court of Appeals, 2008
If a person won’t plead … then I would add weapons charges for trial. The defendant has opened herself up. She made the choice to go to trial.[162]
—Assistant US attorney, Michigan, April 18, 2013
Under 18 U.S.C §924(c)(1)(A), “any person who, during and in relation to any crime of violence or drug trafficking crime … uses or carries a firearm, or who, in furtherance of any such crime, possesses a firearm” shall be sentenced to an additional term of imprisonment.[163] The first conviction carries a mandatory sentence of five years which must be served consecutive to the sentence for the underlying drug offense. The second, and any subsequent such convictions, carry 25-year mandatory sentences, each to be served consecutive to the other.[164]
The gun need not be carried, brandished, or fired to trigger the §924(c) sentence. The presence of guns near where drugs are held, or where a drug dealer lives can suffice. The cases suggest that as a practical matter, any drug dealer who owns a gun is at risk of being charged with possessing that gun to further his drug business, e.g. to protect his drugs and money. Moreover, the defendant can be convicted based on constructive possession. If a defendant’s co-conspirator possesses or uses a gun in furtherance of drug trafficking and it is reasonably foreseeable that he does so, the defendant can be convicted of the §924(c) charge as well, even if he never touched or even saw the gun.[165]
According to Human Rights Watch’s analysis for this report, in fiscal year 2012, 984 drug trafficking defendants received mandatory minimum sentences under §924(c). Among them, 952 were convicted of one §924(c) count, and the rest were convicted of two or more §924(c) counts.[166] Drug defendants are more likely to be charged with §924(c) offenses in some districts than in others. Sentencing Commission research indicates that in 2010, 12 federal districts reported 43.8 percent of all cases with a §924(c) conviction.[167]
For many years, §924(c) was applied as a straightforward recidivism statute: the first §924(c) offense would receive a five-year sentence; if after serving that sentence the defendant then committed another §924(c) offense, that subsequent offense would receive the 25-year sentence. Nevertheless, the Supreme Court in 1993 ruled that multiple §924(c) offenses could be charged in a single indictment (a practice known as “stacking”).[168] If a defendant has a gun present during drug sales on three separate occasions, he can be convicted of three §924(c) offenses, for a total sentence of 55 years consecutive to whatever sentence he receives for the drug offenses.
Stacking quickly leads to astonishing sentences that[169] Jason Hawkins, a federal public defender, described as “irrational, inhumane, and absurd.”[170] For example:
- In 2004, prosecutors charged Eugene Cousins with three §924(c) counts in addition to counts for distributing a mixture containing a detectable amount of methamphetamine. They dropped the third §924(c) in a plea agreement. Cousins received a sentence of 406 months, 46 months on the drug counts and a consecutive 360 months for the guns.[171]
- Mark Wayne Woods was tried in 2003 on nine counts of possession and distribution of methamphetamine and five §924(c) counts. He received a sentence of 94 years (1,128 months), 168 for the drug charges and 960 for four firearm counts (the jury acquitted him of one). The evidence presented at trial showed Woods sometimes received firearms as payment for his drugs.[172]
- In 2008, Rene Zavalas was sentenced to 74 years (895 months) for drug trafficking and a consecutive 660 months for three §924(c) counts. Zavalas did not own or use the firearm, but his co-conspirator did in connection with their drug business. The court said it was “foreseeable” his co-conspirator would carry a gun, so Zavalas was convicted of the gun counts as well.[173]
- Marnail Washington, a 22-year-old with no criminal history, was sentenced to 40 years (481 months) in 2004, after conviction of possession with intent to distribute crack cocaine and two §924(c) counts.[174] That is, 30 years of his 40-year sentence were on the gun counts. The judge who sentenced him described the sentence as “grossly disproportionate” to his crimes. Although Washington broke the law and should be punished, he said, a 40-year sentence was “shockingly harsh given the nature of his offenses and his lack of criminal history.” He said the sentence was the “worst and most unconscionable” that he had given in his 23 years on the federal bench.[175]
§924(c) Sentences: Punishment for Defendants who Won’t Plead
Prosecutors do not seek sentences under §924(c) in all the drug cases in which they could.[176] Their willingness to purse §924(c) charges and the number of charges filed depends greatly on whether the defendant is willing to plead.[177] Our analysis of the 2012 sentencing data for this report reveals defendants who had a weapon in their offense are 2.5 times more likely to receive a mandatory §924(c) enhancement if they were convicted after trial rather than by a plea.
In 2012, 3,523 drug trafficking defendants had sentences increased because a gun was involved in their offense.[178] These defendants could have been sentenced either under §924(c) or with a guidelines gun enhancement.[179] Among the 3,523 defendants eligible for §924(c) sentences, only 27.1 percent received them. The remaining 72.9 percent received the less severe sentences under the guidelines. The chances of avoiding the §924(c) charge rose markedly depending on whether a §924(c)-eligible defendant pled guilty or went to trial: among defendants who pled guilty, 26 percent were convicted under §924(c) in addition to the drug charges. But among defendants who went to trial, 46.7 percent were convicted under §924(c).
Prosecutors we interviewed were remarkably forthcoming about their willingness to threaten §924(c) charges to secure pleas, and to file them (or refuse to withdraw them if already filed) for defendants who went to trial.
A former federal prosecutor in the Southern District of New York told Human Rights Watch that in plea bargaining they would threaten to stack §924(c) counts: instead of charging only one §924(c) violation covering multiple guns, they would threaten to charge separate §924(c) counts for each gun.[180] A current federal prosecutor in Michigan said that he would add §924(c) charges if a defendant refuses to plead. “The defendant has opened herself up. She made the choice to go to trial.”[181] One prosecutor explained that putting a §924(c) charge in the indictment makes it harder to negotiate a plea. Her practice therefore is to negotiate on drug charges first, and she only files a §924(c) if the defendant refuses to plead.[182]
Describing the practice of prosecutors in his district, one federal public defender told us:
[T]he ability or willingness to use §924(c) depends on the individual [prosecutor]. Some will bring it up at indictment, others will use it as hammer to get a plea. Once in the indictment, it is harder to get out from under, but it can be done.[183]
Weldon Angelos[184]In 2002, Weldon Angelos a native of Salt Lake City, was a 22-year-old father of two, and a music executive who had founded the hip hop label Extravagant Records. He was also a marijuana dealer, who the police believed dealt in sizable quantities of the drug. They also suspected that he was affiliated with Varrio Loco Town, a local gang. On three separate occasions in 2002, a confidential informant made "controlled purchases" of eight ounces of marijuana from Angelos. Angelos was arrested in November 2002 and consented to a search of his apartment. The search revealed three pounds of marijuana, a Glock pistol and two other firearms, a large amount of cash, and two opiate suckers. Police found additional marijuana, duffle bags containing marijuana residue, and two more firearms during a subsequent search of another house rented by Angelos. He was indicted and charged with three counts of distribution of marijuana, one §924(c) count of possessing a gun in furtherance of his drug crime, and two lesser charges. The confidential informant claimed Angelos carried a gun during two of the drug transactions. Angelos and federal prosecutors entered into plea negotiations, and in January 2003, prosecutors offered to drop the two lesser charges and recommend a total sentence of 15 years if Angelos agreed to plead guilty to the three counts of marijuana distribution (carrying a 10-year sentence) and one §924(c) count (a 5-year sentence consecutive to the 10 years for the drugs). The prosecutors told Angelos that if he did not accept this offer, they would issue a superseding indictment, including multiple §924(c) counts and other charges. Angelos ultimately rejected the plea offer, and the prosecutors filed a superseding indictment that added five §924(c) charges along with drug and money laundering charges. Following a trial before District of Utah Judge Paul Cassell, Angelos was convicted of three §924(c) counts, in addition to the drug and other counts. The court was required to sentence Angelos to five years for the first §924(c) count and 25 years each for the other §924(c) counts—a total of 55 years to run consecutively to the sentences for the other counts. There was no evidence that Angelos pointed the guns at anyone, threatened to use them, or fired them. The prosecution urged that the court adhere to the guidelines sentencing range of 78 to 97 months, for the remaining counts. Judge Cassell disagreed. Distraught because of the excessively harsh 55-year sentence that he had to impose for the §924(c) counts, he sentenced Angelos to just one day total for the other counts, for a total sentence of 55 years and one day. In his sentencing memorandum, Judge Cassell argued that section 924(c) often resulted in sentences grossly disproportionate to the underlying offense. Finding himself powerless to avoid imposing an unduly harsh sentence on Angelos, in his sentencing memorandum Judge Cassell called on President George W. Bush to commute the sentence. The president did not do so. Human Rights Watch asked Assistant US Attorney Robert Lund, who prosecuted Angelos, why he had filed a superseding indictment carrying five §924(c) charges. [185] Lund said that he believed he was required by Department of Justice policy to charge more than one §924(c) if provable. In addition, since Angelos would not accept responsibility for his crimes, he believed the government should charge all the gun counts and let the jury decide. “I don’t know any prosecutor who wouldn’t charge everything even though it might lead to a high sentence. We don’t know how the jury will go,” he said. He dismissed as a “ridiculous contention” the suggestion that Angelos should not have had to stand trial for “all the crimes he committed.” Even if one were to credit Lund’s explanation, it does not explain why he did not dismiss one or more of the firearm counts after Angelos’ conviction. Prosecutors have the power to dismiss charges after trial but before sentencing. If he had dismissed two of the three counts on which Angelos was found guilty, for example, Angelos would have received a mandatory five-year sentence for the single firearm offense consecutive to his drug sentence. The judge no doubt would have given Angelos a more typical sentence for his drug related conduct, but Angelos would not now be serving a sentence that will keep him behind bars into his old age. |
Mary Beth Looney[186]After a buy and bust methamphetamine operation involving a client of Mary Beth Looney and her husband, Donald Looney, the couple was arrested and their house searched. Within the residence, the police found approximately 136 grams of actual methamphetamine and four weapons. Mary Beth Looney and Donald Looney were indicted on April 8, 2005, on charges of possessing with intent to distribute 50 grams or more of methamphetamine and of possessing three firearms in furtherance of drug trafficking. On June 22, 2005, the prosecutor obtained a superseding indictment adding two more counts: one for conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute 50 grams or more of methamphetamine, one for possession of a firearm in connection with the conspiracy to possess. [187] The prosecutor offered Mary Beth Looney, who had no prior criminal record, a plea of 17 years. She did not think this was a good offer since it amounted to a life sentence for a woman of 52, and she rejected it. She and her husband were tried in December 2005 and convicted on all four counts. They were each sentenced to an aggregate of 548 months—45 years—in prison: 188 months concurrently on the two drug counts; [188] 60 months for the first gun count to run consecutively to the drug counts; and 300 months for the second gun conviction, to run consecutively after all the other sentences. Mary Beth Looney wrote to Human Rights Watch, when the judge said 548 months i was in shock . i was expecting 20 years at the most. we didn't know that 45 years was the minimum. i felt like it wasn't really true , something was going to change and it would be alright. i had faith in the justice system that something so unfair couldn't really happen. [189] The gun counts added 30 years to her sentence. While upholding her sentence, the court of appeals pointed out, “there is no evidence that Ms. Looney brought a gun with her to any drug deal, that she ever used one of the guns, or that the guns ever left the house.” The court concluded, Instead of charging Ms. Looney with two separate §924(c) offenses, the prosecutor might well have charged her with only one, which would have avoided triggering the twenty-five year mandatory, consecutive sentence for the second firearm count.… Instead, the prosecutor exercised his discretion—rather poorly we think—to charge her with counts that would provide for what is, in effect, a life sentence for Ms. Looney. [190] |
Anthonial Irick [191]Anthonial Irick was arrested on May 8, 2006, after a routine traffic stop led to the discovery of more than 5 kilograms of cocaine in a bag in the back of his pick-up truck and a gun in the console. Prosecutors indicted him for possession with intent to distribute over five kilograms of cocaine, a charge with a mandatory minimum sentence of 10 years. The original indictment did not include a gun charge. Irick would have been eligible for a safety valve— i.e., the judge could have sentenced him below a mandatory minimum— but for evidence of the presence of a gun connected with a drug crime. The prosecutor told Irick that she would not file a §924(c) for the gun if Irick would plead. She also agreed to stipulate in a plea agreement that the firearm was not related to the cocaine—a stipulation that would prevent Irick from receiving a sentencing enhancement under the guidelines for possessing the gun and thereby making him eligible for receiving a safety valve sentence below the ten-year mandatory minimum. [192] According to the prosecutor, if Irick had accepted the plea offer, he might have been sentenced to five or six years, not 15. The prosecutor also told Irick that if he pursued his challenge to the legality of the traffic stop and subsequent search, she would withdraw the offer, explaining that once she had gone through a hearing on the motion to suppress, which is the equivalent of a mini trial, there would be little benefit to the government from a plea. Irick did not accept the offer, but rather went forward with the motion to suppress. At the suppression hearing, the prosecutor stated her intent to add the §924(c) count if the government were to prevail on the motion. The government prevailed on the motion, and the prosecutor ultimately filed the §924(c) charge. Irick went to trial, was convicted of the drug and gun counts and was sentenced to 15 years—10 for the drugs and a consecutive 5 for the gun charge. |
IV. Limited Ways to Avoid Mandatory Sentences
A federal defendant convicted—by plea or by trial—of a crime carrying a mandatory minimum sentence will receive that sentence unless one of the following happens: 1) the defendant qualifies for the limited safety valve exception to drug mandatory minimums and/or 2) the prosecutor makes a motion to the court stating the defendant should receive a lower sentence because they have provided substantial assistance to the government.
In fiscal year 2012, 15,131 individuals were convicted of an offense carrying a drug mandatory minimum penalty.[193] Of those, 29 percent (4,395 defendants) benefited from the safety valve; 19 percent (2,928 defendants) receive a reduction because of substantial assistance, and 9 percent (1,474 defendants) received both.[194]
If drug defendants facing mandatory minimum penalties are able to secure relief through the safety valve or substantial assistance motions, the sentencing consequences are dramatic: for fiscal year 2012, the average sentence for a drug trafficking defendant who received relief from a mandatory minimum was almost 5 years (59 months) as compared to over 10 years (128 months) for the offender who did not (see Figure 6).[195]
Safety Valve
Under federal legislation, federal drug defendants can avoid mandatory minimum sentences and have their guidelines sentences reduced if they qualify for the federal safety valve.[196]
Qualifying defendants must have little or no prior criminal history (i.e., they qualify for criminal history category I),[197] did not use violence or possess a firearm in connection with the offense, the offense did not result in death or seriously cause bodily injury to anyone, the defendant was a low-level offender (i.e. not a manager or supervisor of others), and the defendant truthfully tells the government all the information he has concerning the offense or scheme in which he was involved.
Although it is up to the judge to determine whether a defendant qualifies for the safety valve, the prosecutor has significant input. If the government is dissatisfied with the truthfulness and completeness of the defendant’s information, or if it believes the defendant had a gun in connection with the crime, it can oppose safety valve eligibility and courts may withhold the safety valve downward sentencing adjustment in response.[198]
The safety valve’s impact on federal drug sentences is significant. A drug offender’s average sentence without a safety valve is 94.2 months; with a safety valve it is 34.2 months.[199]
In fiscal year 2012, the federal safety valve benefitted 38.5 percent of all federal drug defendants, or 9,445 defendants, including defendants who might have benefitted from substantial assistance motions as well. More than half of those had faced mandatory minimum sentences; the others received sentence reductions under the guidelines.[200] Because qualification for the safety valve requires a low-level drug trafficking position, drug trafficking organizers/leaders and managers receive safety valve relief at low rates (5.8 percent and 8.3 percent, respectively) compared to mules and couriers (53.0 percent and 65.3 percent, respectively), according to the Sentencing Commission.[201]
The safety valve enables the judge to sentence below an otherwise applicable mandatory minimum. But the defendant is still subject to the guidelines. The guidelines themselves provide a two-level safety valve reduction in the offense level, with a corresponding decrease in sentencing range. But the mitigating impact of the two-level reduction can be minimal unless the judge is willing to impose an even lower sentence because the guidelines are now advisory.
Ysidro Diaz—whom the judge characterized as a “run-of-the-mill, low-level participant in a drug distribution offense,” [202] —pled guilty to conspiring to deliver one kilogram of heroin, his first criminal conviction. The applicable statutory minimum sentence for this quantity of heroin was 10 years; his guideline range was ten to twelve-and-a-half years. [203] Because Diaz qualified for the safety valve, the court could ignore the mandatory minimum and sentence Diaz under the guidelines. The safety valve adjustment reduced his guidelines sentencing range to 97 to 121 months, i.e., that is, a still substantial sentence. Because Diaz pled guilty, he was eligible for a three-level downward adjustment for acceptance of responsibility, reducing his guidelines sentencing range to 70 to 87 months. The judge gave him an even lower sentence of four years in prison. [204]
Substantial Assistance
It’s a bounty system. [The defendant] gets credit for bringing in other people’s heads. If they don’t need you, you’re out of luck. If ringleader cooperates, he may get a better deal than people of lower culpability.[205]
—Scott Lassar, former US Attorney, Chicago, April 6, 2013
Absent eligibility for the safety valve, the only way federal drug defendants can avoid otherwise applicable mandatory minimum sentences is to cooperate with the government pursuant to a plea agreement. The sentencing regime permits substantially lower sentences for persons who assist the government. The possibility of a sentence reduction does not redeem mandatory sentences that are too high:
It is one thing to lower an otherwise appropriate sentence to reward a defendant’s cooperation but quite another to threaten to impose an otherwise unjust sentence if he decides not to cooperate or tries but produces no law enforcement results. The latter situation essentially converts a refusal or inability to cooperate into an aggravating sentencing factor, in violation of a basic principle of our sentencing regime.[206]
Judges may impose a sentence below a mandatory minimum if the prosecutor files a motion seeking a lower sentence because the defendant has provided “substantial assistance” to law enforcement.[207] These are typically referred to as §5k1.1 departures, based on the guidelines provision that incorporates this statutory mechanism for relief and authorizes a sentence below the guidelines range because of substantial assistance.[208]
The prosecutor can choose to file a motion seeking a guidelines reduction or a reduction below the statutory minimum as well. Although not required by law, prosecutors typically require defendants to plead guilty as a prerequisite to being eligible for a substantial assistance motion.[209]
The possibility of a reduced sentence is powerful motivation to cooperate with the government. Judge John Gleeson, who was a former federal prosecutor, told Human Rights Watch that before mandatory minimum sentences and the guidelines, it was hard for prosecutors to get people to testify in organized crime cases.[210] But, he also pointed out that the possibility of a reduced sentence because of assisting the government does not cure the injustice of confronting defendants with mandatory sentences that may be disproportionately severe: “it’s fine to give a kingpin a reward for cooperation. But it’s not fine to give someone a 10-year sentence unless he cooperates.”[211]
Our data analysis for fiscal year 2012 shows 29 percent of drug defendants (4,404 individuals) convicted of offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences received relief for providing substantial assistance to the government. As shown in the Appendix, the range varied from 5.4 percent in Arizona to 85.1 percent in North Dakota.
The sentencing benefit for providing “substantial assistance” is considerable.[212] In fiscal year 2012, the average sentence of a drug trafficking defendant facing mandatory minimum sentences who received no relief from those sentences was 128 months; if they received a §5k1.1 motion, their sentence was 69.5 months, a 45.7 percent decrease. In fiscal year 2012, the median guideline sentence for all drug trafficking defendants was reduced 45.8 percent, from 88 to 48 months, as a result of prosecutor’s §5k1.1 motions.[213]
Prosecutorial Discretion in Making Substantial Assistance Motions
Prosecutors control the ability of defendants to escape from mandatory minimum sentences through substantial assistance. They have complete discretion over whether to offer a defendant the chance to cooperate and then whether to make a motion to reduce the defendant’s sentence because he provided such assistance.
Although an offender might want to cooperate, this is no guarantee that the prosecutors will agree. If, in the judgment of the prosecutors, the defendant has no new or important information to offer, prosecutors will decline to enter into a cooperation agreement with him. Prosecutors typically want assistance in the prosecution of someone of equal or greater significance than the defendant.
As one current prosecutor told us, “We do not give a break for turning in evidence that only gets someone lower down the food chain.”[214] Low-level offenders who want to assist often have no useful information to offer the government.[215] The disadvantage low-level drug offenders face compared to those at a higher level is called the “cooperation paradox.”[216]
According to the Sentencing Commission, the highest rates of substantial assistance relief from mandatory minimum sentences for drug offenders were for managers (50.0 percent) and organizers/leaders (39.1 percent) and the lowest rates of substantial assistance relief were for mules (19.5 percent), street-level dealers (23.4 percent), and couriers (27.1 percent).[217] Judge Thelton Henderson recounted one case from Bakersfield, California:
Someone asked the defendant if he wanted to make $350 driving a truck to Los Angeles. He got caught carrying a quantity of drugs that triggered a 10-year mandatory minimum. He said he would cooperate. Told everything he knew. But he didn’t know anything, so no §5k1.1. Later, the head of the same drug operation was caught. He ratted on everyone. And he got three years.[218]
There is no uniformity among federal districts on many key aspects of sentencing reductions:
- First, defendants who agree to cooperate with the government in the hopes of benefitting from a §5k1.1 motion are typically required to enter into a plea agreement with the government. In some districts, prosecutors usually require them to plead to all the charges in the indictment, in others they do not.[219]
- Second, districts vary widely in what defendants must do to benefit from a §5k1.1 motion.[220]
- Third, there is great diversity among districts about whether prosecutors will specify to the court a recommended sentencing reduction.[221]
- Fourth, if a specific sentencing reduction recommendation is made, there is no uniformity among districts in the length of reduction recommended.[222]
These substantial differences among prosecutors and in different districts mean that defendants with similar records who provide similar assistance may have radically different sentencing consequences in return for trying to cooperate with the government.[223] Moreover, courts are not bound to follow any specific sentence reduction recommendations by the government and they vary in their likelihood of doing so.[224]
Even if defendants agree to provide substantial assistance and make their best efforts to do so, the government may not file the requisite substantial assistance motion. According to research by the Sentencing Commission, nearly six out of ten defendants who provided assistance did not receive a §5k1.1.[225]
Prosecutors have unreviewable discretion to decide whether a defendant has in fact provided what they consider “substantial assistance.”[226] The term is not defined by statute, the Guidelines Manual, or the Department of Justice. Individuals who participated in undercover investigations or who testified in court were more likely than not to receive substantial assistance departures, but even then the motions were not guaranteed.[227]
Defendants may plead guilty and give up their right to go to trial only to discover the prosecutors do not value their cooperation enough to make a substantial assistance motion. As one court noted,
Formerly, this power [to decide if assistance had been provided] was lodged in a neutral judge, but now it resides initially in the hands of the prosecutor, an interested party in a criminal proceeding. Such a change in authority has the potential to tilt this aspect of a criminal prosecution unfairly in favor of the government.[228]
A survey for the Sentencing Commission published in 1998 found that 59 percent of judges and 55 percent of chief probation offenders said they personally had cases in which they believed the defendant had provided “substantial assistance” but the prosecutor did not make a §5k1.1 motion.[229]
In a survey of judges in 2010, 25 percent strongly agreed and another 29 percent somewhat agreed that “Congress should amend 18 U.S.C. §3553(e) to authorize judges to sentence a defendant below the applicable statutory mandatory minimum to reflect a defendant’s substantial assistance even if the government does not make a motion,” and equal percentages supported a similar amendment by the Sentencing Commission to USSG §5k1.1.[230]
Jason Pepper[231]In early 2004, Jason Pepper—a 24-year-old from Akron, Iowa—pled guilty to drug charges involving 500 grams of methamphetamine, stipulating in his plea agreement to distributing between 1.5 and 5 kilograms of a methamphetamine mixture. A first time, low-level, nonviolent offender, Pepper qualified for the safety valve, escaping the otherwise applicable 10-year mandatory minimum sentence, but was still looking at a 97 to 121 month guideline range. The government filed a substantial assistance motion recommending that he be given a 15 percent downward departure on the basis of his cooperation in the prosecution of other drug offenders. After considering all the circumstances of Pepper’s crime and history, the court sentenced him to 24 months imprisonment, a nearly 75 percent downward departure from the low end of the guidelines. The government appealed on the grounds that this departure was too generous; the Eighth Circuit overturned and remanded for resentencing. At his first resentencing, the court again sentenced Pepper to 24 months, this time granting a 40 percent downward departure based on his substantial assistance and a further downward variance based on, inter alia, Pepper’s rehabilitation since his initial sentencing. The government again appealed, the Eighth Circuit again overturned and this time ordered another resentencing by a different judge. She granted Pepper a 20 percent reduction and no further downward variance, imposing a 65 month sentence. Pepper was supposed to go back to court to serve another 41 months. By this time, it had been three years since Pepper had finished his two-year sentence. Pepper appealed, the Supreme Court overruled the Eighth Circuit and remanded. As the Supreme Court summarized, “Pepper was a 25-year-old drug addict who was unemployed, estranged from his family, and had recently sold drugs as part of a methamphetamine conspiracy.” But by the time of his second appeal in 2009, Pepper had been out of prison for three years (having finished his 24 month sentence), had been drug-free for nearly five years, had attended college and achieved high grades, was a top employee at his job slated for a promotion, had re-established a relationship with [his formerly estranged] father, and was married and supporting his wife’s daughter. [232] The district court took all of this into consideration in setting a sentence that would be sufficient but not greater than necessary to serve the purposes of sentencing. Despite the government’s strenuous efforts to secure a higher sentence, Pepper was sentenced to time served. |
V. The Plea Process
Criminal justice today [in the United States] is for the most part a system of pleas, not a system of trials.[233]
— Justice Anthony Kennedy, Lafler v. Cooper, 2012
Of course the system is coercive.
—Assistant US attorney (name withheld), Michigan, April 18, 2013
In the United States, plea bargaining, not trials, determine the fate of most criminal defendants.[234] This is certainly true in federal cases, including drug cases. Only three percent of federal drug defendants go to trial.[235] In fiscal year 2012, 97 percent of all federal drug convictions were secured by guilty pleas.[236]
The Supreme Court has acknowledged the inevitability of plea bargaining. Justice Scalia recently noted, “We accept plea bargaining because many believe that without it, our long and expensive process of criminal trial could not sustain the burden imposed on it, and our system of criminal justice would grind to a halt.”[237]
The integrity and reasonableness of the plea bargaining process depends greatly on the quality of defense counsel and the motivations and interests of the defendant. But because of their inordinate power, even more rides on individual prosecutors and their supervisors. In two recent decisions, the US Supreme Court delineated some of defense counsel’s responsibilities to ensure the integrity of plea bargaining.[238] But it has said little about the responsibilities of prosecutors, other than to suggest they have an almost complete carte blanche to get defendants to plead.
Prosecutorial discretion in deciding what cases to pursue and what charges to bring is indispensable to balance the many factors that must be considered in each case.[239] But in a regime of mandatory minimum sentences and sentencing guidelines, prosecutors have too much power to determine sentences by what they charge and what pleas they accept. As Yale law Professor Kate Stith and Judge Jose Cabranes— two experts on federal sentencing—have noted,
[T]he exercise of broad prosecutorial authority over sentencing within a system that severely limits the sentencing discretion of federal judges means that the power of prosecutors is not subject to the traditional checks and balances that help prevent abuse of that power.[240]
As University of Pennsylvania law professor and criminologist Stephanos Bibas has written, prosecutorial “discretion is bad only when it becomes idiosyncratic, unaccountable, or opaque…. When used judiciously it can deliver consistent and tailored results. What we need to watch out for in practice, then, are the forces that push prosecutorial discretion in the wrong direction, away from the public’s sense of justice.… The press of business pushes prosecutors to use their discretion to coerce pleas and threaten higher punishments for those who refuse to bargain.”[241]
Pros and Cons of Plea Bargaining
Because adversarial trials are an important bulwark against official overreaching and protect the fundamental right to liberty, US trials are presided over by independent judges, defendants have the right to counsel, the government has the burden of proof, the defendant has the right against self-incrimination, and numerous evidentiary and other rules seek to ensure the fairness of the trial process.
The procedural safeguards of a trial hold wrongdoers accountable, protect defendants from government arbitrariness and abuse, and honor the rights of victims and the public’s interest in justice and effective law enforcement. Appellate review provides additional layers of transparency and protection.
In contrast, plea bargaining in federal drug cases offers little or no guarantees of transparency, discovery, and fair play. Judicial and appellate review of the plea bargaining process is also limited and superficial. Nevertheless, plea bargaining has become ubiquitous in the United States.[242]
Its defenders argue that plea bargaining permits more efficient resolution of criminal cases. The assumption is the parties are rational economic actors and they jointly agree on a plea that enables the defendant to avoid the anxieties and uncertainties of a trial and to save the government from having to expend the resources necessary to try the case and to spare it the possibility of an acquittal. They also consider plea bargains legitimate to the extent they allocate punishment fairly, i.e., to the extent they are seen as replicating the likely trial results based on the indictment with appropriate sentence discounts to the defendants for pleading.[243]
But others point out that “though trials allocate punishment imperfectly, plea bargaining adds another layer of distortions to warp the fair allocation of punishment.”[244] Most importantly for the purposes of this report is the fact the plea bargaining process can yield highly distorted sentences: the government does not engage in plea bargains to secure sentences that would be similar to a trial outcome; it makes offers and threats to secure pleas.[245] The resulting sentences undermine the accuracy and integrity of the criminal justice process.
Prosecutors can put such pressure on defendants to plead that even innocent defendants may succumb.[246] New York University law Professor Rachel Barkow, who has extensively studied federal prosecutorial conduct has stated,
[P]lea bargaining pressures even innocent defendants to plead guilty to avoid the risk of high statutory sentences. And those who do take their case to trial and lose receive longer sentences than even Congress or the prosecutor might think appropriate, because the longer sentences exist on the books largely for bargaining purposes. This often results in individuals who accept a plea bargain receiving shorter sentences than other individuals who are less morally culpable but take a chance and go to trial.[247]
A recent analysis of trial data suggests that even defendants with strong cases and good chances of acquittal at trial are choosing to plead because of the enormous sentencing benefit of doing so compared to the sentencing risks they face should they lose at trial.[248]
Prosecutors face professional and institutional pressures that encourage them to secure convictions through pleas.[249] Their decisions may be motivated by many factors, including “inexperience or poor judgment, the desire for professional advancement, or vindictiveness.”[250]Plea agreements increase the number of convictions they obtain and enable prosecutors to avoid the burden of trial, to manage their caseload more efficiently, to encourage pleas by other defendants in multi-defendant proceedings, and to eliminate the risks of a defeat at trial.[251] As one current prosecutor in a very large district told us:
There are only so many hours in a day, and there are so many crimes, if a low-level guy comes in and wants to resolve the case, I may charge lower.[252]
Another prosecutor pointed out, prosecutors “are a finite resource…. Pleading benefits us by saving resources.”[253] Prosecutors may also enter into plea bargaining because they recognize the sentence attached to the original charge would be too high, that defendant’s role has turned out to be less significant than they thought initially, or they think a defendant is truly remorseful and should reap the advantages of a plea.
Defense counsel can do their best, but in federal drug cases they have relatively few bargaining chips and they have to counsel their clients accordingly, including clients who strongly reject guilty pleas.[254] The federal prosecutor is a criminal justice decision-maker uniquely empowered by mandatory minimum sentencing laws and sentencing guidelines to make weighty decisions over an individual’s life and liberty, deciding what to charge, what plea bargains to make.[255] Much depends therefore on who the prosecutor is and in which office they work. As one assistant US attorney told us, “It’s the luck of the draw with prosecutors in each office … some make deals, some won’t, some play fast and loose, charge big and plea small.”[256]
In some districts, “the defendant gets hammered. And everyone knows it.”[257] Referring to one prosecutor, a defense attorney said, “He thinks anyone who deals with drugs, even at a low level, is a horrible human being who deserves to be locked up as long as possible.”[258] A defense counsel’s ability to work out a deal,
[d]epends on the individual AUSA you are dealing with. Both his individual approach plus how he is viewed in the office, how close to management, affects how much leeway they have. They will also say it’s policy when they don’t want to give you something you want, but they will ignore policy all the time when it suits them.[259]
What Happens in Plea Bargaining
The process by which the guilty plea is secured can vary considerably in practice. The greatest likelihood of a defendant getting a good plea offer often occurs between the initial complaint and the indictment.[260] In other cases, a plea will follow the indictment, and possibly extensive pre-trial proceedings, including motions, discovery, and even evidentiary hearings. The plea may follow a single offer from the prosecutor; it may take numerous plea offers before the defendant agrees.
There is no transparency to the plea process. There are no formal rules governing whatever give and take occurs. The prosecutor can make and change plea offers without specifying her evidence and without giving reasons for her choices or providing a response to the defense counsel’s arguments. While some federal prosecutors may reveal their evidence to defense counsel to stress the strength of their case and the wisdom of a plea, others do not. Defense counsel may have to evaluate the risks of trial in the dark.[261]
Under the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure, the prosecutor may agree in a plea agreement that the government will,
- (A) not bring, or will move to dismiss, other charges;
- (B) recommend, or agree not to oppose the defendant's request, that a particular sentence or sentencing range is appropriate or that a particular provision of the Sentencing Guidelines, or policy statement, or sentencing factor does or does not apply (such a recommendation or request does not bind the court); or
- (C) agree that a specific sentence or sentencing range is the appropriate disposition of the case, or that a particular provision of the Sentencing Guidelines, or policy statement, or sentencing factor does or does not apply (such a recommendation or request binds the court once the court accepts the plea agreement).[262]
Some prosecutors refuse to offer any concessions in exchange for a guilty plea unless they want the defendant to cooperate with them.[263] We do not know how prevalent this hardball approach to plea agreements is. Defense lawyers told us that when prosecutors refuse to offer concessions, and they do not believe their client would escape conviction after a trial, they may advise their clients to plead guilty to the charges in the indictment without a plea agreement.[264] That way, the client avoids the various waivers, including waivers of right to appeal, that are typically included in plea agreements and will receive the guidelines reduction for “acceptance of responsibility.”[265] In addition, because the sentencing guidelines are now advisory, defendants can seek to persuade the judge to sentence below the guidelines based on the 3553(a) factors.
When a prosecutor will consider a plea agreement, the negotiations typically involve one or more of the following: fact-bargaining, charge bargaining, and sentence bargaining.[266]
fact bargaining: In a fact bargain, the prosecutor agrees to stipulate to certain facts that will affect how the defendant is sentenced. A prosecutor should not stipulate to facts he suspects or believes to be false as part of a deal with the defendant; he should not deliberately mislead the court—or the probation officer who prepares the presentencing report the judge will use to help determine the appropriate sentence.[267] If a defendant is “caught driving a truck carrying 100 kilos, we can’t say in a plea agreement that there were only 5.”[268] But in many drug cases, the drugs are not weighed and the actual quantity of the drugs involved is something of a guess.[269] Such negotiations are particularly likely for individual co-conspirators; prosecutors often negotiate the quantity for which they will be held accountable.[270] Prosecutors will also bargain about “facts” that are factors that can raise or lower offense levels under the guidelines, e.g., role in the offense. The prosecutor may agree to recommend or not to oppose a reduction for minor or minimal role even when the facts do not support that recommendation.[271] The uncertainty and costs inherent in criminal adjudications can predispose defendants and prosecutors to agree to “facts” that will promote a bargaining agreement.[272]
charge bargaining:[273] “The most traditional of the [Department of Justice’s] bargaining chips is the ability to drop charges at will…. The pressure is placed upon the defendant by bringing a multi-count indictment and then trading away charges or counts more difficult to prove in return for a guilty plea to other counts or lesser charges.”[274] During charge bargaining, a prosecutor may also threaten to file superseding charges that will enhance the defendant’s sentencing exposure if the defendant insists on going to trial. If the defendant agrees to waive her right to trial, the prosecutors then agree not to file the additional charges.[275]
sentence bargaining: In a sentence bargain, the prosecutor and defendant agree on a sentence that will be recommended to the judge, typically following an agreement on the charges to which the defendant agrees to plead guilty.[276]
Federal judges have little to do with the plea process itself; indeed, federal law prohibits them from participating in plea negotiations.[277] Plea agreements must be approved by judges, but they will approve most agreements if the defendant has made a “knowing and voluntary” waiver of her right to trial, and if the plea is founded on some “factual basis.”[278] Hearings on plea agreements are pro forma, with judges asking a set series of questions which the defendants have been coached to answer. One scholar has described the judicial evaluation of plea agreements as “anemic, since the facts supporting guilty pleas can be remarkably thin, and many ‘knowing’ and ‘voluntary’ guilty pleas are nevertheless coercive and unjust.”[279] A judge may decline to accept the guilty plea and plea agreement if the charge/s have no factual basis, but this is extremely rare.[280] It is also rare for a judge to impose a sentence that is higher than one to which the parties agreed in a plea agreement; more typically, the judge accepts the parties’ decision in the agreement, or may decide to impose an even lower sentence.[281]
Joseph Ida[282]Joseph Ida’s case illustrates how, if the government is determined to obtain a plea and confronts a defendant reluctant to do so, it may choose to make increasingly attractive plea offers to induce the defendant to plead. Joseph Ida was indicted in March and, along with other defendants, charged with being part of a cocaine and marijuana distribution conspiracy in New York City. The charges carried a 10-year mandatory minimum and a maximum of life. As shown in the chart below, the government made four plea offers to Ida. Under the terms of the first offer, Ida would plead guilty to conspiracy to distribute 5-15 kilograms of cocaine with a mandatory minimum sentence of 10 years and a guidelines sentencing range of 8 to 10 years (97 to 121 months). In the next plea offer, the government sweetened the offer by offering to let Ida plead guilty to a lesser included offense—an unspecified quantity of drugs—which removed the mandatory minimum and made Ida eligible for a sentence of 0 to 20 years. With the lower charges and the offer of a two-level reduction in his guidelines offense level for a “global disposition,” if all the defendants in the case pled guilty, Ida’s sentencing range would drop to 7 to 9 years (87 to 108 months). In the third offer, prosecutors agreed to stipulate that Ida was a “minor participant” in the drug business, which reduced his guidelines sentencing range down to a five to six year range. The last offer, however, slightly increased Ida’s sentencing range because prosecutors had secured a plea from the defendant who had the strongest case, and therefore was no longer willing to offer quite as good a deal to Ida and the remaining defendants as it had before. Ida pled guilty and on August 9 2012, he was sentenced to 63 months. |
VI. Doing Justice
There is an inherent conflict of interest when prosecutors are de facto sentencers. They get reputations based on convictions. They are not disinterested institutionally or individually. This is a big difference from federal judges who have no stake in a case, who seek only to do justice.[283]
—Judge Thelton Henderson, California, June 11, 2013
Prosecutors are not gladiators fighting for victory in a criminal justice arena. They are representatives of the United States. As the Supreme Court pointed out many decades ago, the goal of the sovereign in a criminal prosecution is “not that it shall win a case, but that justice shall be done.”[284]
Most legal and ethical obligations of prosecutors address misconduct and malfeasance, e.g., withholding evidence, suborning perjury.[285] Relatively little has been written or codified about the prosecutors’ obligations regarding the justness of a sentence or their plea bargaining tactics. Federal prosecutors should not file criminal charges or threaten to do so in plea bargaining when they do not believe the charges are supported by the evidence. But if the evidence is there, prosecutors may file or threaten to file whatever charges they choose.
Courts have recognized that prosecutorial charging and plea bargaining decisions should not be based on “tossing a coin” or other arbitrary processes or categorical distinctions. But the absence of utter arbitrariness is not the same as ensuring justice.[286] Bruce Green, a Fordham law professor and former federal prosecutor suggests that one meaning of doing justice can be “seeking to achieve a ‘just’ and not necessarily the most harsh result.”[287]
Department of Justice Policy
To our knowledge, the Department of Justice has never explicitly encouraged or directed prosecutors to exercise their charging and plea negotiation authority to secure just sentences for all convicted defendants.[288] Nor, to our knowledge, has the department ever urged prosecutors to follow Standard 3.3-3.9(b)(ii) of the American Bar Association Standards, under which prosecutors should not pursue charges, even when supported by the evidence, if the authorized punishment is disproportionate to the particular offense or offender.[289]
On the contrary, Department of Justice policy has long encouraged prosecutors to charge defendants with the most serious offense (with the longest sentence) consistent with his conduct that is likely to result in a sustainable conviction.[290] This policy has also required prosecutors to seek sentencing enhancements and §924(c) charges where applicable.[291]
In a 2010 memorandum to prosecutors, Attorney General Holder acknowledged the “long-standing principle” that federal prosecutors should “ordinarily charge the most serious offense” consistent with the defendant’s conduct and the evidence. But he also insisted that charging decisions should be made in the context of,
[A]n individualized assessment of the extent to which particular charges fit the specific circumstances of the case, are consistent with the purpose of the Federal criminal code, and maximize the impact of Federal resources on crime.[292]
He reminded prosecutors that “unwarranted disparities” may result from “failure to analyze carefully and distinguish the specific facts and circumstances of each particular case. Indeed, equal justice depends on individualized justice, and smart law enforcement demands it.”[293] While laudable, these views fall short of expressly urging prosecutors to use their discretion to pursue sentences proportionate to the defendant’s actual conduct.
In August 2013, at a meeting of the American Bar Association, Holder publicly announced that federal laws were sending too many people to prison for too long, called for a rethinking of the role of prison sentences in promoting public safety and, more specifically, pledged his support for reform of federal mandatory minimum sentencing laws. Not waiting for Congress to act, he also issued a memorandum to federal prosecutors on charging and sentencing. As discussed below, his new charging policies, while welcome, are weakened by defective criteria and premises that may decrease their efficacy, even for the limited category of defendants to which they ostensibly apply.
Mandatory Minimum Sentences for Low-Level Offenders
In a speech before the American Bar Association in August, Holder acknowledged mandatory minimum sentences can lead to unduly harsh sentences for certain low-level drug offenders and he announced changes in charging policies for such offenders. He said,
They now will be charged with offenses for which the accompanying sentences are better suited to their individual conduct, rather than excessive prison terms more appropriate for violent criminals or drug kingpins.[294]
Holder directed federal prosecutors to decline to file charges carrying mandatory sentences against certain low-level, nonviolent drug offenders.[295]
Holder’s instructions may not have a significant impact for low-level offenders. According to one analysis, only about 500 of the more than 15,000 defendants convicted in FY 2012 might have received a lower sentence if the Holder memo had been in force then and fully implemented by line prosecutors.[296]
Many of the defendants who might be covered by Holder’s new charging policy did not need the reform because they already benefit from the statutory safety valve exemption.Holder’s policy also contains many criteria which limit the offenders who should not be charged with offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences.[297] There are many offenders excluded from the policy for whom five- or ten-year mandatory sentences may also be excessive, e.g., defendants who occupied the lowest rungs in large-scale trafficking organizations or gangs, who were part of a conspiracy that involved guns even though they personally did not possess or carry a gun, or who had several prior convictions for minor offenses.[298] It is notable that low-level offenders who might avoid mandatory minimum sentences because of the new policy would remain subject to the sentencing guidelines which, as discussed earlier in this report, can themselves produce severe sentences. Finally, we note that Holder acknowledges there may be charges filed that trigger mandatory minimum sentences for a defendant who prosecutors come to learn is a low-level, nonviolent offender. Holder notes the defendant could plead guilty to a lesser included offense. Such a scenario would leave the defendant forced to forgo trial in order to secure a fair sentence.
Prior Felony Conviction Sentencing Enhancements
In the same August 2013 directive to prosecutors, the attorney general instructed prosecutors to refrain from filing an §851 information to secure a prior felony conviction sentencing enhancement “unless the defendant is involved in conduct that makes the case appropriate for severe sanctions.”[299]
Holder instructed prosecutors considering whether to file the enhancement to consider factors such as whether the defendant had a significant role in a criminal organization, used violence, the nature of his criminal history, and other factors. It is clear Holder hopes to reduce the inappropriate use of §851 enhancements, but it remains to be seen whether his directive will have the intended effect.
In a recent opinion lambasting the federal government’s use of prior felony conviction sentencing enhancements to coerce guilty pleas, Judge John Gleeson summarized the problems with Holder’s directive:
- First, it maintains the presumption that §851 informations should be filed against all defendants with prior qualifying convictions unless they fit into a narrow category of exceptions. Instead, Gleeson says, the prosecutor’s job should be to “select the deserving few, not to include all eligible defendants absent an affirmative decision to decline.”
- Second, the exclusionary criteria are too vague and broad. Any federal prosecutor “can easily conclude that any one of the factors that will typically result in a mandatory minimum charge (aggravating role, use or threat of violence, ties to an enterprise, and significant criminal history) will also justify the filing of a prior fel0ny information….”[300]
- Gleeson notes that Holder did not expressly repudiate the long-standing Department of Justice policy that includes prior felony conviction sentencing enhancements among the “most serious, readily provable offenses” that should be brought in every case. He also calls on the Department of Justice to explicitly prohibit the use of prior felony information to coerce defendants into pleading guilty or to punish those who refuse to do so.[301]
§924(c) Charges
Attorney General Holder’s 2013 memorandum to prosecutors regarding charging in certain drug cases did not mention §924(c) charges, nor did he suggest that prosecutors should not seek statutory minimum sentences for low-level drug offenders who possess but do not use guns.[302] This is unfortunate, given the astonishing sentences that can result from §924(c) charges—and the willingness of prosecutors to use those charges to punish defendants who refuse to plead guilty.
At the very least, Holder should have directed prosecutors not to stack §924(c) sentences in a single case. Given Holder’s silence about §924(c), prosecutors presumably may still follow the 2003 memorandum issued by then Attorney General John Ashcroft directing them to charge one count of 18 U.S.C. §924(c) in every case where applicable. If an offender has three or more possible counts and the predicate offenses are crimes of violence, the Ashcroft memorandum directed prosecutors to charge at least two §924(c) counts.[303]
Prosecutorial Culture
Some current and former US Attorneys and assistant US attorneys describe a prosecutorial culture that values high sentences. One former US Attorney told us,
Prosecutors get kudos based on aggressive prosecutions. It’s not just convictions, but also length of sentence.... That’s what earns you pats on the back. We weren’t trained to think about the lowest sentence that serves the goals of punishment. We looked down on low sentences.[304]
When pressed about the fairness of sentences that result from their decisions, prosecutors deflected responsibility for the outcomes, whether by plea or trial. One prosecutor told us: “Congress sets the laws, my job is to carry out the will of Congress.”[305] Another said, “I don’t sentence people, the court does.”[306]
Some prosecutors also told us that judges set the sentences. But as Judge Thelton Henderson told us, “It is disingenuous for prosecutors to say they don’t sentence defendants. The sentence is a function of the charge.”[307] When judges had vast discretion to set sentences ranging anywhere from zero to life, prosecutors could more plausibly deny responsibility for the length of the sentences. But when sentences are triggered by mandatory minimums and still powerful, albeit now advisory, sentencing guidelines that prosecutors can readily manipulate, prosecutors cannot legitimately disclaim responsibility for the sentences defendants receive.
There are certainly prosecutors who do seek reasonable sentences. A former US Attorney told Human Rights Watch, “I always felt that sentences should be fair.” Because he recognized prior conviction enhancements and §924(c) counts “could easily result in sentences that were too high” prosecutors in his district had to get his approval before being able to pursue those increased penalties.[308] A former assistant US attorney told us, “I think prosecutors [in my office] exercised their power responsibly. Our office did a good job of avoiding unjust results…. We made decisions on the right basis.”[309]
Other attorneys told us that “some prosecutors do the right thing and some have more autonomy to help your client,”[310] that prosecutors in their districts are fairly reasonable,[311] and that some prosecutors are truly concerned about fairness.[312]
A current prosecutor insisted, “We’re trying to do the right thing. I will make choices to avoid outcomes that would be unfair.”[313] But he, like other prosecutors with whom we talked, acknowledged prosecutors are not used to thinking about sentencing outcomes in terms of what is proportional to the offense or what is sufficient but not greater than necessary to serve the purposes of punishment.
Going to Trial: All Bets Are Off
Prosecutors try to be fair and offer good deals. But if you offer the defendant a good deal, and you’ve warned him about the consequences of going to trial, and the defendant doesn’t take the deal then all bets are off.[314]
—Former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, April 1, 2013
The criminal justice system punishes people ‘who have the nerve to go to trial.’[315]
—Professor Rachel Barkow, as quoted in The New York Times, September 25, 2011
Some prosecutors we spoke to took pride in making reasonable offers to lower or dismiss charges or to agree not to file higher charges to try to ensure low-level offenders do not receive lengthy sentences more appropriate for significant traffickers.[316]
We have no way to determine how many of the lower sentences obtained through plea bargaining are in fact fair, i.e., would meet the criteria of proportionality and parsimony. Our research does leave us sure that the intentional quest for fairness varies by individual prosecutors and by district. We are also sure that any quest for fairness ends once a defendant insists on standing trial.
If a defendant rejects a plea offer and chooses to go to trial, prosecutors will at the very least try him on the original charges, even if they carry sentences the prosecutors believe are higher than necessary based on his conduct and culpability.[317] Our research found no case in which prosecutors filed superseding indictments to secure a lower sentence for a defendant who insisted on going to trial, unless newly uncovered evidence indicated the original charges were wrong. A former prosecutor acknowledged,
In a drug conspiracy, if the prosecutor indicts everyone for an offense carrying a mandatory minimum, and a mope [very low-level drug offender] refused to plead, he’ll go to trial on the higher charge. I don’t know of a case in which the prosecutor lowered the charge in an indictment if a low-level guy decided to go to trial.[318]
Prosecutors endorsed the goal of using the sentencing differential to pressure defendants to waive their right to trial. As one prosecutor acknowledged candidly, “The key function of the trial penalty is to encourage pleas.”[319]
We asked many prosecutors if they were troubled by the discrepancy between a plea offer of, say, 15 years and a post-trial sentence of 30 years or life without parole. They were not. They see it as part and parcel of plea bargaining. As one former US Attorney told us, “If you reject the plea, we’ll throw everything at you. We won’t think about what is a ‘just’ sentence.”[320] Another former federal prosecutor in California explained that the higher sentencing exposure if a defendant goes to trial is “the defendant’s choice. He was fully informed and rolled the dice.” He added he was “not bothered” by disparity between a shorter plea offer and far longer post-trial sentence.[321] Added another prosecutor: “If the defendant won’t accept a plea that is reasonable, then I’m not going to be sympathetic after trial. Otherwise no one would ever plead guilty.”[322]
Asked if the higher sentence post-conviction would satisfy requirements of proportionality and being no greater than necessary to serve the purposes of punishment, prosecutors essentially dodged the question. They fell back on the notion that defendants could have taken a plea and thereby avoided the higher sentence.
Every time a prosecutor makes good on a threat to seek higher sentences for a defendant who will not plead has a chilling effect in other cases. This is one of the reasons prosecutors carry out their threats. They want their threats to be effective at securing pleas in the current and future cases. To do so, they cannot get a reputation for bluffing or walking away from the possibility of hitting defendants who will not plead with higher sentences.[323] As a former prosecutor told us,
If you have threatened to file the superseding charges if the defendant goes to trial, you have to do it. Because if we don’t no one will ever listen seriously to our offers [in the future], the word will get out. And you want the next guy to take you seriously.[324]
Prosecutors may realize making good on their threat will lead to an excessive and unfair sentence, but maintaining their credibility often appears to take priority. In a recent case, the judge asked the prosecutor whether a mandatory life sentence triggered by a prior felony information was “just.” The defendant had been told he would face the sentence if he refused to plead guilty and had gone to trial. The prosecutor told the judge,
[W]hen you’re a prosecutor and you’re making concessions before trial and offering to make concessions that are declined, you know, you lose some credibility going forward if you then make those same concessions.[325]
VII. Measuring the Trial Penalty
In this section we present statistics that quantify the significantly longer sentences drug defendants receive if they go to trial rather than plead guilty. The statistics consist primarily of average sentences based on Human Rights Watch’s analysis of 2012 sentencing data obtained from the Sentencing Commission.[326] We recognize that many other factors besides the decisions to plead or go to trial may be reflected in the sentences. We think they nonetheless illuminate the sentencing risk defendants face if they refuse to plead.[327]
As seen in Table 3, the mean sentence for all drug trafficking offenses in which conviction was obtained by plea was 5 years, 4 months, and the mean sentence for cases in which conviction was obtained at trial was 16 years, i.e., three times longer.[328] The average sentence after trial is over 10 years longer than the average sentence from a guilty plea.
If we look at average sentences for drug offenders by type of drug involved in the offense, the sentence received after trial is also about three times longer than the sentence after pleading.
Defendants who pled guilty were more likely to receive sentences below the guideline range than those who went to trial: 56 percent of those who pled received lower than guideline range sentences compared to 33 percent of those convicted after trial.[329]
Pleading also greatly reduces the sentences for defendants convicted of offenses carrying mandatory minimum sentences. As shown in Figure 9, for federal drug offenders convicted of drug offenses carrying mandatory minimum penalties, the average sentence of those who pled guilty was 6 years, 10 months compared to 17 years, 11 months for defendants convicted after trial—a difference of 11 years.
The most commonly imposed mandatory minimum penalties for drug trafficking offenses are those with a minimum of 5 years (6,948 individuals, or 28 percent of convicted drug offenders) and 10 years (7,362 individuals, or 29.7 percent). For those convicted by plea of offenses carrying the 5-year minimum, their average sentence was 5 years, 3 months compared to 9 years, 3 months for those convicted after trial. For who pled and faced a minimum of ten years, their average sentence was 7 years, 11 months; for those who were convicted after trial, the average sentence was 18 years, 3 months.
Critical to the lower sentences defendants convicted of offenses carrying mandatory minimum penalties receive if they plead instead of going to trial, is the fact that defendants who plead are more likely to receive relief from mandatory sentences. As shown in Table 4, only 4.9 percent of the defendants who went to trial received relief from the mandatory minimum sentences. In contrast, 60.4 percent of the defendants who pled guilty received relief. This no doubt helps explain why, in Figure 9, the average sentence of defendants who pled guilty to offenses carrying mandatory minimums was 11 years lower than the sentence of those who went to trial. It also helps explain why in Figure 10, among defendants facing mandatory minimum penalties of 10 years or more, the average sentence for those who pled was below that minimum.
We realize the differences in average sentences to some unknown extent may reflect salient differences among the individual cases that we cannot identify or quantify, e.g., quantity of drugs involved in the offenses and prior records. Such factors could affect the sentence wholly apart from whether the defendants pled or went to trial.
To more carefully assess the trial penalty, we created a sample of drug offender cases that were similar in important respects except for the fact that some of the defendants pled guilty while others went to trial. The sample consists of all federal drug defendants in FY 2012 who were subject to drug mandatory minimum penalties, who had little or no criminal history (they fall in criminal history category I), who did not have a weapon involved in their offense, and who all had base offense level of 32 under the guidelines based on the quantity of the drug involved. In this group, as shown in Figure 11, defendants who went to trial received average sentence of 9 years, 10 months, compared to the average sentence of 4 years, 11 months for those who pled. Among defendants matched in the most relevant sentencing factors, those who went to trial received sentences just about twice as long as those who pled.
We also looked at this sample to determine the likelihood of receiving relief from the mandatory minimums. Among those who pled, 87 percent received some form of relief; among those who went to trial, only 22 percent received relief. Defendants who pled and received some form of relief had average sentences considerably lower than those who went to trial, with the length varying by kind of relief received.
Trial Penalties for Defendants with Prior Felony Records or Guns
When comparing sentences among all drug offenders who pled guilty or went to trial, we know the sentences to some unknown— and unknowable—extent may reflect legitimate and important differences among the defendants in the two groups, e.g., quantity of drugs involved or role of the defendant. But when we look at defendants receiving increased sentencing penalties based on prior convictions or the presence of guns in their offense, data is available to determine who was eligible for such penalties as well as who had the penalties applied. We can determine the different rates at which the penalties were applied according to whether defendants pled or went to trial. By doing so, we can more precisely delineate the trial penalty in these cases.
Prior Felony Conviction
As noted, defendants who are eligible for a sentencing enhancement because of prior convictions are 8.4 times more likely to have the enhancement applied if they go to trial than if they plead guilty. This differential application already testifies to a trial penalty.
Moreover, among defendants who had the §851 sentence enhancement applied, those convicted after trial received average sentences of nearly 25 years (299 months) compared to average sentences of 13 years (157 months) for those who pled guilty, a 12-year difference.[330] The Sentencing Commission data we analyzed does not indicate the number of prior convictions in the §851 informations that were filed. Prosecutors are willing to reduce the number of prior convictions for defendants who plead, and this may be reflected in their shorter sentences.
As Figure 12 also shows, there were 4,236 defendants in the Sentencing Commission’s sample who were eligible for the sentencing enhancement because of their prior convictions who pled guilty and did not have it applied. Avoiding the enhancement had a significant sentencing impact—their sentences were on average five years shorter than the sentences of defendants who also pled but had the enhancement applied. It is also notable that among the defendants who were eligible for the enhancement but it was not applied, the average sentence of those who went to trial was nine years longer than the sentence of those who pled.
§924(c)
As noted previously, among convicted drug defendants eligible for §924(c) sentences, those who plead are considerably less likely to receive them than those who go to trial. Among §924(c) eligible defendants, 26 percent of those who pled guilty received §924(c) sentences compared to 46.7 percent of those who went to trial. Those who did not receive §924(c) sentences were sentenced under the gun enhancement provisions of the sentencing guidelines which are considerably less onerous.
Among the 984 drug defendants in 2012 convicted of §924(c) violations, 890 pled guilty. Those who did were more likely to be charged with only one §924(c) violation than those who went to trial: 98 compared to 87 percent, which in and of itself would result in significantly lower sentences.[331]
Even among defendants convicted of a single §924(c) count, there is a striking difference in the sentence for those who pled compared to those who went to trial. According to Human Rights Watch’s calculations, the average total sentence for a drug defendant whose sentence included a single §924(c) count was 10 years, 11 months if the defendant pled, and 19 years, 3 months for those who went to trial—a difference of more than eight years, as shown in Figure 13. The average total sentence for a drug defendant whose sentence included two or more §924(c) convictions was 14 years, 3 months if they pled; but more than 58 years if they did not—a difference of 44 years.[332]
These sentences reflect the sentences for the underlying drug offenses as well as for the §924(c) counts. As noted, the sentences of drug defendants who plead are considerably lower than of those who go to trial, which might contribute to the difference in sentences including §924(c) counts. There were only twelve cases of defendants who went to trial and were convicted of two or more §924(c) counts. We assume their long average sentence reflects the stacking of §924(c) charges in at least some of their cases.
Also of considerable sentencing significance is the fact that among those facing one or more §924(c) counts, 29 percent received sentences below the applicable mandatory minimum—because they pled guilty and the government filed a substantial assistance motion in return for their cooperation in the investigation or prosecution of others.[333] Those who did not receive a §5k1.1 motion had an average sentence of 13 years, 8 months, compared to a sentence of 8 years, 9 months for those who did receive the motion.
The chance to receive a substantial assistance motion depends on the willingness of the defendant to plead, and thus the lack of such an opportunity becomes part of the trial penalty for those who go to trial. Defendants convicted of §924(c) offenses faced an average sentence of 105 months if they pled and received a §5k1.1. Those who went to trial and did not receive a §5k1.1 had an average sentence of 294 months.
VIII: Plea Bargains and Punishment: Legal Standards
[A] significant number of innocent defendants are pressured to plead to crimes they did not commit. And within the much larger universe of guilty defendants, those who are punished most severely are often those who made the worst deals, not those who committed the worst crimes.[334]
—William J. Stuntz, The Collapse of American Criminal Justice
Plea agreements do not necessarily violate human rights; defendants may choose to give up their right to trial in return for a sentencing concession.[335] Nevertheless, plea bargaining as practiced in federal drug cases raises significant human rights concerns.[336] We focus here on the power of prosecutors to set sentences; the coercion of pleas through the trial penalty; and the disproportionately long sentences that the trial penalty can yield.
Prosecutorial Sentencing Power
The federal sentencing regime for drug offenders has transferred significant sentencing power from an independent federal judiciary with no personal stake in the outcome of a case, to prosecutors, representatives of the executive branch with personal, as well as institutional, interests in securing convictions. Judges have more sentencing discretion now than they did under the regime of mandatory sentencing guidelines. But their hands are still tied by mandatory minimum sentencing legislation and the guidelines continue to constrain many of their sentencing decisions.
The mandatory sentences are the most troubling. Because of them, judges lack the discretion to countermand prosecutorial charging decisions that yield disproportionately long or cruelly excessive sentences. Prosecutors can charge or threaten to charge offenses carrying high sentences to force defendants to plead and they can use them to punish defendants who choose to go to trial.
Prosecutors have many functions, but sentencing is not one of them. Nor should it be. However responsible and conscientious prosecutors are in the exercise of their discretion, they represent the executive branch. Their principal role in the criminal justice system is to serve the public by investigating and prosecuting cases against defendants whom they believe guilty of crime.
Unlike federal judges, prosecutors are not impartial adjudicators, but have numerous professional and institutional pressures that can lead them to file charges and pursue sentences that may be utterly disproportionate to the defendant’s conduct and far longer than necessary to serve the purposes of punishment. Prosecutors are part of the executive branch of government and are subject to policies and priorities that reflect the government’s political choices. In contrast, judges—who have life tenure—have the independence to serve only the law.
Coercion and Retaliation
Most people would agree that a defendant presented with the choice of pleading to a 10-year sentence or receiving a life sentence if convicted after trial is being coerced. The fact that in a plea bargaining context the government is threatening to do something that is legal—trying the defendant on charges already filed or filing a superseding charge—does not diminish the coercive power of what has been called “prosecutorial extortion.”[337] US constitutional jurisprudence holds otherwise.
In the infamous 1978 case of Bordenkircher v. Hayes, the Supreme Court gave a green light to prosecutors to secure pleas through inducements or threats—including by threats of far greater punishment for exercising the right to trial. In that case, Paul Lewis Hayes was indicted for a forged check in the amount of $88.30, an offense punishable under Kentucky law by two to ten years.
The prosecutor offered to recommend a sentence of five years if Hayes agreed to plead guilty. He also threatened Hayes that if he would not plead, the prosecutor would indict under Kentucky’s Habitual Offender Act, which would subject Hayes to a mandatory life sentence because he had two prior convictions. Hayes refused to plead, the prosecutor indicted and convicted him as a habitual offender, and Hayes was sentenced to life in prison. The Supreme Court brushed off concerns that prosecutor threats to file enhanced charges during plea bargaining might amount to coercion: “Although a defendant presented with the risk of a more severe punishment faces a difficult choice, this is a permissible reality.”[338] The Supreme Court has never recognized that the voluntariness of a defendant’s guilty plea may be vitiated because of the penalty threatened by prosecutors.[339]
In Bordenkircher, the Court also ruled that a prosecutor would not violate due process if he adds additional charges, “solely to punish a defendant for exercising a constitutional or statutory right.”[340] As one court has stated, “actual retaliatory behavior is acceptable” during plea bargaining.[341] Or, as another concluded, “As a general matter, prosecutors may charge and negotiate as they wish.”[342] Courts will not find unconstitutional vindictiveness, “even assuming … the government sought the superseding indictment in retaliation for [the defendant’s] persistence in a plea of not guilty.”[343]
The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which the United States is a party, codifies the right to trial and the right not to be compelled to testify against oneself or to confess guilt.[344] Defendants may not be subject to “forms of direct or indirect physical or psychological pressure, ranging from torture and inhuman treatment … to various methods of extortion or duress” to compel them to testify.[345]
While it is clear that this guarantee is violated by subjecting a defendant to torture or other cruel treatment to induce a decision to forgo trial or to confess, there is scant jurisprudence that establishes the other kinds of “direct or indirect” psychological coercion that would constitute impermissible duress.[346] The European Court of Human Rights has noted that the key question is whether the defendant’s will is overborne, including by psychological pressure that does not amount to torture or other cruel mistreatment.[347] Defendants are able to waive their right against self-incrimination and the waiver will be upheld if it is free and voluntary.
In Germany, for example, the Federal Constitutional Court has emphasized that a defendant must not be pressed to confess through threats of a higher sentence. A significant gap between sanctions secured by plea or after trial is “often treated, in itself, as an illegal influence on the defendant’s free will in making trial decisions…. [I]f the upper and lower limits of the sanctions gap remain within the recognized [sentencing] parameters of guilt and if the difference can be justified by the mitigating effects of the confession, the possible resulting coercive influence on the defendant’s free will is allowed.”[348]
Where the differential between a bargained for sentence and a sentence proportionate to the offense is too great, appellate courts may step in. But the reward German defendants receive for acknowledging guilt is likely to be much lower than defendants receive in the US: “The difference between the bargained for and post-trial sentences is at most five years; more often it is mere months.”[349]
LaShonda Hall[350]LaShonda Hall’s father was murdered when she was 8 years old, and she became a mother at the age of 14. Her son’s father died, leaving her a single mother, and her two brothers were in the criminal justice system. In July 2006, Hall began a relationship with Johnnie Martin, a man with a history of abusing women, which he continued in his relationship with Hall. He was also the leader of a large-scale drug operation: his organization obtained crack, powder cocaine, ecstasy and marijuana from suppliers in Atlanta, Georgia and redistributed them in the Knoxville, Tennessee area where Martin was based. Hall became part of his drug operation: she drove Martin's “right-hand man” to Atlanta, Georgia to purchase drugs, made phone calls regarding drug deals, delivered drugs, and also occasionally handled money for the drug conspiracy. Martin had several “stash houses” throughout Knoxville, each set up to sell a certain type of drug. Martin, Hall, and Hall’s minor child resided in one of these stash houses. In May of 2007, law enforcement agents executed search warrants for each of the stash houses. Hall was arrested at one of the houses in which drugs and paraphernalia were found along with a gun under a couch cushion. A search of the house where Martin and Hall resided resulted in the discovery of marijuana, over $60,000 in cash, and a loaded firearm, which was located between the bed and the nightstand. In May 2007, a federal grand jury returned an indictment against Hall, Martin, and 10 others. The original indictment charged Hall with a single count of conspiracy to distribute cocaine and crack. It did not include charges for marijuana, any other drugs, or possession of the firearms. In June 2007, the prosecution informed the defendants that if any of them wished to enter a plea agreement, they needed to do so before a superseding indictment with additional charges was filed. Several of Hall’s co-defendants entered into plea agreements. Prosecutors also pressured Hall to enter into a plea agreement but she did not, and in December 2007, the government filed a superseding indictment against her charging her with conspiracy to distribute drugs, possession with intent to distribute marijuana, money laundering, and two §924(c) charges of possessing a weapon in furtherance of drug offenses. Plea negotiations apparently continued between Hall and the government, but ultimately did not bear fruit. In June 2009, Hall was tried and convicted of all five counts set forth in the superseding indictment. She was sentenced to a total of 548 months (45.6 years) in prison made up of 188 months on the cocaine charge and a consecutive 60 months on the first §924(c) charge plus an additional consecutive 300 months on the second §924(c) charge. She was also sentenced to 60 months on the marijuana charge and a sentence of 188 months on the money laundering charge, both of which ran concurrently with the above. There was no evidence introduced at trial that Hall owned, carried, or used the guns involved in the §924(c) violations. But the court found that it was reasonably foreseeable that Hall knew of the existence and purpose of the firearms to further the drug business. Also, the court found that Hall could be properly sentenced for two separate §924(c) offenses because they were predicated on two different offenses: one a conspiracy to distribute and the other the substantive offense of possession of marijuana with intent to distribute. On appeal, Hall unsuccessfully argued that the additional charges in the superseding indictment were improperly added in retaliation for her refusal to enter into a plea agreement. The appellate court also rejected her arguments that the sentence she received was unconstitutionally cruel. |
Cruel Sentences
In theory, the Eighth Amendment to the US Constitution prohibits as cruel and unusual punishment sentences that are grossly disproportionate to the crime. Drug defendants facing sentences of decades and even life in prison for the nonviolent distribution of drugs have argued such sentences are unconstitutionally disproportionate. Their arguments fall on deaf ears. In Harmelin v. Michigan, the Supreme Court upheld a life without parole sentence for a 42-year-old first-offender convicted of transporting a pound of cocaine.[351]
Even when federal courts consider long drug sentences to be excessively severe, they do not rule them unconstitutional. For example, a federal appeals court assessed the constitutionality of the 45-year sentence Mary Beth Looney, a first time offender, received for selling methamphetamine from her house and possessing guns in the house. The court agreed with Looney that her sentence was unduly harsh, but concluded it was not so “‘grossly disproportionate’” as to violate the Eighth Amendment.[352] Similarly, an appellate court upheld the constitutionality of Paul Bernall’s sentence of life without parole after a conviction for conspiring to possess with intent to distribute five kilograms or more of cocaine.[353] The life without parole sentence followed the decision of the government in his case to file an §851 information informing the court of two prior drug convictions.
Under international human rights standards, criminal sanctions should be proportionate to the crime and the culpability of the particular offender, and should be no greater than necessary to meet the purposes of punishment—retribution, deterrence, incapacitation, and rehabilitation.[354] Disproportionately long prison terms may violate the prohibition on cruel and inhuman punishment.[355] They may also constitute arbitrary deprivations of liberty in violation of the right to liberty. In either case, they are inconsistent with respect for human dignity. Sentences such as that imposed on Sandra Avery—life without parole for minor drug dealing and having a few prior minor drug convictions— cannot pass human rights muster. Life without parole sentences may be appropriate in certain cases of horrific and deliberate unlawful violence. But sentencing someone to die in prison for nonviolent drug dealing cannot be justified. Of course, Avery’s life sentence was not calculated to punish her for her drug dealing or to further the purposes of punishment. She is living the rest of her life behind bars as punishment for refusing to accept a 10-year plea offer and insisting on her right to trial.
IX: Conclusion
The trial penalty’s effectiveness at securing plea agreements is purchased at the cost of disproportionate and unjust sentences for those who exercise their right to trial.
We believe Attorney General Eric Holder should make just and proportionate sentences a goal prosecutors keep forefront in their charging and plea bargaining decisions. But Congress must also take steps to end the trial penalty.
Legislative reform should restore judicial discretion over sentencing—either by eliminating mandatory minimums or by permitting judges to go below them in individual cases in the interests of justice. Such legislative reform would prevent prosecutors from being able to bludgeon defendants into pleading guilty with the threat of exorbitant mandatory sentences should they go to trial. Judges would also be able to provide relief to defendants who pled to disproportionately long sentences in order to avoid the risk of even longer if convicted after trial.
We recognize it is likely that were the trial penalty significantly reduced, more defendants might decide to take their chances at trial and to insist the government prove its case. The federal criminal justice system would adapt. The government might provide the resources to increase the number of prosecutors, judges, defense counsel, courtrooms, and court staff. Federal prosecutors might become more selective in the cases they prosecute and the charges they pursue. The federal government might decide to put more resources into non-penal strategies to reduce drug consumption and weaken drug markets—e.g. public health and education-based programs. We cannot predict all the possible consequences. But we can safely predict that taking away from federal prosecutors the ability to threaten drug defendants with the trial penalty will ensure fairer charges and sentences.
Appendix: Data by Federal District, FY 2012
|
US FEDERAL DISTRICT |
DISTRICT POPULATION |
TOTAL DRUG TRAFFICKING DEFENDANTS |
AVERAGE PRISON SENTENCE (MONTHS) FOR DRUG TRAFFICKING DEFENDANTS |
DRUG CASES AS PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL FEDERAL CASES |
% OF GUILTY PLEAS IN DRUG TRAFFICKING CASES |
% OF DRUG TRAFFICKING SENTENCES WITHIN GUIDELINE RANGE |
% OF DRUG TRAFFICKING SENTENCES WITH 5K1.1 SUBSTANTIAL ASSISTANCE |
|
Alabama, Middle |
1,147,971 |
39 |
88 |
19.0% |
87.2% |
30.8% |
64.1% |
|
Alabama, Northern |
2,816,862 |
78 |
104 |
17.4% |
76.0% |
34.6% |
53.8% |
|
Alabama, Southern |
790,130 |
157 |
65 |
35.0% |
98.1% |
42.0% |
31.0% |
|
Alaska |
731,449 |
107 |
76 |
51.2% |
100.0% |
29.9% |
29.9% |
|
Arizona |
6,553,255 |
2,351 |
25 |
29.5% |
98.9% |
41.2% |
5.4% |
|
Arkansas, Eastern |
1,635,507 |
161 |
77 |
42.2% |
93.8% |
64.0% |
13.7% |
|
Arkansas, Western |
1,313,624 |
122 |
90 |
37.8% |
95.9% |
53.3% |
35.2% |
|
California, Central |
18,945,051 |
451 |
82 |
26.4% |
96.7% |
30.4% |
20.8% |
|
California, Eastern |
7,753,480 |
265 |
79 |
28.5% |
97.7% |
53.2% |
25.7% |
|
California, Northern |
7,988,888 |
169 |
83 |
26.9% |
97.0% |
39.6% |
18.9% |
|
California, Southern |
3,354,011 |
1,731 |
44 |
32.2% |
98.0% |
8.5% |
16.5% |
|
Colorado |
5,187,582 |
114 |
70 |
22.0% |
98.2% |
20.2% |
63.2% |
|
Connecticut |
3,590,347 |
191 |
63 |
47.8% |
97.4% |
34.6% |
22.5% |
|
Delaware |
917,092 |
16 |
59 |
17.2% |
100.0% |
25.0% |
43.8% |
|
District of Columbia |
632,323 |
135 |
78 |
39.4% |
95.6% |
29.6% |
39.3% |
|
Florida, Middle |
10,994,126 |
663 |
99 |
39.7% |
96.5% |
39.8% |
34.8% |
|
Florida, Northern |
1,775,071 |
116 |
128 |
33.8% |
87.9% |
56.0% |
29.3% |
|
Florida, Southern |
6,548,371 |
595 |
77 |
27.6% |
95.8% |
57.8% |
14.8% |
|
Georgia, Middle |
2,722,194 |
107 |
84 |
28.3% |
95.3% |
70.1% |
23.4% |
|
Georgia, Northern |
5,664,233 |
159 |
102 |
25.7% |
95.6% |
34.0% |
20.8% |
|
Georgia, Southern |
1,533,518 |
118 |
78 |
22.5% |
97.5% |
63.6% |
26.3% |
|
Hawaii |
1,378,129 |
99 |
100 |
41.7% |
98.0% |
20.2% |
38.4% |
|
Idaho |
1,595,728 |
85 |
89 |
30.5% |
94.1% |
41.2% |
51.8% |
|
Illinois, Central |
2,255,868 |
165 |
160 |
39.7% |
97.6% |
46.1% |
23.6% |
|
Illinois, Northern |
9,028,785 |
236 |
90 |
30.1% |
91.5% |
31.8% |
24.2% |
|
Illinois, Southern |
1,545,979 |
147 |
114 |
33.0% |
98.0% |
77.6% |
7.5% |
|
Indiana, Northern |
2,569,828 |
123 |
64 |
33.3% |
98.4% |
43.9% |
46.3% |
|
Indiana, Southern |
3,967,506 |
158 |
104 |
38.1% |
98.1% |
50.0% |
15.8% |
|
Iowa, Northern |
1,325,594 |
166 |
118 |
41.5% |
96.4% |
33.7% |
42.8% |
|
Iowa, Southern |
1,748,592 |
201 |
113 |
47.2% |
97.5% |
26.4% |
45.3% |
|
Kansas |
2,885,905 |
182 |
100 |
28.3% |
89.6% |
35.2% |
30.8% |
|
Kentucky, Eastern |
2,176,405 |
247 |
76 |
49.6% |
96.8% |
50.6% |
33.2% |
|
Kentucky, Western |
2,204,010 |
115 |
78 |
28.7% |
97.4% |
50.4% |
25.2% |
|
Louisiana, Eastern |
1,629,155 |
125 |
123 |
34.9% |
96.8% |
58.4% |
20.8% |
|
Louisiana, Middle |
815,298 |
51 |
87 |
22.6% |
90.2% |
54.9% |
29.4% |
|
Louisiana, Western |
2,157,440 |
137 |
102 |
32.3% |
92.1% |
44.5% |
35.8% |
|
Maine |
1,329,192 |
58 |
46 |
30.5% |
98.3% |
39.7% |
43.1% |
|
Maryland |
5,884,563 |
381 |
84 |
35.9% |
95.0% |
26.8% |
35.4% |
|
Massachusetts |
6,646,144 |
183 |
71 |
35.5% |
92.9% |
39.3% |
10.9% |
|
Michigan, Eastern |
6,449,717 |
244 |
82 |
28.0% |
94.3% |
45.1% |
28.3% |
|
Michigan, Western |
3,433,643 |
128 |
98 |
30.1% |
96.1% |
43.0% |
23.4% |
|
Minnesota |
5,379,139 |
185 |
75 |
41.5% |
99.5% |
25.4% |
33.5% |
|
Mississippi, Northern |
1,113,669 |
35 |
67 |
20.5% |
94.3% |
54.3% |
37.1% |
|
Mississippi, Southern |
1,871,257 |
64 |
76 |
22.8% |
98.4% |
62.5% |
17.2% |
|
Missouri, Eastern |
2,904,855 |
308 |
66 |
32.2% |
99.4% |
34.7% |
23.1% |
|
Missouri, Western |
3,117,133 |
224 |
89 |
28.8% |
93.3% |
32.6% |
37.5% |
|
Montana |
1,005,141 |
135 |
85 |
35.6% |
96.3% |
42.2% |
35.6% |
|
Nebraska |
1,855,525 |
208 |
94 |
33.8% |
96.2% |
68.8% |
8.2% |
|
Nevada |
2,758,931 |
139 |
76 |
24.0% |
95.0% |
63.3% |
10.1% |
|
New Hampshire |
1,320,718 |
62 |
53 |
39.2% |
93.5% |
30.6% |
29.0% |
|
New Jersey |
8,864,590 |
235 |
56 |
29.5% |
98.7% |
39.1% |
43.4% |
|
New Mexico |
2,085,538 |
544 |
38 |
17.9% |
98.7% |
46.3% |
10.1% |
|
New York, Eastern |
8,157,640 |
409 |
46 |
42.5% |
97.1% |
19.6% |
21.3% |
|
New York, Northern |
3,435,887 |
254 |
52 |
41.2% |
98.4% |
28.7% |
48.0% |
|
New York, Southern |
5,155,224 |
635 |
64 |
42.0% |
96.4% |
24.7% |
18.4% |
|
New York, Western |
2,821,510 |
221 |
68 |
36.8% |
96.4% |
25.3% |
54.3% |
|
North Carolina, Eastern |
3,875,478 |
307 |
125 |
38.3% |
97.7% |
40.7% |
51.8% |
|
North Carolina, Middle |
2,851,482 |
95 |
117 |
23.3% |
93.7% |
67.4% |
25.3% |
|
North Carolina, Western |
3,025,113 |
116 |
84 |
26.9% |
96.6% |
41.4% |
50.0% |
|
North Dakota |
699,628 |
74 |
103 |
26.0% |
97.3% |
6.8% |
85.1% |
|
Ohio, Northern |
5,664,167 |
248 |
67 |
27.3% |
99.2% |
43.5% |
43.5% |
|
Ohio, Southern |
5,880,058 |
244 |
60 |
40.4% |
99.2% |
18.4% |
46.3% |
|
Oklahoma, Eastern |
747,374 |
31 |
86 |
33.7% |
96.8% |
19.4% |
48.4% |
|
Oklahoma, Northern |
1,029,062 |
54 |
73 |
27.7% |
96.3% |
48.1% |
38.9% |
|
Oklahoma, Western |
2,038,384 |
83 |
78 |
18.8% |
92.8% |
43.4% |
20.5% |
|
Oregon |
3,899,353 |
124 |
65 |
19.2% |
100.0% |
24.2% |
33.9% |
|
Pennsylvania, Eastern |
5,645,619 |
232 |
83 |
28.4% |
90.9% |
25.0% |
44.8% |
|
Pennsylvania, Middle |
3,318,769 |
167 |
60 |
36.1% |
98.8% |
26.3% |
29.9% |
|
Pennsylvania, Western |
3,799,148 |
183 |
76 |
35.2% |
97.8% |
41.0% |
29.0% |
|
Puerto Rico |
3,667,084 |
676 |
77 |
46.6% |
97.3% |
72.0% |
6.2% |
|
Rhode Island |
1,050,292 |
58 |
62 |
29.4% |
96.6% |
29.3% |
10.3% |
|
South Carolina |
4,723,723 |
331 |
123 |
37.0% |
97.3% |
39.0% |
33.8% |
|
South Dakota |
833,354 |
63 |
80 |
15.9% |
92.1% |
69.8% |
11.1% |
|
Tennessee, Eastern |
2,519,930 |
433 |
90 |
50.6% |
97.2% |
44.8% |
40.4% |
|
Tennessee, Middle |
2,353,762 |
96 |
90 |
28.8% |
94.8% |
36.5% |
30.2% |
|
Tennessee, Western |
1,582,551 |
199 |
72 |
34.8% |
98.5% |
32.7% |
36.2% |
|
Texas, Eastern |
3,678,891 |
395 |
99 |
39.4% |
95.4% |
66.3% |
15.2% |
|
Texas, Northern |
6,882,936 |
336 |
113 |
34.0% |
98.8% |
39.0% |
33.3% |
|
Texas, Southern |
8,906,738 |
1,424 |
71 |
21.8% |
97.2% |
66.6% |
18.8% |
|
Texas, Western |
6,590,638 |
2,216 |
59 |
24.1% |
97.8% |
68.9% |
18.6% |
|
Utah |
2,855,287 |
142 |
74 |
22.8% |
98.6% |
18.3% |
17.6% |
|
Vermont |
626,011 |
105 |
63 |
46.3% |
93.3% |
11.4% |
38.1% |
|
Virginia, Eastern |
3,886,417 |
397 |
99 |
21.7% |
94.2% |
56.4% |
5.8% |
|
Virginia, Western |
4,299,450 |
179 |
91 |
47.2% |
98.3% |
44.1% |
31.8% |
|
Washington, Eastern |
1,526,858 |
59 |
78 |
19.1% |
96.6% |
25.4% |
22.0% |
|
Washington, Western |
5,370,154 |
175 |
61 |
24.5% |
97.1% |
18.3% |
12.0% |
|
West Virginia, Northern |
865,597 |
164 |
54 |
50.3% |
98.2% |
63.4% |
14.0% |
|
West Virginia, Southern |
989,816 |
193 |
50 |
64.3% |
99.0% |
48.7% |
11.4% |
|
Wisconsin, Eastern |
3,386,342 |
231 |
67 |
48.8% |
98.3% |
14.7% |
36.8% |
|
Wisconsin, Western |
2,340,056 |
47 |
96 |
28.8% |
93.6% |
48.9% |
0.0% |
|
Wyoming |
576,412 |
63 |
123 |
25.6% |
92.1% |
27.0% |
14.3% |
Source: Population data compiled from 2010 US Census. Other data from United States Sentencing Commission, 2012 Federal Sentencing Statistics. http://www.ussc.gov/Data_and_Statistics/Federal_Sentencing_Statistics/State_District_Circuit/2012/index.cfm
Acknowledgments
Human Rights Watch dedicates this report to Peter B. Lewis, a longtime supporter of our work and a steadfast friend who passed away on November 23, 2013. We will miss his generous spirit, his commitment to human rights, and his dedication to the pursuit of “joy, love, and peace.”
Jamie Fellner, senior advisor in the US Program of Human Rights Watch, researched and wrote this report. Brian Root, the quantitative analyst at Human Rights Watch, helped analyze and develop graphic representations of the sentencing data presented in the report. Paul Hofer, adjunct assistant professor at Johns Hopkins and former special project director at the United States Sentencing Commission, was a consultant to Human Rights Watch for this report. He provided invaluable assistance regarding federal sentencing practices and policies, helped edit this report, and also developed statistics on the sentencing differential in drug convictions secured by plea versus trial. Alison Parker, director of the US Program of Human Rights Watch and Danielle Haas, senior editor of Program edited the report, and Dinah Pokempner, general counsel, provided the legal review. Samantha Reiser, US Program associate, provided research and production assistance. Layout and production were coordinated by Samantha Reiser. Fitzroy Hepkins, administrative manager, provided production assistance.
Valuable factual and legal research assistance was provided by Erin Lovall, Margaret Weirich, and Maya Goldman, all Human Rights Watch interns. Additional extremely helpful research for this report was undertaken pro bono by Benjamin Peacock, an attorney at the law firm of Clifford Chance, and by a team of lawyers and summer associates at the law firm of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton. We are also grateful for the encouragement and assistance provided by Norman Reimer and members of the National Association of Criminal Defense Lawyers. Glen McGorty, a partner at Crowell & Moring and Mary Price, general counsel at FAMM, also reviewed the report and provided helpful comments and insights. Human Rights Watch also wishes to acknowledge our debt to the willingness of private law firms to provide pro bono assistance for this and many other projects.
This report draws extensively from the information, insights, and perspectives provided by numerous legal practitioners we interviewed—former and current federal prosecutors, defense attorneys, and judges. Many did not want to be cited by name, but whether named or not, our gratitude to each one is immense. They steered us to cases, provided candid, unvarnished descriptions of their work, argued ideas and interpretations with us, and sought to help us understand their legal practice as they lived it. Human Rights Watch is, of course, solely responsible for the conclusions we have drawn from these interviews and other research.
We are also grateful to the federal prisoners who responded to our queries about their cases. Their shock at receiving long or even life sentences for nonviolent drug crimes after they refused to plead guilty still reverberates with and inspires us.
[1] Statement of Reasons, United States v. Kupa, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922, 9-10 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[2] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Mary Pat Brown, former Prosecutor and senior Department of Justice official, Washington, D.C., June 5, 2013.
[3] United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), 2012 Sourcebook of Federal Sentencing Statistics (2012 Sourcebook), “Table 43: Drug Offenders Receiving Mandatory Minimums in Each Drug Type,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table43.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). We have no way of knowing how many others were originally charged with offenses carrying mandatory sentences but plea bargains led to charges that did not carry mandatory sentences.
[4] Information on the case of Lulzim Kupa obtained from documents filed in United States v. Kupa, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 1:11-cr-00345, which are available on PACER
[5]United States v. Midyett, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 07-CR0874, Transcript of Sentencing Hearing, June 17, 2010.
[6] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former US Attorney (name withheld), April 25, 2013.
[7] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Figure A: Offenders in Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/FigureA.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013).
[8] Information on the case of Sandra Avery obtained from documents filed in United States v. Avery, United States District Court for the Middle District of Florida, Case No. 8:05-CR-389, which are available on PACER; from Human Rights Watch correspondence with Avery; and from Human Rights Watch telephone interview with James Preston, federal prosecutor, Middle District of Florida, August 6, 2013.
[9] Except as otherwise noted, information on the case of Roy Lee Clay obtained from documents filed in United States v. Clay, United States District Court for the District of Maryland, Case No. 1:11-cr-00569, which are available on PACER; Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Michael D. Montemarano, defense attorney, Baltimore, Maryland, September 4, 2013; and Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Christopher J. Romano, assistant US attorney, Baltimore, Maryland, September 3, 2013.
[10] Ian Duncan, “Heroin dealer gets mandatory term of life without parole,” Baltimore Sun, August 27, 2013, http://www.baltimoresun.com/news/maryland/crime/blog/bs-md-ci-heroin-dealer-sentence-20130827,0,6489102.story (accessed September 17, 2013).
[11] The coercive charging and plea bargaining practices of federal prosecutors in drug cases may well be similar to those they use in other federal criminal cases. We believe state criminal prosecutions for drugs and other offenses may also be marred by excessive trial penalties. Although this report is focused solely on federal drug prosecutions, the concerns we raise regarding proportionate sentences and defendants’ rights may apply equally in these other contexts.
[12] See USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm (accessed October 1, 2013), pg. 254 for a description of the sample data.
[13]United States v. Young, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 116042 (N.D. Iowa 2013), Discussing the dramatic national disparity in the Department of Justice’s application of 21 U.S.C. § 851 enhancements.
[14] The federal prison population has quintupled— from 42,000 in the mid-1980s when the new federal sentencing regime of mandatory minimum sentences and sentencing guidelines was instituted— to over 219,000 today. Federal prisons are overcrowded— currently 38 percent over capacity— and consume an increasing portion of the Justice Department’s budget. Government Accountability Office, “Bureau of Prisons: Growing Inmate Crowding Negatively Affects Inmates, Staff, and Infrastructure,” GAO -12-743, September 2012, http://www.gao.gov/assets/650/648123.pdf (accessed September 30, 2012). The Department of Justice’s (DOJ) Fiscal Year 2014 Budget requests a total of $8.5 billion for federal prisons and detention, out of a total DOJ request of $27.6 billion. United States Department of Justice, “FY 2014 Budget Summary,” http://www.justice.gov/jmd/2014summary/pdf/fy14-bud-sum.pdf#bs (accessed September 30, 2013), p. 11. See Letter from Lanny A. Breuer, assistant attorney general, and Jonathan J. Wroblewski, director, Office of Policy and Legislation, to Hon. Patti B. Saris, chair, U.S. Sentencing Commission, July 23, 2012, http://www.justice.gov/criminal/foia/docs/2012-annual-letter-to-the-us-sentencing-commission.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013).
[15] See Quick Facts about the Bureau of Prisons, http://www.bop.gov/news/quick.jsp#2 (accessed October 28, 2013). This is an increase from 2011 when 48 percent of federal prisoners were serving time for drug offenses. E. Ann Carson and William J. Sabol, Bureau of Justice Statistics, US Department of Justice, “Prisoners in 2011,” December 2012, http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/p11.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013), Table 11.
[16] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 3: Change in Guideline Offenders in Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2011 – 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table03.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013).
[17] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former US Attorney (name withheld), April 25, 2013.
[18] The analysis was undertaken in 2010 based on a sample of drug offenders from 2009. According to the Sentencing Commission’s definitions, couriers transport or carry drugs using a vehicle or other equipment; street-level dealers distribute retail quantities (less than one ounce) directly to users; and wholesalers buy or sell at least one ounce or possess at least two ounces. USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, pp. 166-169.
[19] Percentage calculated on basis of whether the defendants received an aggravating role adjustment under the guidelines 2012 Sourcebook. USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 37: Criminal History Category of Drug Offenders in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table37.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013). See USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” November 1, 2012, http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), section 3B1.1 for an explanation of aggravated role sentence adjustment.
[20] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 39: Weapon Involvement of Drug Offenders in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table39.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013); United States v. Leitch, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 27796, 53(E.D.N.Y 2013).
[21] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 37,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table37.pdf. Fifty-three percent of federal drug defendants in 2012 were in criminal history category I, which means they had no more than one criminal history point. Criminal history points are based on state or federal sentences. See USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf, Chapter Four, Part A.
[22] Government Accountability Office, “Bureau of Prisons: Growing Inmate Crowding Negatively Affects Inmates, Staff, and Infrastructure,” http://www.gao.gov/assets/650/648123.pdf.
[23] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 13: Sentence Length in Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table13.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013). The average sentence length has decreased from 82 months in 2008, primarily as a consequence of the Fair Sentencing Act which reduced sentences for crack offenses. Ibid., “Figure E: Length of Imprisonment in Each General Crime Category, Fiscal Years 2008-2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/FigureE.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013). The length of prison sentences varied by type of drugs: from an average of 97 months for crack offenders to 36 months for marijuana. Ibid., “Figure J: Length of Imprisonment in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/FigureJ.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013).
[24] Kamala Mallik-Kane, Barbara Parthasarathy, and William Adams, Urban Institute, “Examining Growth in the Federal Prison Population, 1998 to 2010,” September 2012, http://www.urban.org/UploadedPDF/412720-Examining-Growth-in-the-Federal-Prison-Population.pdf (accessed September 30 , 2013).
[25] For example, selling heroin is illegal under federal law as well as state laws. State sentences tend to be less severe than federal. Drug law enforcement in the United States is carried out by federal, state, and local agencies. Local agents are responsible for most drug arrests, but local prosecutors often let federal prosecutors handle larger drug conspiracies, violent gangs, or cases in which they want to ensure the harsher federal sentences are imposed on particular defendants. Agents with the federal Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) primarily investigate major narcotics violators, enforce regulations governing the manufacture and dispensing of controlled substances, and perform various other functions to prevent and control drug trafficking. In 2012, DEA agents made 30,476 arrests. United States Drug Enforcement Administration, “DEA Domestic Arrests,” http://www.justice.gov/dea/resource-center/statistics.shtml#arrests (accessed September 30, 2013). The FBI employed 16,835 full-time personnel with arrest and firearm authority. These agents investigate more than 200 types of federal crimes. The FBI has concurrent jurisdiction with the DEA over drug offenses under the Controlled Substances Act. Brian A. Reaves, Bureau of Justice Statistics, US Department of Justice, “Federal Law Enforcement Officers, 2008,” June 2012, http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/fleo08.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013).
[26] See Appendix showing average sentences by federal district. In fiscal year 2012, out of a total of 26,560 federal drug cases, 24,736, or 93 percent, involved drug trafficking; the remainder were cases for simple possession and use of a communications facility to facilitate a drug offense. Calculated from data in USSC, “Federal Sentencing Statistics by District, Circuit & State for Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Data_and_Statistics/Federal_Sentencing_Statistics/State_District_Circuit/2012/index.cfm (accessed October 1, 2013), Table 1. Under the federal sentencing guidelines, a “drug trafficking offense” is “an offense under federal, state, or local law that prohibits the manufacture, import, export, distribution, or dispensing of a controlled substance (or a counterfeit substance) or the possession of a controlled substance (or a counterfeit substance) with intent to manufacture, import, export, distribute, or dispense.” U.S.S.G. § 2L1.2(b)(1).
[27] We analyzed available district-level data to determine whether there were any associations between variables that could help explain district variations in drug offender sentencing, but none of the variables correlated with each other. The variables we looked at included: the total population of the district; the percent of total offenders who were drug offenders; the percent of drug offenders who pled guilty; the average prison sentence for drug offenders; the percent of drug offender sentences that were within guideline range; the percent of cases that had lower sentences because the defendants provided substantial assistance to the government (§5k1.1 sentences); and the percent of drug offenders who received below-guidelines sentences that were not sponsored by the government. We did not have data that would enable us to examine district-level variations in the proportion of defendants convicted of more serious trafficking offenses. If such variations existed, they might contribute to district differences in average sentence lengths. Based on our research, however, we do not believe there are significant variations in offense seriousness between the districts such as might account for the differences in average sentence lengths.
[28] With the Sentencing Reform Act of 1984, Congress abolished parole, instituted determinate sentencing, authorized the creation of the United States Sentencing Commission to establish sentencing guidelines, and set forth factors for federal courts to consider when imposing a sentence of imprisonment. Title II of the Comprehensive Crime Control Act of 1984, P.L. no. 98-473, 98 Stat.1987, 1987-1988 (codified as amended through Titles 18 and 28 of the U.S. Code). The factors courts are to consider in sentencing are set forth in 18 U.S.C. § 3553(a). The Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986 established the basic framework of mandatory minimum penalties still applicable to federal drug trafficking offenses. Pub. L. No. 99-570, 100 Stat. 3207 (1986).
[29] Administrative Office of the United States Courts, from Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics Online, “Table 5.38: Defendants sentenced for violation of drug laws in U.S. District Courts,” http://www.albany.edu/sourcebook/pdf/t5382010.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). In 2007, the average sentence length reached its highest, 88.9 months. See Paul J. Hofer, Charles Loeffler, Kevin Blackwell, and Patricia Valentino, United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “Fifteen Years of Guidelines Sentencing: An Assessment of How Well the Federal Criminal Justice System Is Achieving the Goals of Sentencing Reform,” November 2004, (accessed October 1, 2013), p. 53, Figure 2.6.
[30] See USSC, “Fifteen Years of Guidelines Sentencing,” https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/Digitization/208044NCJRS.pdf, Figure 2.6, at 53.
[31] 18 U.S.C. 3553: Imposition of a Sentence: a) Factors To Be Considered in Imposing a Sentence.—The court shall impose a sentence sufficient, but not greater than necessary, to comply with the purposes set forth in paragraph (2) of this subsection. The court, in determining the particular sentence to be imposed, shall consider—
(1) the nature and circumstances of the offense and the history and characteristics of the defendant;
(2) the need for the sentence imposed—
(A) to reflect the seriousness of the offense, to promote respect for the law, and to provide just punishment for the offense;
(B) to afford adequate deterrence to criminal conduct;
(C) to protect the public from further crimes of the defendant; and
(D) to provide the defendant with needed educational or vocational training, medical care, or other correctional treatment in the most effective manner;
(3) the kinds of sentences available;
(4) the kinds of sentence and the sentencing range established for—
(A)the applicable category of offense committed by the applicable category of defendant as set forth in the guidelines—
(i)issued by the Sentencing Commission pursuant to section 994(a)(1) of title 28, United States Code, subject to any amendments made to such guidelines by act of Congress (regardless of whether such amendments have yet to be incorporated by the Sentencing Commission into amendments issued under section 994(p) of title 28.
[32] John S. Martin, Jr., “Why Mandatory Minimums Make No Sense,” Notre Dame Journal of Law, Ethics & Public Policy, vol. 18 (2004), p. 317.
[33] Senior United States District Judge Roger Vinson, quoted in John Tierney, “For Lesser Crimes, Rethinking Life Behind Bars,” The New York Times, December 12, 2012, p. A1.
[34] Under federal law it is unlawful for a person to “manufacture, distribute, or dispense, or possess with intent to manufacture, distribute, or dispense, a controlled substance,” and it is unlawful to import or export such substances. See 21 U.S.C. §841 and 18 U.S.C. §960. Conspiracies to commit these offenses carry the same sentences as the substantive offense 21 U.S.C. §846, 963. Controlled substances, hereinafter referred to as drugs, include powder cocaine, crack cocaine, marijuana, methamphetamine, and heroin, among others. 21 U.S.C. §802. In this report we use the term drug offender to refer to a person engaging in the activities prohibited by Sections 841 and 960 or who conspires to do so. The new legislation was enacted with little debate or preparatory deliberation.
[35] The Anti-Drug Abuse Act (ADAA) of 1986 was expedited through Congress, passing without the usual subcommittee hearings, markups of bills, and amendments passed at the committee level. Some individual members of Congress delivered floor statements, but there was no committee report analyzing the act’s key provisions. Drug quantities triggering the mandatory minimum sentences were based on anecdotal evidence, and did not reflect research, statistical data, or input from expert agencies. See Testimony of Eric E. Sterling, president, Criminal Justice Policy Foundation, before United States Sentencing Commission on Proposed Guideline Amendments for Public Comment, March 22, 1993; United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “Special Report to Congress: Cocaine and Federal Sentencing Policy,” 1995, p. 117.
[36] Prior to the ADAA, federal drug offenders were subject to maximum sentences and no statutory mandatory minimum sentences. See, e.g., 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(A) (1982). Crack cocaine offenses were subjected to uniquely harsh penalties because that drug was linked in the mainstream’s collective consciousness with dangerous, poor, minority, inner-city dwellers (even though there were and still are more white users of crack than black users), and because of the erroneous but widespread belief that crack (which is pharmacologically identical to powder cocaine) was uniquely dangerous. USSC, “Special Report to Congress: Cocaine and Federal Sentencing Policy,” pp. 118-121; Michael S. Nachmanoff and Amy Baron-Evans, “Booker Five Years Out: Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Department of Justice Charging Policies Continue to Distort the Federal Sentencing Process,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 22 (December 2009), pp. 96-99; Jamie Fellner, “Race and Drugs” in The Oxford Handbook of Ethnicity, Crime, and Immigration, Sandra M. Bucerius and Michael Tonry, eds., (forthcoming); Jamie Fellner, “Race, Drugs, and Law Enforcement in the United States,” Stanford Law & Policy Review, vol. 20 (2009), pp. 257-292. Under the notorious federal 100-1 law governing powder and crack sentences, federal defendants with five grams of crack cocaine received the same mandatory minimum five-year sentence as defendants with 500 grams of powder cocaine. As the United States Sentencing Commission has amply documented, there is no scientific evidence or empirical research to support subjecting crack offenders to higher sentences than powder. USSC, “Special Report to Congress: Cocaine and Federal Sentencing Policy,” pp. 63-67, 72-98. The Fair Sentencing Act of 2010 (FSA) reduced the statutory penalties for crack offenses by increasing the quantity threshold required to trigger a mandatory sentence. The ten-year threshold was increased from 50 to 280 grams; the amount to trigger a five-year minimum sentence was increased from 5 to 28 grams. Congress thus reduced from 100-1 to 18-1 the disparity between the quantities of crack and powder cocaine that triggered mandatory sentences. The Fair Sentencing Act (FSA) is not retroactive. In Dorsey v. United States, the Supreme Court ruled that the FSA applies to defendants convicted of crack offenses before the enactment of the FSA but sentenced after it took effect. Dorsey v. United States, 132 S. Ct. 2321 (2012). The sentencing guidelines for crack offenses, which were reduced after enactment of the FSA to incorporate the 18-1 ratio, are retroactive. Defendants sentenced under the old guidelines may be eligible for a reduction, but only to the extent their sentences were based on a sentencing range. They are not eligible for reductions below the statutory mandatory minimum term of imprisonment for their offenses. Politics and public concern have also driven the extremely high sentences for methamphetamine offenses. While it takes one kilogram of heroin to trigger a ten-year mandatory sentence, it only takes 50 grams of pure methamphetamine to trigger the same sentence.
[37] Certain other drug offenses also do not carry mandatory minimum sentences, e.g. use of property as a drug storage facility or a trafficking offense that does not have a specified drug amount. See 21 U.S.C. §856. If prosecutors decline to charge the amount of drug necessary to trigger a mandatory minimum sentence for drug trafficking then the mandatory will not apply and convicted defendants can receive sentences ranging from zero to forty years of prison. For an excellent overview of federal drug mandatory minimums, their application, the defendants victimized by them, and expert opinions about them, see generally, the website of FAMM (Families Against Mandatory Minimums), http://famm.org/about/ (accessed October 28, 2013).
[38]“For the kingpins— the masterminds who are really running these operations— and they can be identified by the amounts of drugs with which they are involved— we require a jail term upon conviction. If it is their first conviction, the minimum term is 10 years…. Our proposal would also provide mandatory minimum penalties for the middle-level dealers as well…. [They] would have to go to jail—a minimum of 5 years for the first offense.” USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 24 (quoting Senator Robert Byrd, 132 Cong. Rec. 27, 193-194 (September 30, 1986)) (internal footnotes omitted). Congress also thought the mandatory minimums would “give greater direction to the DEA and the US Attorneys on how to focus scarce law enforcement resources.” Ibid. Nachmanoff and Baron-Evans, “Booker Five Years Out,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, p. 96.
[39] The government can influence the amount of drugs for which a defendant is charged. Law enforcement agents or confidential informants working for the government may make multiple buys from a drug seller until he has sold a total quantity that triggers a higher mandatory minimum. They may also aggressively solicit offenders to influence the amount they sell. Human Rights Watch interview with A.J. Kramer, federal public defender in the District of Columbia, Washington, D.C., February 12, 2013.
[40] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 262.
[41]United States v. Dossie, 851 F. Supp. 2d 478, 481 (E.D.N.Y. 2012).
[42] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 43: Drug Offenders Receiving Mandatory Minimums in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table43.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013).
[43] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 165. The proportion of all federal drug offenders subject to a mandatory minimum penalty at sentencing— e.g., who did not benefit from safety valve or substantial assistance—has remained relatively stable: 55.9 percent in 1995 and 52.9 percent in 2010. Ibid.
[44] 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(c).
[45] Because Dossie had two prior misdemeanor convictions, he was ineligible for the safety valve, which allows judges to avoid applying the mandatory minimum sentence to low-level and nonviolent defendants with little or no criminal background. See discussion of safety valve exemptions from mandatory minimum sentences in Section IV, below.
[46] At sentencing, a prosecutor assured the judge that there were factors beside the drug selling justifying the five-year sentence for Dossie, including information linking him to a gang. The government did not have to prove such links, offer them to judicial scrutiny or afford Dossie the opportunity to contest them. “There is no fairness in a system that allows that to happen,” Judge Gleeson concluded. United States v. Dossie, 851 F. Supp. 2d 478, 485(E.D.N.Y. 2012). See also Judge Jack B. Weinstein’s detailed critique of the mandatory minimum sentences imposed in United States v. Bannister, 786 F. Supp. 2d 617 (E.D.N.Y. 2011).
[47] In 1988, Congress made the mandatory minimum penalties applicable to drug distribution offenses subject also to conspiracies to commit those substantive offenses. Omnibus Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988, P.L. 100-690.
[48] 21 U.S.C. §846 states, “Any person who attempts or conspires to commit any offense defined in this subchapter shall be subject to the same penalties as those prescribed for the offense, the commission of which was the object of the attempt or conspiracy.” The elements necessary to prove a drug conspiracy are: “(1) an agreement to violate the federal drug laws; (2) knowledge and intent to join the conspiracy; and (3) participation in the conspiracy.” See United States v. Alexander, No. 12-1672, 2013 U.S. App. LEXIS 15857, 3 (6th Cir. 2013) (citations omitted). “When calculating drug quantity in ... a narcotics trafficking conspiracy, the sentencing court may consider all transactions [,] known or reasonably foreseeable to the defendant.” United States v. Payton, 636 F.3d 1027, 1046 (8th Cir. 2011) (citations omitted). Courts must “ascertain on an individual basis the scope of the criminal activity that the particular defendant agreed jointly to undertake.” United States v. Carrozza, 4 F.3d 70, 76 (1st Cir. 1993); see also United States v. Cruz–Rodríguez, 541 F.3d 19, 24 (1st Cir. 2008) (“When making the individualized finding of drug quantity responsibility, the court must not automatically shift the quantity attributable to the conspiracy as a whole to the defendant.”). Therefore, the evidence must demonstrate the defendant’s “level of involvement so as to explain why the nature of the conspiracy or [the defendant’s] relationship with the leaders of the conspiracy showed [that the defendant] could foresee a given quantity of drugs.” United States v. Correy, 570 F.3d 373, 388 (1st Cir. 2009).
[49] Information on the case of Natacha Jihad Pizarro-Campos obtained from documents filed in United States v. Campos, United States District Court for the Middle District of Florida, Case No. 6:2010-cr-00191, which are available on PACER.
[50] Information on the case of Anthony Bowens obtained from court documents filed in United States v. Bowens, District Court for the Southern District of New York, Case No. 1:04-cr-00048, which are available on PACER and from Human Rights Watch interview with Melinda Sarafa, Anthony Bowens’ defense counsel, New York, New York, February 23, 2013.
[51] The superseding indictment in 2007 deletes the number of vials amount and simply states that Bowens sold crack cocaine to another individual on May 11, 2004.
[52] As is typical in such cases, many of the co-defendants pled guilty to get sentences more commensurate with their individual level of culpability. By the time of the superseding indictment, Bowens was one of only seven named defendants.
[53] Bowens had a negligible criminal record – one conviction for larceny.
[54] Most of the co-defendants who were not “bosses” received sentences of less than 120 months, sometimes considerably less, e.g., nine defendants received sentences of 60 months. The bosses received 120 month sentences.
[55] Laurie L. Levenson, professor at Loyola Law School, Testimony Before United States Sentencing Commission, Washington, D.C., May 27, 2010, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Public_Hearings_and_Meetings/20100527/Testimony_Levenson.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), pp. 1-2.
[56] Anthony M. Kennedy, Associate Justice, Supreme Court of the United States, “Speech at the American Bar Association Annual Meeting in San Francisco,” August 9, 2003.
[57] For example, according to Judge Jack B. Weinstein, mandatory minimums “bear little relationship to the harm a defendant has done to society or to the danger of his inflicting further harm. Harsh, disproportionate mandatory sentences impose grave costs not only on the punished but on the moral credibility upon which our system of criminal justice depends…. Such laws are overly blunt instruments, bringing undue focus upon factors (such as drug quantities) to the exclusion of other important considerations, including role in the offense, use of guns and violence, criminal history, risk of recidivism, and many personal characteristics of an individual defendant.” United States v. Bannister, 786 F. Supp. 2d 617, 690 (E.D.N.Y. 2011) (internal quotations omitted). See also, Chief United States District Judge for the Western District of North Carolina Robert J. Conrad, Jr.’s “View from the Bench” paper presented before the United States Sentencing Commission, Washington, D.C., February 11, 2009, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Public_Hearings_and_Meetings/20090210-11/Judge%20Robert%20Conrad%20021109.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013) (“In too many cases a sledge hammer is the only tool available to dispatch a fly. Sentencing decisions are always difficult, but the required application of mandatory minimums in cases where they are not warranted is repugnant.”); Paul Cassell, US district judge for the District of Utah, paper presented before the House Judiciary Committee Subcommittee on Crime, Terrorism, and Homeland Security, Washington, D.C., June 26, 2007, (available in Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 19, p. 344) (“Mandatoryminimum sentences mean one-size-fits-all injustice…. Mandatory minimum sentences require judges to put blinders on to the unique facts and circumstances of particular cases, producing what the late Chief Justice Rehnquist has aptly identified as ‘unintended consequences.’”).
[58] See for example, the letter to Congress signed by 46 former prosecutors, in addition to federal judges and other law enforcement officials, supporting proposed safety valve legislation that would limit, as the letter states, “the negative effects of federal mandatory minimum sentencing laws by providing for greater judicial discretion.” Letter from signatories to the Honorable Robert C. Scott and the Honorable Thomas Massie, July 17, 2013, http://www.constitutionproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/JSVA-Letter-from-Former-Prosecutors-and-Judges-to-House-7-17-2013.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013).
[59] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Scott Lassar, former US Attorney, Chicago, Illinois, April 8, 2013.
[60] See data in Statement of Michael Nachmanoff, federal public defender for the Eastern District of Virginia, Public Hearing Before the United States Sentencing Commission: Mandatory Minimum Sentencing Provisions Under Federal Law, May 27, 2010, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Public_Hearings_and_Meetings/20100527/Testimony_Nachmanoff.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013).
[61]According to Justice Kennedy, this “transfer of sentencing discretion from a judge to an Assistant U.S. Attorney, often not much older than the defendant, is misguided.” It “gives the decision to an assistant prosecutor not trained in the exercise of discretion and takes discretion from the trial judge . . . , the one actor in the system most experienced with exercising discretion in a transparent, open, and reasoned way.” Anthony M. Kennedy, “Speech at the American Bar Association Annual Meeting in San Francisco,” August 9, 2003.
[62] Human Rights Watch interview with Judge Rakoff, March 18, 2013.
[63] Paul J. Hofer, “Has Booker Restored Balance? A Look at Data on Plea Bargaining and Sentencing,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 23, no. 5 (June 2011), p. 327 (“Before the mandatory Guidelines and statutes … plea bargaining was more likely to result in fair and accurate sentences because it took place in the ‘shadow’ of a trial and neutral judicial sentencing. Unproven facts could not be asserted and unreasonable demands could not be made because defendants had recourse to the full panoply of protections afforded at trial. Under a mandatory sentencing regime, defendants often face overbearing pressure to plead guilty and waive important rights designed to ensure reliable results.”); American Bar Association Justice Kennedy Commission, “Reports with Recommendations to the ABA House of Delegates,” August, 2004, http://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/publishing/criminal_justice_section_newsletter/crimjust_kennedy_JusticeKennedyCommissionReportsFinal.authcheckdam.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), p. 59 (“With the removal of judicial discretion and the introduction of sentencing guidelines and mandatory minimum laws, policy makers essentially empowered prosecutors to predetermine the sentence through their charging and plea bargaining decisions.”).
[64] Plea bargains resolve most federal criminal cases, including but not limited to drugs. We have not explored the high rates of plea bargaining in non-drug cases in this report. Administrative Office of the United States Courts, from Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics Online, “Table 5.24.2010: Criminal defendants disposed of in U.S. District Courts,” http://www.albany.edu/sourcebook/pdf/t5242010.pdf (accessed October 25, 2013).
[65] Michael Tonry, “The Mostly Unintended Effects of Mandatory Penalties: Two Centuries of Consistent Findings,” Crime & Justice, pp. 65-114. (there is no certainty or uniformity because some defendants avoid mandatory minimums through the safety valve or plea agreements; there is no transparency or predictability because prosecutors do not have to explain why they chose charges or agree to specific plea agreements; indeed, plea agreements are not readily ascertainable, even to researchers with access to electronic databases of court records; and there is no evidence that mandatory minimum sentences—or even long sentences— have a deterrent effect or reduce the number of drug sellers). In 2004, the Sentencing Commission heard expert testimony that “retail level drug traffickers are readily replaced by new drug sellers so long as the demand for a drug remains high. Incapacitating a low-level drug seller prevents little, if any, drug selling; the crime is simply committed by someone else.” Paul J. Hofer, Charles Loeffler, Kevin Blackwell and Patricia Valentino, US Sentencing Commission, “Fifteen Years of Guidelines Sentencing: An Assessment of How Well the Federal Criminal Justice System Is Achieving the Goals of Sentencing Reform,” November 2004, https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/Digitization/208044NCJRS.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), p. 134. See also discussion of literature on deterrence in letter from Jon M. Sands, federal public defender, to Honorable Richard H. Hinojosa, acting chair, United States Sentencing Commission, regarding Comments on Proposed Amendments Regarding the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008, March 27, 2009, http://www.ussc.gov/Meetings_and_Rulemaking/Public_Comment/20090300/FPD_Haight_032709.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013). Regarding mandatory minimums and impact on crime see also Barbara S. Vincent and Paul Hofer, Federal Judicial Center, “The Consequences of Mandatory Minimum prison Terms: A Summary of Recent Findings,” 1994, http://www.fjc.gov/public/pdf.nsf/lookup/conmanmin.pdf/$file/conmanmin.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), p. 12.; Alfred Blumstein et al., Criminal Careers and "Career Criminals" (Washington, D.C. : National Academy Press, 1986); Jeffrey Fagan & Tracey L. Meares, “Punishment, Deterrence and Social Control: The Paradox of Punishment in Minority Communities,” Ohio State Journal of Criminal Law, vol. 6 (2008), p. 176; Alfred Blumstein et al., Deterrence and Incapacitation: Estimating the Effects of Criminal Sanctions on Crime Rates (National Academy Press: 1978), p. 95; Philip Cook, “Research in Criminal Deterrence: Laying the Groundwork for the Second Decade,” in Crime and Justice: An Annual Review of Research, eds. Norval Morris and Michael Tonry (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1980), vol. 2, p. 213; Anthony N. Doob & Cheryl Marie Webster, “Sentence Severity and Crime: Accepting the Null Hypothesis,” in Crime and Justice: A Review of Research, ed. Michael Tonry (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003), vol. 30, p. 143; Daniel Nagin, “Criminal Deterrence Research at the Outset of the Twenty-First Century,” in Crime and Justice: A Review of Research, (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), vol. 23, p. 1; Daniel Nagin, “Deterrence and Incapacitation,” in The Handbook of Crime and Punishment, ed. Michael Tonry (New York: Oxford University Press, 1988), p. 345; Lawrence W. Sherman, “Defiance, Deterrence and Irrelevance: A Theory of the Criminal Sanction,” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, vol. 30 (1993), p. 453; Michael Tonry, “Purposes and Functions of Sentencing,” Crime and Justice, vol. 34 (2006), pp. 28-29; Andrew von Hirsch et al., Criminal Deterrence and Sentence Severity: An Analysis of Recent Research (Oxford: Hart Publishing, 1999), p. 45; Don M. Gottfredson, Effects of Judges' Sentencing Decisions on Criminal Careers (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Dept. of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, National Institute of Justice, 1999); United States Department of Justice, “An Analysis of Non-Violent Drug Offenders with Minimal Criminal History,” 1994, on file at Human Rights Watch; Cassia Spohn & David Holleran, “The Effect of Imprisonment on Recidivism Rates of Felony Offenders: A Focus on Drug Offenders,” Criminology, vol. 40, no. 2 (2002), p. 329.
[66] “Many in the law enforcement community view mandatory minimum penalties as an important investigative tool. The threat of a mandatory minimum penalty gives law enforcement leverage over defendants who may be encouraged to cooperate in exchange for lesser charges or substantial-assistance benefits.” USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 89.
[67] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, May 19, 2013.
[68] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Michigan, April 18, 2013.
[69] Frank O. Bowman, “Mr. Madison Meets a Time Machine: The Political Science of Federal Sentencing Reform,” Stanford Law Review, vol. 58 (2005), p. 252.
[70] Lanny A. Breuer, “The Attorney General’s Sentencing and Corrections Working Group: A Progress Report,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 23 (December 2010), p. 112.
[71] Anthony M. Kennedy, “Speech at the American Bar Association Annual Meeting in San Francisco,” August 9, 2003.
[72] Judge John Gleeson, United States v. Diaz, No. 11-CR-00821-2 (JG), 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 11386, 67-68 (E.D.N.Y. 2013) (Memorandum Explaining a Policy Disagreement with the Drug Trafficking Offense Guideline).
[73] Human Rights Watch interview with Gerald McMahon, attorney, New York, New York, July 1, 2013.
[74] Comprehensive Crime Control Act of 1984, Pub. L. 98-473, title II, October 12, 1984, 98 Stat. 1976, 28 U.S.C. §991. Supporters of sentencing guidelines thought they would eliminate unchecked and unguided judicial sentencing discretion and would, as a result, lead to more uniformity, truthfulness, and proportionality in sentencing. For a comprehensive analysis of the development and operation of the federal sentencing guidelines and their impact on federal criminal justice see Kate Stith and Jose A. Cabranes, Fear of Judging: Sentencing Guidelines in the Federal Courts (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998). Professor Kate Stith recently summarized some of the ongoing problems with the guidelines. The guidelines, “which sought to avoid unwarranted disparity in sentencing, are unreasoned and arbitrary in their treatment of many key factors. Some of the more objectionable structural features of the Guidelines include the specification of many aggravating adjustments without regard to mens rea; a sprawling definition of relevant conduct that would perhaps be more appropriate were the issue civil, rather than criminal, liability; the persistent double-counting of aggravating facts; the undue sentencing weight accorded to quantity of loss/drugs; and the failure to address true first-time offenders.” Kate Stith, Yale Faculty Scholarship Series, “Two Fronts for Sentencing Reform,” 2008 (internal quotation marks and citations omitted), http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/fss_papers/1286 (accessed October 1, 2013).
[75] 28 U.S.C. §991(b)(1)(B).Congress further directed the Sentencing Commission to study the effectiveness of guidelines in meeting the purposes of sentencing and to revise them as necessary based on its research. The Sentencing Commission was expected to draw on empirical data, national experience and the expertise of its staff to develop coherent, evidence-based national sentencing policies.
[76]Federal sentencing guidelines are extraordinarily detailed and complicated; the Sentencing Commission’s Guidelines Manual consists of more than 500 pages. USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf, p. 394, Sentencing Table.
[77]The specific guideline applicable to most drug offenses is §2D1.1. There are 43 offense levels of increasing severity in the Sentencing Table. For drugs, the offense level is tied to the quantity of drugs involved in the offense start at offense level 6 and continues through offense level 38. Offense level 26 applies to drug quantities that trigger the five-year mandatory minimum and level 32 applies for quantities triggering the ten-year mandatory minimum. The quantities of drugs for other offense levels are arrayed upwards and downwards as set forth in the Drug Quantity Table.The Sentencing guidelines were supposed to be the “product of [the Sentencing Commission’s] careful study based on extensive empirical evidence derived from the review of thousands of individual sentencing decisions.” But instead the Sentencing Commission set its drug guidelines to reflect the mandatory minimum sentences. Gall v. United States, 552 U.S. 38, 46 (2007); USSC, “Fifteen Years of Guidelines Sentencing: An Assessment of How Well the Federal Criminal Justice System Is Achieving the Goals of Sentencing Reform,” https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/Digitization/208044NCJRS.pdf. Many guideline critics have faulted the Sentencing Commission for relying too heavily on drug quantity and creating drug sentencing ranges that are far too severe. See, e.g. Amy Baron-Evans and Kate Stith, “Booker Rules,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review, vol. 160 (January 16, 2012) pp. 1632, 1660; Hofer, “Federal Sentencing for Violent and Drug Trafficking Crimes Involving Firearms: Recent Changes and Prospects for Improvement,” American Criminal Law Review, p. 72.
[78] For example, the guidelines set a two- to four-level increase for defendants who were organizers, leaders, supervisors, or managers, and a two- to three-level decrease in level for minimal or minor participants. First time low-level offenders may also qualify for the safety valve (see discussion below) which will give them a two-level reduction. But these possible decreases in guideline levels do not fully mitigate the harshness of the guidelines keyed to drug quantity.
[79]There is typically a 25 percent spread between the minimum and maximum sentences within a guidelines sentencing range.
[80] Nachmanoff and Baron-Evans, “Booker Five Years Out,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, p. 97; Stephen J. Schulhofer, “Assessing the Federal Sentencing Process: The Problem is Uniformity not Disparity,” American Criminal Law Review, p. 853; Baron-Evans and Stith, “Booker Rules,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review, pp. 1632, 1660. Paul J. Hofer, “New Federal Sentencing Data and Response: Review of the U.S. Sentencing Commission’s Report to Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 24 (2012).
[81] Executive Office of the President, Office of National Drug Control Policy, “The Price and Purity of Illicit Drugs: 1981
Through the Second Quarter of 2003,” November 2004, https://www.ncjrs.gov/ondcppubs/publications/pdf/price_purity.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013).
[82] Mark Osler, “Amoral Numbers and Narcotics Sentencing,” University of St. Thomas (Minnesota) Legal Studies Research Paper No. 13-21, 2013,http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2271380 (accessed October 1, 2013). See USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf, §§2A3.1, 2A1.3, 2B3.2, 2M3.3
[83] His base level offense would be 34, he would get a two-level upward adjustment for his managing role in the operation, and he would be in criminal history 11 because of the prior felony.
[84]United States v. Ingram, 721 F.3d 35, 43 (2nd Cir. 2013) (emphasis in original).
[85] During this period, the guidelines varied from presumptively binding to mandatory, as Supreme Court decisions and legislation during the period varied the amount of discretion judges had to sentence outside the guideline range. Human Rights Watch correspondence with Paul J. Hofer, October 23, 2013.
[86]United States v. Booker, 543 U.S. 220 (2005). The Court’s remedy was to strike those portions of the Sentencing Reform Act of 1984 that rendered the guidelines binding on the judiciary. Going beyond Booker, in two subsequent decisions, Gall v. United States, 552 U.S. 38, 46 (2007) and Kimbrough v. United States, 552 U.S. 85 (2007), the Supreme Court affirmed the key role of the judge not just in finding the facts that are relevant to punishment under the guidelines, but “in judging the statutory purposes of sentencing, including the justness of the punishment at hand.” See Kate Stith, “The Arc of the Pendulum: Judges, Prosecutors, and the Exercise of Discretion,” Yale Law Journal, vol. 117 (2008), p. 1489.
[87]Peugh v. United States, 133 S. Ct. 2072, 2080 (2013) (citing Gall v. United States, 552 U.S. 38, 46, 49 (2007)).
[88]Nelson v. United States, 555 U.S. 350 (2009).
[89] See 18 U.S.C. §3553 for factors Congress instructed judges to consider in sentencing. A sentence from the guidelines range occurs in one of two ways: as a “departure” that is permitted by the guidelines themselves, or as a sentence warranted by application of the factors in 18 U.S.C. §3553(a). Rita v. United States, 551 U.S. 338, 344 (2007).
[90]As Judge Nancy Gertner stated, “False uniformity occurs when we treat equally individuals who are not remotely equal because we permit a single consideration, like drug quantity, to mask other important factors. Drug quantity under the Guidelines treats as similar the drug dealers who stood to gain a substantial profit … and the deliveryman … who receive little more than piecework wages.” United States v. Cabrera, 567 F. Supp. 2d 271, 273 (D. Mass. 2008). See also, Eric L. Sevigny, “Excessive Uniformity in Federal Drug Sentencing,” Journal of Quantitative Criminology, vol. 25 (2009), p. 156.
[91] Information on the case of Corey James obtained from documents filed in United States v. James, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. No. 8-CR-681, which are available on PACER.
[92] The judge could not sentence James below 120 months because of a ten-year mandatory minimum sentence that was applicable to his offenses due to the quantity of drugs involved.
[93] See Section IV for discussion of reduced sentences because of substantial assistance. Fast track programs permit federal prosecutors to secure plea agreements expeditiously in criminal immigration cases that give the defendants significant sentence reductions. See James M. Cole, deputy attorney general, US Department of Justice, “Memorandum for all United States Attorneys: Department Policy on Early Disposition or ‘Fast-Track’ Programs,” January 31, 2012, http://www.justice.gov/dag/fast-track-program.pdf(accessed September 30, 2013).
[94] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 27A: Sentences Relative to the Guideline Range by Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table27a.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013). Among individual districts, the percent of within-guidelines sentences ranged from 6.8 percent in North Dakota to 77.6 percent in the Southern District of Illinois. See Appendix which includes sentencing information only for federal drug traffickers. Judges rarely give sentences to convicted drug defendants that are higher than the guidelines range. In 2012, they gave higher than guidelines sentences in 0.9 percent of federal drug trafficking cases. USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 27A.”
[95] Ibid.
[96]Peugh, supra note 109 at 2080 (citing Gall v. United States, 552 U.S. 38, 46, 49 (2007) (citations omitted).The continuing predominance of guidelines sentences in drug cases to some extent reflects judicial familiarity and comfort with them. Many federal judges began their tenure while the guidelines were mandatory. “Most judges, all they know are the guidelines.” Human Rights Watch interview with Tony Gallagher, federal public defender in Montana, Great Falls, Montana, April 9, 2013. Indeed, most federal judges were appointed after the guidelines became effective. Kate Stith, “The Arc of the Pendulum: Judges, Prosecutors, and the Exercise of Discretion,” Yale Law Journal, p. 1496, fn 333. The guidelines also exert what has been called an “anchoring” effect or a gravitational pull on sentences. See, e.g., United States v. Ingram, 721 F.3d 35, 43 (2ndCir. 2013); United States v. Cavera, 550 F.3d 180, 189 (2nd Cir. 2008); Ryan W. Scott, “Inter-Judge Sentencing Disparity After Booker: A First Look,” Stanford Law Review, vol. 63, no. 1 (2010), http://www.stanfordlawreview.org/sites/default/files/articles/Scott_63_Stan._L._Rev._1_0.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), p. 45; Daniel M. Isaacs, “ Baseline Framing in Sentencing,” The Yale Law Journal, vol. 121 (2011), http://www.yalelawjournal.org/images/pdfs/1022.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), p. 426; Nancy Gertner, “What Yogi Berra Teaches About Post-Booker Sentencing,” The Yale Law Journal Pocket Part, vol. 115 (2006), http://www.thepocketpart.org/2006/07/gertner.html (accessed November 1, 2013), p. 138. Judges may also sentence within the guidelines either because they do not realize the Sentencing Commission did not develop the guidelines based on its own research or because they believe the guidelines reflect the policy choices of Congress, even though the Supreme Court has given judges the green light to disagree with the policies reflected in the guidelines. Human Right Watch correspondence with Paul J. Hofer, October 23, 2013.
[97] Information on the case of Darlene Eckles obtained from court documents filed in United States v. Eckles, District Court for the Western District of North Carolina, Case No. 5:05-cr-00009, which are available on PACER; Human Rights Watch correspondence with Eckles; and conversations and correspondence with Glen McGorty, one of several attorneys with the law firm of Crowell & Moring who are seeking a new or commuted sentence for her.
[98] Some guidelines critics have insisted that the “increasing prosecutorial power and the severity of criminal punishments was not the unintended consequence of guidelines designed to reduce sentencing disparity … [but] the point all along.” Albert W. Alschuler, “Disparity: The Normative and Empirical Failure of the Federal Guidelines,” Stanford Law Review vol. 58, no. 85 (October 28, 2005), p. 116. As Professor Kate Smith has explained, the guidelines “provided prosecutors with indecent power relative to both defendants and judges, in part because of prosecutors’ ability to threaten full application of the severe Sentencing Guidelines.” Kate Stith, “The Arc of the Pendulum: Judges, Prosecutors, and the Exercise of Discretion,” Yale Law Journal, p. 1425. See also, Stith and Cabranes, Fear of Judging: Sentencing Guidelines in the Federal Courts, pp. 130-139 (increased prosecutorial discretion in criminal sentencing under mandatory guidelines).
[99] “Assistant U.S. Attorneys … have been heard to say, with open candor, that there are many ‘games to be played,’ both in charging defendants and in plea bargaining, to circumvent the Guidelines. Because of this reality, sentences under the Guidelines often bear no relationship to what the Sentencing Commission may have envisioned as appropriate.” United States v. Harrington, 947 F.2d 956, 964 (D.C. Cir. 1991). Based on their research, Stephen J. Schulhofer and Ilene Nagel estimated that plea negotiation practices circumvented the guidelines in roughly 20-35 percent of cases resolved through a guilty plea— via charge bargaining, fact bargaining, and guideline factor bargaining— and was particularly likely in drug cases. Stephen Schulhofer and Ilene H. Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period,” Northwestern University Law Review, vol. 91 (1997), p. 1284. See also their earlier study, Nagel and Schulhofer, “A Tale of Three Cities: An Empirical Study of Charging and Bargaining Practices under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines,” Southern California Law Review, vol. 66 (1992), p. 501. (Prosecutorial charging discretion more likely to circumvent guidelines in cases, such as drug cases, in which mandatory minimum sentences and guidelines anchored by mandatory minimums are tied to the charges for which the defendant is convicted). See also Stith and Cabranes, Fear of Judging: Sentencing Guidelines in the Federal Courts, pp. 137-140.
[100] As Stith notes, had the court in Booker adopted the remedy proposed by Justice Stevens and left the guidelines with the force of law, the guidelines would have remained mandatory, but guidelines’ factors that result in enhancement of punishment would have to be charged in the indictment. The prosecutor would have had to prove such factors beyond a reasonable doubt, providing an additional incentive to the prosecutor to agree to a plea more favorable to the defendant. Kate Stith, “The Arc of the Pendulum: Judges, Prosecutors, and the Exercise of Discretion,” Yale Law Journal, p. 1479.
[101] See data in Statement of Michael Nachmanoff, federal public defender for the Eastern District of Virginia, Public Hearing Before the United States Sentencing Commission: Mandatory Minimum Sentencing Provisions Under Federal Law, May 27, 2010, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Public_Hearings_and_Meetings/20100527/Testimony_Nachmanoff.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013).
[102] Information on the case of Efrain Vega obtained from court documents filed in United States v. Vega, United States District Court for the District of Connecticut (New Haven), Case No. 3:11-cr-00117, which are available on PACER.
[103] The prosecutor argued, “The defendant sold cocaine. He sold cocaine in the community in which he lived. He sold a drug which he knew from his personal experience was addictive and destroyed families. He knew it was wrong. He knew as a husband, son and father how drugs fracture families. He sold cocaine anyway.... A definitive and clear message must be sent that this type of conduct will be punished.” United States v. Vega, United States District Court for the District of Connecticut, Case No. 3:11-cr-00117, Government’s Sentencing Memorandum, November 7, 2012, p. 6.
[104] Ibid., Judgment, p. 1. Judge Underhill also recently rebuffed efforts by federal prosecutors to treat an addict who purchased drugs as a conspiracy member. United States v. Orkisz, District Court for the District of Connecticut, Case No. 3:2011-cr-00069, Judgment, June 19, 2013.
[105] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, March 21, 2013.
[106] 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1). See generally, Sarah French Russell, “Rethinking Recidivist Enhancements: The Role of Prior Drug Convictions in Federal Sentencing,” U.C. Davis Law Review, vol. 43(2010), http://lawreview.law.ucdavis.edu/issues/43/4/articles/43-4_russell.pdf (accessed October 7, 2013).
[107] The statute provides that no person convicted of a drug offense “under this part be sentenced to increased punishment by reason of one or more prior convictions, unless before trial, or before entry of a plea of guilty, the United States attorney files in information with the court … stating in writing the previous convictions to be relied upon.” 21 U.S.C. §851(a)(1). The defendant may challenge the prior convictions, including by arguing they were invalid or unconstitutional. If the defendant prevails on the argument, the prior sentencing enhancement will not be applied. 21 U.S.C. §851(c). Because the information is required under 21 U.S.C. §851, it is often referred to as an §851 information and the sentence enhancements are similarly often referred to as §851 enhancements.
[108] A detailed history of prior felony enhancements for federal drug offenders is provided in United States v. Kupa, No. 11-CR-345,2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[109] The predicate “felony drug offense” conviction need not be for a crime designed as a felony under state or federal law. Any offense “punishable by imprisonment for more than one year” for a drug offense qualifies. 21 U.S.C. §802(44).
[110] Bill Oscar Lee pled guilty to one count of conspiracy to distribute 5 kilograms of cocaine. The government claimed the defendant had two prior state felony convictions in Alabama and filed an §851 information. One of Lee’s prior convictions was for unlawful distribution of a controlled substance. The second was for simple possession of marijuana. This was the defendant’s second conviction for possessing marijuana for personal use. Under Alabama law, the first marijuana possession charge is a misdemeanor. But if someone has a predicate misdemeanor marijuana possession conviction, the second marijuana possession conviction is a felony. The federal prosecutor, was willing to have Lee sentenced to life without parole because of this record. Fortunately for Lee, he was able to challenge the constitutionality of the first marijuana possession conviction because he was not provided counsel, and of the second conviction because counsel was ineffective. The prosecutor withdrew the §851 information and Lee was sentenced to 15 years. Information on the case of Bill Oscar Lee obtained from court documents filed in, United States v. Lee, United States District Court for the Northern District of Alabama, Case No. 5:10-CR-00313, which are available on PACER.
[111]United States v. Berry, 701 F.3d 374 (11th Cir.2012). The enhancement doubled Berry’s drug sentence from five to ten years.
[112] Information on the case of Terrence Watson obtained from documents filed in, United States v. Watson, United States District Court for the Northern District of Florida, Case No. 3:11cr37, which are available on PACER; from Human Rights Watch interview with his attorney, George Murphy, Valparaiso, Florida, June 13, 2013; and from The United States Attorney’s Office - Northern District of Florida press release, “Life Sentences Handed Down in On-Going Federal Drug Prosecutions,” August 10, 2011, http://www.justice.gov/usao/fln/press/2011/aug/watson.html(accessed October 7, 2013). Other convictions as part of his task force have resulted in four life sentences and five sentences of 20 years or more on charges involving narcotics, firearms, and related violence.
[113] According to Mr. Watson’s lawyer, prosecutors in the northern district of Florida routinely file §851 informations if the prior drug felonies exist. The only way to avoid the enhanced sentences is for the defendant to plead and to cooperate with the government. Human Rights Watch telephone interview with George Murphy, private attorney, Valparaiso, Florida, June 13, 2013. After he was sentenced, Mr. Watson agreed to cooperate with the government. Prosecutors filed a Rule 35 motion seeking a sentence reduction and the judge reduced his sentence 144 months.
[114] Information on Juan Gonzalez (pseudonym) obtained from court documents filed in his case, and from Human Rights Watch email correspondence with his attorney on June 20, 2013 and September 4, 2013.
[115] In both cases, Gonzalez was convicted of a violating New York Penal Code Section 220.29, a Class B felony.
[116] At trial, two individuals who had supplied Gonzalez with drugs testified against him. One of the cooperating suppliers received a five-year prison sentence and the other received a four-year sentence.
[117] See Attorney General Eric Holder, “Remarks at the Annual Meeting of the American Bar Association's House of Delegates,” August 12, 2013, http://www.justice.gov/iso/opa/ag/speeches/2013/ag-speech-130812.html (accessed November 1, 2013). The Holder memorandum is discussed below in Section 6.
[118]Regardless of whether prosecutors file an §851 information, federal drug defendants with prior convictions for drug or violent offenses in the last fifteen years face dramatically increased sentences as “career offenders” under the sentencing guidelines. A “career offender” is a defendant convicted of a controlled substance offense who has at least two prior felony convictions for a crime of violence or a controlled substance. The offense level of a career offender is based on the maximum statutory term a defendant faces and the defendant is automatically placed in criminal history category VI, the highest category. Career offender sentences can be extremely long, even if the offender’s prior criminal history is minor. If the offender is facing a mandatory maximum term of life, the offender’s sentencing range is 30 years to life. United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “2012 Guidelines Manual,”http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf, §4B1.1, Career Offender.
[119] The United States Sentencing Commission analyzed a sample group of cases for 13,935 drug defendants from three fiscal years (FY 2006, 2008, and 2009) to determine eligibility for an §851 enhancement because of prior qualifying convictions and to determine in how many of the cases the enhancement was applied. At the request of Federal District Judge Mark Bennett, the Sentencing Commission provided him with the number and percentage of defendants in the sample who were eligible for the §851 penalty enhancement for each of the 94 federal districts and the number and percentage of the defendants against whom the §851 was applied. Judge Bennett kindly provided the data to Human Rights Watch. The data does not tell us the number or percentage of cases in which the §851 was filed and then withdrawn as part of a plea agreement, which may happen quite frequently, as we discuss below. Nor does it tell us whether a defendant had two prior convictions, but the §851 was filed based on only one prior conviction. See also, USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” October 2011, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, §851 Analysis, pp. 252-260. See Judge Bennett’s decision in United States v. Young, No. CR-12-4107-MWB, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 116042 (N.D. Iowa 2013) for detailed examination of application of §851 enhancements based on Sentencing Commission data.
[120] Our analysis of the data indicates an eligible federal offender in the Northern District of Florida is 350 times more likely to receive an §851 enhancement than a similar offender in the Middle District of Georgia. Defendants in the Eastern District of Tennessee were 143 times more likely to receive an §851 enhancement than in the Western District of Tennessee, an eligible offender in the Eastern District of Pennsylvania is 51 times more likely to receive an enhancement than a similar offender in the Middle District of Pennsylvania, and offenders in the Western District of Texas were 41 times more likely to receive an enhancement than those in the Northern District of Texas. According to our data analysis, the rate at which prior felony enhancements are applied to eligible defendants does not correlate with the size of the federal district, the number of drug cases in a district, or the percentage of eligible defendants in a district. We do not have data that would show if there is a correlation between the prevalence of more serious cases in a district and the rate at which §851 enhancements were applied.
[121]United States v. Young, No. CR-12-4107-MWB, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 116042, 2 (N.D. Iowa 2013).
[122] Ibid. at 22. Patterns of drug trafficking, community concerns, politics, social-economic circumstances, office culture, and the predilections of individual US Attorneys with regard to charging and plea bargaining may help explain some of the district differences in the application of prior felony enhancements, but we do not have the data necessary to undertake such an analysis.
[123] Information on the case of Tyquan Midyett obtained from documents filed in United States v. Midyett, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 1:07-cr-00874, which are available on PACER.
[124] According to Midyett’s counsel, Midyett refused to accept the 10 year plea because believed he was not guilty of the conspiracy count because he acted as a “lone operator.”
[125] After conviction but before sentencing, Midyett claimed that his lawyer had not advised him of the 10-year plea offer or of the significance of the §851 information and that he would face a 20-year sentence if convicted. After an evidentiary hearing, the sentencing judge concluded that the weight of the credible evidence did not support a finding of deficient representation by Midyett’s counsel. United States v. Midyett, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 07-CR0874, Memorandum and Order, February 2, 2010.
[126] Sentencing was June 17, 2010. Midyett was therefore sentenced before the Fair Sentencing Act became law. Midyett was convicted of several other counts but his sentences for the other counts were to run concurrent with the 20-year sentence.
[127] Ibid., Transcript of Sentencing Hearing, June 17, 2010. Under the Fair Sentencing Act, which became law 45 days after Midyett’s sentencing, Midyett’s mandatory sentence given the quantity of drugs he dealt would have been only five years, not ten. On August 29, 2013, Judge Kiyo Masumoto reduced Midyett’s sentence to ten years (five years for the drugs, doubled because of the prior conviction) because of the unique circumstances in his case (he had repeatedly requested that his sentencing be delayed until after the Fair Sentencing Act had been enacted) and to serve the purposes of punishment laid out in 18 U.S.C. §3553(c)(2).
[128] Information on the case of Brian Moreland obtained from documents filed in his District Court and Court of Appeals cases, United States v. Moreland, District Court for the Southern District of West Virginia, Case No. 2:04-cr-00142 and Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, Case Nos. 05-4476 and 05-4571, respectively, which are available on PACER.
[129]United States v. Moreland, Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, Case Nos. 05-4476 and 05-4571, Appellate Brief of Appellee/Cross-Appellant, July 27, 2005.
[130] Ibid.
[131]Rita v. United States, 551 U.S. 338, 344 (2007) (appellate court reviews for abuse of discretion and may but is not required to apply a presumption of reasonableness when a sentence is within guidelines range); Gall v. United States, 552 U.S. 38, 46, 49 (2007) (appellate review should not require extraordinary circumstances to justify sentence outside guidelines range and while it may consider extent of deviation, it must give due deference to district court’s decision that §3553(a) factors justify extent of variance).
[132] In its appellate brief, the government insisted that the specific facts of Moreland’s prior or current offenses were irrelevant in light of Congress’s policy regarding weight to be given prior criminal history. The government, notably, did not point out that Congress left it to the discretion of the prosecutor to decide whether to file the §851 information.
[133]United States v. Moreland, District Court for the Southern District of West Virginia, Case No. 2:04-cr-00142, Memorandum Opinion and Statement of Reasons, April 3, 2008, pp. 22-23. The court strongly criticized the career offender guidelines: “two relatively minor and non-violent prior drug offenses, cumulatively penalized by much less than a year in prison … vaulted this defendant into the same category as major drug traffickers engaged in gun crimes or acts of extreme violence. The career offender Guideline provision provides no mechanism for evaluating the relative seriousness of the underlying prior convictions. Instead of reducing unwarranted sentencing disparities, such a mechanical approach ends up creating additional disparities because this Guideline instructs courts to substitute an artificial offense level and criminal history in place of each individual defendant’s precise characteristics.” Ibid. pp. 24-25. See also, United States v. Andrew Williams, 481 F. Supp. 2d 1298 (M. D. Fla. 2007), in which the defendant also faced a career offender guidelines sentence enhanced because the government filed an §851 information. Williams was a 29-year-old petty street-level drug user/dealer with a ninth-grade education, marginal employment skills, a daily drug habit, and a pattern of criminal conduct (primarily drug dealing) since age 16. He was convicted after selling a total of 34.8 grams of crack over four months in three sales to a government agent. The government urged a sentence within the guidelines range of 360 months to life; the judge sentenced Mr. Williams to 204 months in prison, concluding he needed a relatively harsh sentence because prior punishments had not deterred him from continued criminal conduct, but that a greater sentence would have exceeded what was necessary to advance the purposes of 3553(a).
[134] Information on the case of Lori Ann Newhouse obtained from documents filed in United States v. Newhouse, United States District Court for the Northern District of Iowa, Case No. 3:11-cr-03030, which are available on PACER.
[135] There was a legal oddity in Newhouse’s case: her two prior convictions were based on offenses that occurred at the same time and in the same place. If the prosecutor had chosen to prosecute them jointly, Newhouse would only have had one prior conviction.
[136] United States v. Kupa , No. 11-CR-345, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[137] [A] prosecutorial tool that should be used only against the worst of the worst drug trafficking defendants has instead become a tool to prevent all recidivist drug trafficking defendants from exercising their Sixth Amendment right to trial by jury.” Ibid. at 44.
[138] Human Rights Watch interview with Judge Paul Friedman, US district judge, Washington D.C., May 12, 2013.
[139] See Methodology section.
[140] No data indicates how often an §851 is initially filed and then dismissed due to a plea agreement, or showing how frequently prosecutors file an §851 enhancement only after a defendant refuses to plead guilty. Nor is there data showing whether prosecutors limit the number of prior convictions included in an §851 information depending on whether the defendant pleads. One former New York prosecutor told us, for example, that in his office they might seek an enhancement based on one prior conviction for a defendant who would not plead guilty, an enhancement that would double his sentence, but they rarely filed a prior conviction that would secure a life sentence. Human Rights Watch interview with prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, August 19, 2013.
[141] Numerous cases indicating the use of prior felony enhancements to threaten or punish drug defendants are provided in United States v. Kupa, No. 11-CR-345,2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[142] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, March 21, 2013.
[143] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 22, 2013.
[144] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Stephen R. Sady, chief deputy federal public defender, Portland, Oregon, May 9, 2013.
[145] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Angela L. Campbell, defense attorney, Des Moines, Iowa, May 3, 2013.
[146] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Robert O’Neill, US Attorney for the Middle District of Florida, Tampa, Florida, May 30, 2013. Curiously, an assistant US attorney in the same office said the policy was to routinely file §851s whenever applicable.
[147] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 13, 2013.
[148]United States v. Jones, 569 F.3d 569, 573-74 (6th Cir. 2009).
[149] Information on the case of Lulzim Kupa obtained from documents filed in United States v. Kupa, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 1:11-cr-00345, which are available on PACER.
[150] United States v. Kupa , No. 11-CR-345, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922, 48-49 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[151] After filing the §851 information, the government offered a plea deal in which it would recommend a sentencing range of 130 to 162 months. When Kupa refused and with trial date approaching, the government made another offer, this time for a sentencing range of 140 to 175 months. This assumed Kupa would be sentenced as a career offender; would receive only a two-level reduction for acceptance of responsibility; and would receive a two-level reduction for participating in a global plea disposition
[152] Human Rights Watch attended the sentencing hearing on August 9, 2013.
[153] United States v. Kupa, No. 11-CR-345,2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922, 55 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[154] Ibid. at 56.
[155] Information on the case of Patricio Paladin obtained from documents filed in United States v. Paladin, United States District Court for the District of New Hampshire, Case No. 09-CR-186-01, which are available on PACER and from Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Michael Iacopino, defense attorney in New Hampshire, Manchester, New Hampshire, June 24, 2013.
[156] Paladin unsuccessfully challenged the constitutionality of one of the convictions.
[157]United States v. Paladin, United States District Court for the District of New Hampshire, Case No. 1:09-cr-00186, Transcript of Sentencing Hearing, October 9, 2012, pp. 14-15.
[158] Ibid., pp. 40-41.
[159] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Jason Hawkins, federal public defender, Dallas, Texas, April 10, 2013.
[160]United States v. Paladin, United States District Court for the District of New Hampshire, Case No. 1:09-cr-00186, Transcript of Sentencing Hearing, October 9, 2012, p. 15.
[161] United States v. Looney, 532 F. 3d 392, 398 (5th Cir. 2008)(per curiam).
[162] Human Rights Watch interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Michigan, April 18, 2013.
[163] In 1984, Congress amended 18 U.S.C. §924 to require a five-year penalty for offenders using or carrying a firearm during a crime ofviolence. Two years later, it expanded the statute to include using or carrying a firearm during a drug trafficking crime. In 1998, it again amended the statute to also require the mandatory five-year penalty for drug offenders who possessed a firearm “in furtherance” of their drug trafficking crime. It also increased to seven years the mandatory penalty in such cases if the gun were brandished and to ten years if the gun were discharged. United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” October 2011, (accessed October 1, 2013), pp. 25-26. The mandatory penalties also depend on the type of firearm involved, e.g. ten years if it is a semiautomatic assault weapon and 30 years if it is a machine gun.
[164] Although it is not commonly done, prosecutors have sought §924(c) sentences for both the substantive drug offense and for the conspiracy to commit that offense. In the cases of Mary Beth Looney and LaShonda Hall, discussed below, the prosecutors included one §924(c) count predicated on possession with intent to distribute and a second §924(c) count on conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute.
[165] See, e.g., United States v. Zavala, Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit, Case No. 6:06-cr-00027-LED-JKG, Unpublished Decision, August 11, 2008. In Pinkerton v. United States, the Supreme Court held that a defendant may be held responsible for a substantive offense committed by a co-conspirator, even absent participation in or knowledge of that offense, as long as the co-conspirator’s act was reasonably foreseeable to the defendant.
[166]Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm (accessed October 7, 2013). We do not know how many defendants benefitted from plea agreements according to which the government either did not file one or more possible §924(c) charges or dismissed one or more already indicted §924(c) charges.
[167] By way of comparison, those districts circuits accounted for 28.6 percent of all federal criminal cases heard that year. The §924(c) cases included all defendants convicted of §924(c) offenses and not just drug offenders. USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 276. These statistics cover all defendants convicted of §924(c) offenses and not just drug offenders.
[168]Deal v. United States, 508 U.S. 129 (1993). The Court held that the statutory language in §924(c) “second or subsequent conviction” means a finding of guilt, rather than the entry of a final judgment of a conviction, and that a first sentence does not have to become final prior to the second one in order for the second one to count as a “second or subsequent offense.” Ibid. See United States v. Washington, 301 F. Supp. 2d 1306, 1309 (M.D. Ala. 2004), for a strong critique of the irrational and draconian sentences that result from Supreme Court’s interpretation. As the court in that case points out, under Deal, an offender who deals drugs and carries a gun on two occasions before arrest and conviction is treated the same as someone who serves 5 years for a first §924(c) conviction and after release returns to drug dealing and guns.
[169] The United States Sentencing Commission has suggested Congress amend §924(c) to eliminate the ability of prosecutors to stack the charges and to require a prior conviction to trigger the repeat offender enhancement. See Charles Doyle, Congressional Research Service, “Federal Mandatory Minimum Sentencing: The 18 U.S.C. 924(c) Tack-On in Cases Involving Drugs or Violence,” October 21, 2013, http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R41412.pdf (accessed October 30, 2013).
[170] Jason D. Hawkins, first assistant federal public defender for the Northern District of Texas, Statement before the United States Sentencing Commission, Austin, Texas, November 19, 2009, (accessed October 7, 2013), p. 12.
[171]United States v. Cousins, United States District Court for the Western District of Virginia, Case No. 5:06-cr-00008. When imposing the sentence, the district judge said he thought the sentence was “way more than needed.” Ibid.
[172] Information on the case of Mark Wayne Woods obtained from documents filed in United States v. Woods, United States District Court for the Western District of Virginia, Case no. 5:03-cr-30054 and Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, Case no. 04-4231.
[173]United States v. Zavala, Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit, Case No. 6:06-cr-00027-LED-JKG, Unpublished Decision, August 11, 2008.
[174] He pled guilty to possessing different guns in connection with different quantities of drugs in two separate locations and on two separate occasions.
[175]United States v. Washington, 301 F. Supp. 2d 1306, 1309 (M.D. Ala. 2004).
[176] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” , p. 273. In 1991, only 45 percent of drug offenders who qualified for a §924(c) enhancement were charged under the statute, and the firearms charge was dismissed for 26 percent of the offenders initially charged. United States Sentencing Commission, “Fifteen Years of Guidelines Sentencing: An Assessment of How Well the Federal Criminal Justice System Is Achieving the Goals of Sentencing Reform,” November 2004, https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/Digitization/208044NCJRS.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), p. 90. In 2000, only 20 percent of all offenders (not limited to drug offenders) who used a firearm received the statutory enhancement, 35 percent received the guidelines enhancement, and 35 percent received no weapons increase at all. Ibid.
[177] Willingness to plead is not the only consideration for prosecutors when deciding whether to file a §924(c) charge and if so how many. As one prosecutor told us, “I try to size up the defendant. For example, suppose a defendant drug dealer is found to possess two guns, one at home, one in the car. If the defendant has a long and violent history, has actually shot people, I’m likely to charge both §924(c) because I think he is a danger to the public and should be incapacitated for a long time. But say he is just a kid, no prior history, no use of guns, [then] hitting him with two §924(c) would make no sense.” Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 13, 2013.
[178] Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm. We do not know the extent to which prosecutors dropped §924(c) counts for defendants willing to plead.
[179] The drug trafficking guideline provides for a two-level increase for defendants who possess a weapon in connection with their offense. To avoid punishing defendants twice for the same conduct, the guideline also stipulates that the adjustment should not be applied to defendants who are convicted under §924(c). The two-point guideline adjustment is almost always less severe than the statutory minimum enhancement, so defendants who are charged under the mandatory minimum receive harsher punishment at the sole discretion of the prosecutor.
[180] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York May 19, 2013. Another former prosecutor from the same district told us it was rare for the office to insist on pleas that included more than one §924(c) count except for cooperating witnesses. “The office might charge two 924(c)s when the defendant is pleading guilty and is going to be a cooperating witness; by enhancing his sentence, the prosecutors sought to enhance the witness credibility at trial, even though after his testimony, a §5k1.1 motion would be filed, enabling the judge to give the defendant a sentence lower than the 924(c) minimum.” E-mail correspondence from former federal prosecutor (name withheld) to Human Rights Watch, August 29, 2013.
[181] Human Rights Watch interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Michigan, April 18, 2013.
[182] Irick v. United States, United States District Court for the Middle District of Georgia, Case Nos. 3:06-cr-00032 and 3:09-cv-90047-CAR, Transcript of 2255 Hearing, July 22, 2009.
[183] Human Rights Watch interview with federal public defender (name withheld), Nevada, June 5, 2013.
[184] Information on the case of Weldon Angelos obtained from documents filed in United States v. Angelos, United States District Court for the District of Utah, Case No. 2:02-cr-00708, which are available on PACER.
[185] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Robert Lund, assistant US attorney for the District of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, March 25, 2013.
[186] Information on the case of Mary Beth Looney obtained from documents filed in United States v. Looney, United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas, Case No. 7:05-CR-005-R, which are available on PACER; Human Rights Watch interview with Jason Hawkins, federal public defender, Dallas, Texas, April 10, 2013; and from Human Rights Watch email correspondence with Looney.
[187] The other defendant, Ernest Green, pled guilty to distribution of 5 grams or more of methamphetamine, agreed to cooperate with the government, and received a five-year sentence.
[188] Looney faced a mandatory minimum sentence of 10 years for the drug charges and a guidelines sentencing range of 188 to 235 months. The district court judge could have varied downward from the guidelines sentence, but did not.
[189] Corrlinks (email) message from Mary Beth Looney to Human Rights Watch, July 24, 2013, on file at Human Rights Watch.
[190]United States v. Looney, 532 F. 3d 392, 397-398 (5th Cir. 2008).
[191] Information on the case of Anthonial Irick obtained from documents filed in United States v. Irick, United States District Court for the middle District of Georgia, Case No. 3:06-cr-00032, which are available on PACER.
[192] Even if there were no §924(c) charges, the presentencing report may have indicated the presence of a gun in the truck and Irick might have faced a guidelines enhancement for possessing a gun in the course of the drug crime.
[193]Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm (accessed October 7, 2013).
[194] Ibid.
[195]Ibid. See United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” October 2011, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm (accessed November 1, 2013), p. 161, for equivalent data for fiscal year 2010.
[196] Congress enacted a safety valve statute in 1994 to provide certain offenders relief from the ADAA’s mandatory minimum sentences. 18 U.S.C. §3553(f). The statute requires courts to sentence drug offenders without respect to any otherwise applicable statutory mandatory minimum if the offender meets the safety valve criteria. The Sentencing Commission then established a parallel safety valve adjustment in its guidelines, granting a two-level decrease for drug offenders who meet the statutory safety valve requirements, regardless of whether a mandatory minimum sentence would have applied. United States Sentencing Commission, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” November 1, 2012, http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), 2D1.1(b)(16); 5C1.2. Now that guidelines are advisory, judges may choose to sentence even below the two-level decrease specified by the guidelines for safety valve eligible defendants.
[197] The calculation of criminal history points is complex. To qualify for the safety valve an offender may have no more than one criminal history point, which as a practical matter means either no prior convictions or only for extremely minor crimes. Criminal history points can be obtained for state or federal misdemeanors or felonies, including minor crimes subject to a sentence of 30 days or a year of probation. See generally, United States Sentencing Commission, “Impact of Prior Minor Offenses on Eligibility for Safety Valve,” March 2009, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Publications/2009/20090316_Safety_Valve.pdf (accessed October 9, 2013).
[198]United States v. Green, 346 F.Supp.2d 259, 273, 274 (D. Mass. 2004).
[199] Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm . The percentage that benefited from safety valve varied markedly by drug. Only 7.6 percent of crack cocaine offenders facing mandatory minimums benefitted from the safety valve, compared to 32.3 percent of powder cocaine offenders. United States Sentencing Commission, 2012 Sourcebook of Federal Sentencing Statistics (2012 Sourcebook), “Table 44: Drug Offenders Receiving Safety Valve and Mandatory Minimums in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table44.pdf (accessed October 9, 2013, 2013).
[200] United States Sentencing Commission, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 44,” .
[201] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” , p. 171.
[202]United States v. Diaz, No. 11-CR-00821-2 (JG), 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 11386, 1 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[203] Under the guidelines, a drug trafficking offense involving at least one kilogram of heroin, but less than three kilograms has a base offense level of 32, which corresponds to a sentencing range of 121 to 151 months. USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” November 1, 2012, http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013), 2D1.1(a)(5) & (c).
[204]United States v. Diaz, No. 11-CR-00821-2 (JG), 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 11386 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[205] Human Rights Watch telephone interview, with Scott Lassar, former US Attorney, Chicago, Illinois April 6, 2013.
[206]United States v. Dossie, 851 F. Supp. 2d 478, 487 (E.D.N.Y. 2012).
[207] Under 18 U.S.C. 3553(e), courts are authorized to impose a sentence below a mandatory minimum upon motion of the prosecutor. The section provides that upon motion of the government, “the court shall have the authority to impose a sentence below a level established by statute as a minimum sentence so as to reflect a defendant’s substantial assistance in the investigation or prosecution of another person who has committed an offense.” Guideline Policy Statement §5k1.1 authorizes the courts to depart from the sentencing guidelines upon motion of the government that a defendant has provided substantial assistance. Courts are only able to go below the statutory minimum if the prosecutor specifically invokes 18 U.S.C. 3553(e) in the motion. If the prosecutor only invokes §5k1.1, then the court is bound by any applicable statutory minimum, but may lower guidelines sentences down to that minimum.
[208] USSC, “2012 Guidelines Manual,” November 1, 2012, http://www.ussc.gov/Guidelines/2012_Guidelines/Manual_PDF/2012_Guidelines_Manual_Full.pdf, 5k1.1 (Substantial Assistance to Authorities).
[209] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 110. By requiring the defendant to acknowledge his guilt in a plea and leaving the sentencing benefit unspecified, prosecutors seek to enhance the credibility of the defendant should he become a cooperating witness at the trial of someone else. If there is no specific sentence mentioned in the plea agreement, then all that can be said to impeach the cooperating witness is that he has pled guilty to a charge carrying a certain sentence or sentencing range, and that the judge has not yet sentenced him. In rare instances, the government will file a Rule 35 motion after sentencing to seek a lower sentence for a defendant who provides substantial assistance after trial.
[210] Human Rights Watch interview with John Gleeson, federal judge for the District Court in the Eastern District of New York, New York, New York, March 21, 2013.
[211] Ibid.
[212] In rare instances, the government will file a Rule 35 motion after sentencing to seek a lower sentence for a defendant who provides substantial assistance after trial. Only 2.3 percent of defendants who went to trial benefitted from substantial assistance motions. Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm.
[213] USSC, 2012 Sourcebook of Federal Sentencing Statistics, “Table 30: §5K1.1 Substantial Assistance Departure Cases: Degree of Decrease for Offenders in Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table30.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). The average extent in months of substantial assistance departures varied by drug type. For example, the average extent of such departures in powder cocaine cases was 66 months (48.6 percent), in crack cocaine 87 months (49.7 percent), and in methamphetamine 66 months (45.2 percent). USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, pp. 264-265.
[214] Human Rights Watch interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Florida, May 29, 2013.
[215] See, e.g. Stephen J. Schulhofer, “Rethinking Mandatory Minimums,” Wake Forest Law Review, vol. 28 (1993), pp. 211-13. (The best sentencing breaks given to the most knowledgeable, and hence the most culpable, of conspirators.)
[216] “The American College of Trial Lawyers, Report and Proposal on Section 5k1.1 of the United States Sentencing Guidelines,” American Criminal Law Review, vol. 38 (2001), pp. 1524-25.
[217] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, Figure 8-11, p. 171. Percentages include relief from substantial assistance alone as well as from substantial assistance and safety valve together. The Sentencing Commission’s recent data regarding likelihood of drug offenders receiving substantial assistance benefits depending on their drug trade function differs from earlier analysis finding that higher level drug offenders were not more likely to receive §5k1.1 motions. See Drazga Maxfield and John H. Kramer, United States Sentencing Commission, “Substantial Assistance: An Empirical Yardstick Gauging Equity in Current Federal Policy and Practice,” January 1998, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Publications/1998/199801_5K_Report.pdf (accessed October 1, 2013).
[218] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Thelton Henderson, senior district judge, Northern District of California, San Francisco, June 11, 2013.
[219] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 110.
[220] Some districts require defendants to go undercover and wear a “wire” to help law enforcement agents apprehend other suspects; some only make substantial assistance motions if the defendant’s cooperation results in additional charges of convictions against others; some make the motion only if the defendant’s information results in the prosecution higher up “the criminal food chain” and some will make the motion as long as the defendant has provided truthful information. “The American College of Trial Lawyers, Report and Proposal on Section 5k1.1 of the United States Sentencing Guidelines,” American Criminal Law Review, p. 1515.
[221] Districts differ markedly as to whether prosecutors will make a specific sentencing reduction recommendation to the court: in some districts, prosecutors will recommend a specific reduction, either a percentage below the applicable guideline range or as a certain number of levels below the final offense level. In other districts, no specific recommendation is made.
[222] “For example, in one district, wearing a wire or providing testimony at trial warranted a recommended reduction of up to 50 percent below the applicable guideline range, while in another district, similar cooperation warranted no more than a 30 percent recommended reduction.” USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 111.
[223] Prosecutors may also enter into substantial assistance plea agreements and make subsequent motions for reasons wholly unrelated to the assistance a defendant actually provides. See “The American College of Trial Lawyers, Report and Proposal on Section 5k1.1 of the United States Sentencing Guidelines,” American Criminal Law Review, p. 1519.
[224] USSC, “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 111.
[225] Maxfield and Kramer, “Substantial Assistance: An Empirical Yardstick Gauging Equity in Current Federal Policy and Practice,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Publications/1998/199801_5K_Report.pdf, p. 10.
[226] Prosecutors may not, however, withhold the motion in bad faith if the defendant has in fact complied with all the terms of the cooperation agreement.
[227] Maxfield and Kramer, “Substantial Assistance: An Empirical Yardstick Gauging Equity in Current Federal Policy and Practice,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Publications/1998/199801_5K_Report.pdf, pp.9-10.
[228]United States v. Ming He, 94 F.3d 782, 785 (2d Cir. 1996); John Gleeson, “The Sentencing Commission and Prosecutorial Discretion: The Role of the Courts in Policing Sentence Bargains,” Hofstra Law Review, vol. 36 (2008), http://law.hofstra.edu/pdf/academics/journals/lawreview/lrv_issues_v36n03_bb1-gleeson.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), p. 645, fn. 26.
[229] Maxfield and Kramer, “Substantial Assistance: An Empirical Yardstick Gauging Equity in Current Federal Policy and Practice,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Publications/1998/199801_5K_Report.pdf, p. 15.
[230] United States Sentencing Commission, “Results of Survey of United States District Judges January 2010 through March 2010,” June 2010, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Research_Projects/Surveys/20100608_Judge_Survey.pdf (accessed October 16, 2013).
[231] Information on the case of Jason Pepper obtained from documents filed in United States v. Pepper, United States District Court for the Northern District of Iowa, Case No. 5:03-cr-04113, which are available on PACER.
[232]United States v. Pepper, 131 US. Ct. 1229 (2011).
[233]Lafler v. Cooper, 132 S. Ct. 1376, 1381 (2012).
[234] Guilty pleas accounted for 97 percent of all federal convictions. United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), 2012 Sourcebook of Federal Sentencing Statistics (2012 Sourcebook), “Figure C: Guilty Pleas and Trial Rates, Fiscal Years 2008-2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/FigureC.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). They accounted for 95 percent of state felony defendant convictions in the largest US counties. Thomas H. Cohen and Tracey Kyckelhahn, Bureau of Justice Statistics, “State Court Processing Statistics Felony Defendants in Large Urban Counties, 2006,” May 2010, http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/ascii/fdluc06.txt (accessed November 1, 2013). See generally, Robert E. Scott and William J. Stuntz, “Plea Bargaining as Contract,” Yale Law Journal, vol. 101 (1992), p. 1912. For a history of plea bargaining in the United States, see generally, George Fisher, Plea Bargaining’s Triumph: A History of Plea Bargaining in America (Stanford, California: Stanford University Press, 2003).
[235] The percentage of defendants who go to trial is calculated on the basis of all drug cases in 2010, excluding those that were dismissed. Administrative Office of the United States Courts, from Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics Online, “Table 5.38: Defendants sentenced for violation of drug laws in U.S. District Courts,” 2010, http://www.albany.edu/sourcebook/pdf/t5382010.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). The rate of guilty pleas in drug cases ranges among federal districts from a low of 76 percent in the Northern District of Alabama to 100 percent in Alaska, Delaware, and Oregon. See Appendix.
[236] Out of more than 25,000 convicted federal drug defendants in 2012, only 771 were convicted after trial. USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 38: Plea and Trial Rates of Drug Offenders in Each Drug Type, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table38.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). Acquittals are extremely rare—only 0.3 percent of all drug defendants 2009 were acquitted. Mark Motivans, Bureau of Justice Statistics, “Federal Justice Statistics 2009,” December 2011, http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/fjs09.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), table 9, p. 12.
[237]Lafler v. Cooper, 132 S. Ct. 1376, 1397 (2012) (Scalia, J. dissenting).
[238] Ibid at 1388; Missouri v. Frye, 132 S. Ct. 1399, 1407 (2012). The cases establish the defendant’s sixth amendment right to effective assistance of counsel during plea bargaining.
[239] See Geraldine Szott Moohr, “Prosecutorial Power in An Adversarial System: Lessons from Current White Collar Cases and the Inquisitorial Model,” Buffalo Criminal Law Review, vol. 8 (2004), p. 165 (quoting Justice Robert Jackson that a federal prosecutor has “more control over life, liberty and reputation than any other person in America.”). Stephanos Bibas, “Symposium: Examining Modern Approaches to Prosecutorial Discretion: The Need for Prosecutorial Discretion,” Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review, vol. 19(2010), p. 374. We agree with Stephanos Bibas that prosecutorial “discretion is bad only when it becomes idiosyncratic, unaccountable, or opaque…. Discretion is far from lawless or arbitrary. When used judiciously it can deliver consistent and tailored results. What we need to watch out for in practice, then, are the forces that push prosecutorial discretion in the wrong direction, away from the public’s sense of justice.… The press of business pushes prosecutors to use their discretion to coerce pleas and threaten higher punishments for those who refuse to bargain.… Without the practical press of business, prosecutors would be freer to exercise discretion to suit justice. The trick, then, is not to abolish discretion but to counteract the agency costs that in practice drive a wedge between discretion and justice.” Ibid.
[240] Kate Stith and Jose A. Cabranes, Fear of Judging: Sentencing Guidelines in the Federal Courts (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), p. 141. Although Stith and Cabranes wrote when the guidelines were mandatory, their concern is still relevant given the ongoing existence of mandatory minimum sentences and the continuing power of the now advisory guidelines.
[241] Bibas, “Symposium: Examining Modern Approaches to Prosecutorial Discretion: The Need for Prosecutorial Discretion,” Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review, p. 374.
[242] For a sense of the controversy over plea bargaining see e.g., Albert W. Alschuler, “The Prosecutor’s Role in Plea Bargaining,” The University of Chicago Law Review, vol. 36 (1968), pp. 50-112; Stephanos Bibas, “Plea Bargaining Outside the Shadow of Trial,” Harvard Law Review, vol. 117, no. 8 (2004), pp. 2463-2547; Stephen J. Schulhofer, “Plea Bargaining as Disaster,” Yale Law Journal, vol. 101 (1992), pp. 1979-2009; Robert E. Scott & William J. Stuntz, “Plea Bargaining as Contract,” Yale Law Journal, vol. 101 (1992), pp. 1909-1968; William J. Stuntz, “Plea Bargaining and Criminal Law’s Disappearing Shadow,” Harvard Law Review, vol. 117 (2004), pp. 2548-2568; Ronald F. Wright, “Trial Distortion and the End of Innocence in Federal Criminal Justice,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review, vol. 154 (2005).
[243] See, e.g., Scott and Stuntz, “Plea Bargaining as Contract,” Yale Law Journal, p. 1909; Frank H. Easterbrook, “Plea Bargaining as Compromise,” Yale Law Journal, vol. 101 (1992), p. 1969.
[244] Stephanos Bibas, “Plea Bargaining Outside the Shadow of Trial,” Harvard Law Review, p. 2464, 2467. As Stephanos Bibas describes, there are many factors that distort the plea process. There are “structural impediments” such as poor lawyering, agency costs, and lawyers’ self-interest, and the pressures of pretrial detention. Participants in plea bargaining, moreover, are not purely rational beings; their efforts can reflect “overconfidence, self-serving biases, framing, denial mechanisms, anchoring, discount rates, and risk preferences. Ibid., pp. 2467-68.
[245] In any given case, prosecutors are likely to give the biggest sentencing breaks to defendants who have the strongest cases and are also most likely to be innocent. Ronald Wright develops a “trial distortion” theory that in some jurisdictions there are too many dysfunctional guilty pleas that distort the pattern of outcomes that would have resulted from trials. He challenges the legitimacy of steep sentencing discounts to defendants offered in weak cases because they led to outcomes that differ from what the trial outcome was likely to be and hence undermine confidence in the outcome and the accuracy of the conviction. Wright, “Trial Distortion and the End of Innocence in Federal Criminal Justice,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review, https://www.law.upenn.edu/journals/lawreview/articles/volume154/issue1/Wright154U.Pa.L.Rev.79(2005).pdf
[246] See, e.g., Abraham Goldstein, “Converging Criminal Justice Systems: Guilty Pleas and the Public Interest,” Southern Methodist Law Review, vol. 49 (1996), p. 571 (“Even innocent defendants may be willing to abandon their defense if the stakes are high enough and the probabilities of conviction are great enough. We think the fact that innocent defendants may plead guilty indicates the force of the pressure brought to bear on a defendant. But even guilty defendants should not be coerced into giving up their right to trial.”).
[247] Rachel Barkow, “Separation of Powers and the Criminal Law,” Stanford Law Review, vol. 58, no. 4 (2006), p. 1034.
[248] Wright, “Trial Distortion and the End of Innocence in Federal Criminal Justice,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review. Wright draws this conclusion from data he has compiled showing the decreasing rate of acquittals at trial in federal cases as the rates of pleas has risen.
[249]A defendant does not have a right to a plea bargain, although prosecutors will typically listen to a defense attorney’s arguments with regard to the charges and the defendant’s culpability and may have their own personal and institutional reasons for seeking to resolve the case through a plea agreement. Defense counsel often urge drug defendants to plead, knowing it is the only way to obtain even a half-way decent sentence and knowing the odds of prevailing at trial are usually slim. Defense counsel know that federal prosecutors choose their drug cases carefully and have enormous resources to put into investigation and prosecution to marshal the evidence to establish a defendant’s guilt.
[250] Statement of Michael Nachmanoff, federal public defender for the Eastern District of Virginia, Public Hearing Before the United States Sentencing Commission: Mandatory Minimum Sentencing Provisions Under Federal Law, May 27, 2010, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Public_Hearings_and_Meetings/20100527/Testimony_Nachmanoff.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013). Nachamanoff includes in his statement the following quote: “Today, it is scarcely debatable that prosecutors exercise vast and largely unchecked discretion at each stage of the criminal process. Likewise, most agree that this discretion is subject to outrageous abuses, due to the belligerent nature of American adversarialism, the politicization of the criminal justice system, and the self-interests of prosecutors, whose success and career prospects are often measured by the quantity and notoriety of their convictions.” Erik Luna, “The Curious Case of Corporate Criminality,” American Criminal Law Review, vol. 46 (2009), p. 1513.
[251] For example, the government explained to the court in a recent New York case that the proposed plea agreement “appropriately balances the defendant’s criminal history and the seriousness of the defendant’s conduct against the significant prosecutorial risks and burdens avoided through a negotiated resolution, and permits careful allocation of prosecutorial and other governmental resources that would otherwise be devoted to trial litigation…. [Without a plea agreement], the government would have been faced with the risk of trial, which in all cases includes the possibility of adverse verdicts on one or more counts of the indictment.” United States v. Kupa, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 1:11-cr-00345-JG, letter from United States Attorney to Judge John Gleeson, August 7, 2013. For an overview of the pressures and incentives prosecutors face in plea bargaining, see Bibas, “Plea Bargaining Outside the Shadow of Trial,” Harvard Law Review, pp. 2470-2476.
[252] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 13, 2013.
[253] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Robert Lund, assistant US attorney, Salt Lake City, Utah, March 25, 2013.
[254] Defendants who persist in exercising their right to trial do so for many reasons: because they are convinced they are innocent or that the government has a weak case, because they face such long sentences they feel they have nothing to lose, because they are dumbfounded by the disconnect between the charges and the conduct they actually engaged in, or because they simply do not understand the risks of trial. The quality— the savvy, experience, commitment, and energy— of defense attorneys has an impact on whether a defendant will plead. Defense counsel are also subject to professional and financial pressures and incentives which influence their conduct during plea bargaining. If they are overburdened with cases or face funding pressures they may not be able to secure the careful investigation and expert opinions necessary to strengthen the case for the defense and to press harder for a better plea offer. Some attorneys are more experienced than others with sentencing guidelines, mandatory minimum statutes, and substantial assistance in drug cases and thus more able to identify bargaining opportunities and take advantage of ambiguities that might elude less experienced practitioners.
[255] Gerard Lynch, a federal judge and former law professor, pointed out years ago because of the prevalence of plea bargaining and the power of the prosecutor, the federal criminal justice system looks more like an administrative, “inquisitorial” model of justice than the traditional adversarial model described in the textbooks. In plea bargaining, the “prosecutor does not sit … as a neutral fact-finder adjudicating between adversarial parties, nor as a representative of one interest negotiating on an equal footing with an adversary, but as an inquisitor seeking the ‘correct’ outcome. Defendants influence the decision by submitting their arguments and evidence to the decision-maker, who can give these arguments such weight as she thinks they deserve.” Gerard E. Lynch, “Our Administrative System of Criminal Justice,” Fordham Law Review, vol. 66 (1998), p. 2123.
[256] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Michigan, April 18, 2013.
[257] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 19, 2013.
[258] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Jeffrey B. Steinback, private attorney, Chicago, Illinois, March 20, 2013.
[259] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with federal public defender (name withheld), Nevada, June 5, 2013. Professor Kate Stith made the same point to us in an interview. Human Rights Watch interview with Kate Stith, professor, Yale Law School, New Haven, Connecticut, April 5, 2013.
[260] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, May 19, 2013.
[261] Prosecutors are not required to disclose material impeachment or affirmative defense information prior to entry of a guilty plea. United States v. Ruiz, 536 U.S. 622 (2002). It remains unsettled whether prosecutors must disclose exculpatory materials prior to guilty plea. Defense counsel told us that witness statements often only arrive a week or two before trial and they often did not have the information necessary to evaluate the wisdom of a plea, e.g., about whom the cooperators are and what they will say, before having to make a decision. Human Rights Watch interviews with Deborah Colson and Justine A. Harris, private attorneys, New York, New York, May 2, 2013. See also, Ellen Yaroshefsky, “Ethics and Plea Bargaining: What’s Discovery Got to Do With It?,” Criminal Justice, vol. 23, no.3 (fall 2008), http://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/publishing/criminal_justice_section_newsletter/crimjust_cjmag_23_3_yaroshefsky.authcheckdam.pdf (accessed October 7, 2013) (mandatory disclosure of exculpatory and inculpatory facts prior to plea bargaining crucial to produce reliable results).
[262] Federal Rule of Criminal Procedure 11(c). If the plea agreement is of the type specified in Rule 11(c)(1)(A) or (C) , “the court may accept the agreement, reject it, or defer a decision until the court has reviewed the presentence report.” Federal Rule of Criminal Procedure 11(c)(3)(A). If the agreement is of the type specified in Rule 11(c)(1)(B) , “the court must advise the defendant that the defendant has no right to withdraw the plea if the court does not follow the recommendation or request.” Federal Rule of Criminal Procedure 11(c)(3)(B).
[263] In the Middle District of Florida, for example, the only advantage a drug defendant can typically secure from a plea agreement is the opportunity to secure a §5k1.1 motion from the government if it concludes the defendant has provided substantial assistance. We were told the prosecutors will not drop charges in exchange for a plea. Human Rights telephone interview with Richard S. Dellinger, private attorney, Orlando, Florida, June 27, 2013.
[264] Human Rights Watch interview with A.J. Kramer, federal public defender for the District of Columbia, Washington, D.C., February 12, 2013; Human Rights Watch interview with federal public defender (name withheld), Orlando, Florida, May 20, 2013.
[265] Under the sentencing Guidelines, the defendant will ordinarily get two points off of offense level for pleading and if the government chooses, it can also recommend a third point off for “timeliness” of plea. In fiscal year 2012, 87.4 percent of drug trafficking offenders received a 3-level adjustment for acceptance of responsibility, 7.7 percent received a 2-level adjustment and 4.9 percent received no adjustment. USSC, 2012 Sourcebook, “Table 19: Offenders Receiving Acceptance of Responsibility Reductions in Each Primary Offense Category, Fiscal Year 2012,” http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Annual_Reports_and_Sourcebooks/2012/Table19.pdf (accessed September 30, 2013). Some prosecutors will not give a defendant the third point if they had to go through extensive pretrial proceedings, e.g. suppression hearings. Human Rights Watch interview with A.J. Kramer, February 12, 2013.
[266] While we are focusing in this report only on the length of prison sentences, plea agreements can and do address other sentencing issues such as the length of supervision, and whether property or funds will be forfeited and for how much. Plea agreements also may include the defendants agreeing to cooperate with the government, which is discussed below.
[267] False or erroneous factual representations might be picked up by the probation officer preparing the pre-sentencing report for the court, although we are told by many federal practitioners that probation officers usually use the facts to which the prosecutor has agreed.
[268] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 22, 2013.
[269] Gerald McMahon told us the government “picks a number out of the air.” Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Gerald J. McMahon, private attorney, New York, New York, July 1, 2013. In a multi-year, multi-defendant drug selling conspiracy, for example, there is typically no evidence that provides a firm basis for determining how much was actually sold. In such cases, negotiations with the prosecutor may lead to reductions in the amount the government claims was involved
[270] As one defense attorney told us, “I’ve had cases in which there is a small group of defendants in a conspiracy and I’ve convinced the prosecutor that my client sold such a small amount he should be subject to sentencing only for the weight he sold, rather than the weight attributable to the entire conspiracy.” The plea agreement then reflects the prosecutor’s agreement to the lower amount. Human Rights Watch interview with Justine A. Harris, private attorney, New York, New York, May 2, 2013. When we met with Judge Jed S. Rakoff, he told us he was currently presiding over a case with a group indicted in a drug conspiracy. If a defendant wants to plead guilty, the prosecutor will file a superseding information that lowers the quantities and the maximum sentence faced by that defendant. Since probation officers typically take their facts for the presentence report from the indictment, the information in the new indictment will reflect the lower applicable quantity. Human Rights Watch interview with Jed S. Rakoff, district court judge for the Southern District of New York, New York, NY, March 18, 2013.
[271] Stephen Schulhofer and Ilene H. Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period,” Northwestern University Law Review, vol. 91 (1997), p. 1293. The sentencing judge typically accepts the government’s representation even if it is “factually dubious.”
[272] Stith and Cabranes, Fear of Judging: Sentencing Guidelines in the Federal Courts, p. 134
[273] Special charge bargaining rules govern fast-track or early disposition programs that are used primarily in federal districts with huge caseloads from immigration cases or crimes connected to unlawful entry. Fast track programs permits charge bargaining by prosecutors that permit defendants to plead to less than most serious readily probable offense and permit downward departures of up to four levels from the sentencing guidelines base offense level.See former Attorney General John Ashcroft, “Department Principles for Implementing an Expedited or ‘Fast-Track’ Prosecution Program in the District,” September 22, 2003, http://www.lb7.uscourts.gov/documents/09-39321.pdf (accessed October 7, 2013). While there has been considerable criticism of such “assembly line justice,” defendants who do not take the fast track offer risk losing at trial and facing a decade or more in prison. Human Rights Watch, Turning Migrants Into Criminals: The Harmful Impact of US Border Prosecutions, May 2013, http://www.hrw.org/sites/default/files/reports/us0513_ForUpload_2.pdf.
[274]United States v. Green, 346 F.Supp.2d 259, 272 (D. Mass. 2004). An indictment may count many different charges, but since sentences typically run concurrently, if the charge carrying the longest sentence is maintained, dismissing the others will not affect the defendant’s sentence. See also Schulhofer and Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period,” Northwestern University Law Review, p. 1293 (charge bargaining which leads to the dismissal of readily provable counts is the most important vehicle for guidelines evasion). In theory, prosecutors are supposed to charge the most serious provable offense and to insist on pleas to the most serious offense, although they may dismiss counts pursuant to a plea if the ultimate sentence would not be reduced. Nevertheless, prosecutors sometimes will permit defendants to plead guilty to a lesser included offense that does not carry a mandatory minimum or that carries a lower mandatory minimum. See Attorney General Eric Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” August 12, 2013, http://www.popehat.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/holder-mandatory-drug-minimums-memo.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013) and John Ashcroft, “Memo Regarding Policy on Charging of Criminal Defendants,” September 22, 2003, http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/2003/September/03_ag_516.htm (accessed November 1, 2013).
[275] See Schulhofer and Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period, “Northwestern University Law Review.
[276] Such a plea may also delineate the various guidelines factors adjusting the sentencing range to which the prosecutor and the defendant have agreed. If the plea agreement falls under Rule 11b(1)(B), the defendant is bound by the plea agreement even if the judge does not adopt the recommended sentence. If the plea agreements falls under Rule 11b(1)(C) and the judge accepts the plea agreement, then the sentence is binding on the court. This latter type of plea agreement was rarely used in the past. Defense counsel suggested to Human Rights Watch that its use has increased since the sentencing guidelines became advisory because it provides a way for prosecutors to bind judges who might otherwise exercise their discretion to sentence below the guidelines range. See also United States Sentencing Commission (USSC), “Report to the Congress: Mandatory Minimum Penalties in the Federal Criminal Justice System,” October 2011, http://www.ussc.gov/Legislative_and_Public_Affairs/Congressional_Testimony_and_Reports/Mandatory_Minimum_Penalties/20111031_RtC_Mandatory_Minimum.cfm, p. 109 (prosecutors in some districts reported that the use of 11(c)(1)(C) agreements had increased after the Supreme Court decision in Booker rendering the guidelines advisory).
[277] Federal Rule of Criminal Procedure 11(c). For an overview of role of US and German judges in plea bargaining and an argument for greater judicial participation to encourage a plea process that is more likely to be fair, transparent and true to the facts, see Jenia Iontcheva Turner, “Judicial Participation in Plea Negotiations: A Comparative View,” American Journal of Comparative Law, vol. 54 (2006), p. 199.
[278] Federal Rule of Criminal Procedure 11(b) provides:
“(1) Before the court accepts a plea of guilty or nolo contendere, the defendant may be placed under oath, and the court must address the defendant personally in open court. During this address, the court must inform the defendant of, and determine that the defendant understands, the following:
(A) the government's right, in a prosecution for perjury or false statement, to use against the defendant any statement that the defendant gives under oath;
(B) the right to plead not guilty, or having already so pleaded, to persist in that plea;
(C) the right to a jury trial;
(D) the right to be represented by counsel—and if necessary have the court appoint counsel—at trial and at every other stage of the proceeding;
(E) the right at trial to confront and cross-examine adverse witnesses, to be protected from compelled self-incrimination, to testify and present evidence, and to compel the attendance of witnesses;
(F) the defendant's waiver of these trial rights if the court accepts a plea of guilty or nolo contendere;
(G) the nature of each charge to which the defendant is pleading;
(H) any maximum possible penalty, including imprisonment, fine, and term of supervised release;
(I) any mandatory minimum penalty;
(J) any applicable forfeiture;
(K) the court's authority to order restitution;
(L) the court's obligation to impose a special assessment;
(M) in determining a sentence, the court's obligation to calculate the applicable sentencing-guideline range and to consider that range, possible departures under the Sentencing Guidelines, and other sentencing factors under 18 U.S.C. §3553(a); and
(N) the terms of any plea-agreement provision waiving the right to appeal or to collaterally attack the sentence.
(2) Ensuring That a Plea Is Voluntary. Before accepting a plea of guilty or nolo contendere, the court must address the defendant personally in open court and determine that the plea is voluntary and did not result from force, threats, or promises (other than promises in a plea agreement).
(3) Determining the Factual Basis for a Plea. Before entering judgment on a guilty plea, the court must determine that there is a factual basis for the plea.”
[279] Wright, “Trial Distortion and the End of Innocence in Federal Criminal Justice,” University of Pennsylvania Law Review.
[280] See, e.g., United States v. Orkisz, United States District Court for the District Court of Connecticut, Case No. 3:11CR-69, Transcript of Sentencing Hearing, February 5, 2013. United States v. Vega, United States District Court for the District of Connecticut, Case No. 3:11 CR 117, Sentencing Memorandum.
[281] See Schulhofer and Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period,” Northwestern University Law Review, pp. 1303-1305 for overview of why judicial oversight of pleas, the principal guidelines mechanism for controlling charge reductions in plea bargaining, has not worked as intended.
[282] Information on the case of Joseph Ida obtained from documents in United States v. Ida, United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, Case No. 1:11-cr-00345-08, which are available on PACER.
[283] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Judge Thelton Henderson, senior district judge, Northern District of California, San Francisco, California, June 11, 2013
[284]Berger v. United States. 295 U.S. 78, 88 (1935).
[285] See generally Bruce A. Green, “Why Should Prosecutors Seek Justice?,” Fordham Urban Law Journal, vol. 26 (1999), p. 607. Jonathan A. Rapping, “Who’s Guarding the Henhouse: How the American Prosecutor Came to Devour Those He Is Sworn to Protect,” Washburn Law Journal, vol. 51 (2012), p. 520. American Bar Association Standards, “Prosecution Function: Part I, General Standards,” http://www.americanbar.org/publications/criminal_justice_section_archive/crimjust_standards_pfunc_blk.html (accessed October 8, 2013), Standard 3-1.2(b) (“The prosecutor is an administrator of justice, an advocate, and an officer of the court.”). The American Bar Association Model Rules of Professional Conduct include a special rule 3.8 for prosecutors, “Special Responsibilities of a Prosecutor.”
[286] Green, “Why Should Prosecutors Seek Justice?,” Fordham Urban Law Journal, p. 620 (citing cases).
[287] Ibid., p. 608. Green also notes, “[P]rosecutorial conduct may implicate ethics in the broader sentence of involving what a prosecutor should do in situations where the law offers a choice, in other words, what are the most desirable ways to exercise ‘prosecutorial discretion,’ when is an exercise of discretion unfair or unwise, and when does the prosecutor engage in an ‘abuse of discretion’ (albeit, one that may not be subject to any sanction or remedy). For the most part, these kinds of questions are not squarely answered by legal provisions, judicial decisions or disciplinary rules. Often they are not asked.” Ibid., p. 619.
[288] Just punishments are generally understood as being proportionate to the conduct and culpability of the offender and no greater than necessary to advance the purposes of punishment. The closest to a directive to seek just sentences may be a memorandum to prosecutors from former Attorney General Janet Reno stating that in making charging and plea decisions, “it is appropriate that the attorney for the government consider, inter alia, such factors as the sentencing guideline range yielded by the charge, whether the penalty yielded by such sentencing range (or potential mandatory minimum charge, if applicable) is proportional to the seriousness of the defendant’s conduct, and whether the charge achieves such purposes of the criminal law as punishment, protection of the public, specific and general deterrence, and rehabilitation.” Janet Reno, “Reno Bluesheet on Charging and Plea Decisions,” October 12, 1993 (“Reno Memorandum”), reprinted in Federal Sentencing Reporter, vol. 1 (May/June 1994). Nevertheless, the memorandum is ambiguous as to whether the concern is to ensure sentences that are sufficiently long to be commensurate with the offense, or whether concern about proportionality also includes sentences that might be disproportionately long. We also note that the Reno formulation does not call for sentences no longer than necessary to further the purposes of punishment. Reno’s position is reflected in the non-binding principles of the US Attorneys’ manual:“[I]n determining ‘the most serious offense that is consistent with the nature of the defendant's conduct that is likely to result in a sustainable conviction,’ it is appropriate that the attorney for the government consider, inter alia, such factors as the Sentencing Guideline range yielded by the charge, whether the penalty yielded by such sentencing range (or potential mandatory minimum charge, if applicable) is proportional to the seriousness of the defendant's conduct, and whether the charge achieves such purposes of the criminal law as punishment, protection of the public, specific and general deterrence, and rehabilitation. Note that these factors may also be considered by the attorney for the government when entering into plea agreements.” Department of Justice, US Attorneys’ Criminal Resources Manual, “Principles of Federal Prosecution,” http://www.justice.gov/usao/eousa/foia_reading_room/usam/title9/27mcrm.htm#9-27.300 (accessed November 1, 2013), Section 9-27.300.
[289] American Bar Association Standards, “Prosecution Function: Part I, General Standards,” http://www.americanbar.org/publications/criminal_justice_section_archive/crimjust_standards_pfunc_blk.html, Standard 3-3.9(b)(ii).
[290] The Principles of Federal Prosecution, originally published by the Department of Justice in 1980 and revised periodically, suggest prosecutors ordinarily should charge a defendant with the most serious offense consistent with his conduct. Department of Justice, US Attorneys’ Criminal Resources Manual, “Principles of Federal Prosecution,” Part C, http://www.justice.gov/usao/eousa/foia_reading_room/usam/title9/27mcrm.htm#9-27.300.
[291] Attorney General Eric Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” August 12, 2013, http://www.popehat.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/holder-mandatory-drug-minimums-memo.pdf, p. 2: “[P]rosecutors should ordinarily charge the most serious offense that is consistent with the nature of the defendant’s conduct, and that is likely to result in a sustainable conviction.” Attorney General Eric H. Holder, “Memorandum to all Federal Prosecutors, Department Policy on Charging and Sentencing,” May 19, 2010; Eric Tirschwell, “Holder Memorandum Presents New Opportunities for Defense Advocacy,” The New York Law Journal, vol. 243 (June 16, 2010). Ashcroft, “Memo Regarding Policy on Charging of Criminal Defendants,” September 22, 2003, http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/2003/September/03_ag_516.htm. Attorney General Ashcroft’s memorandum said prosecutors must choose the “most serious, readily provable charge” and that the most serious offense must be part of any plea agreement subject to limited exceptions in which not including them was in the government’s interest. See also Reno, “Reno Bluesheet on Charging and Plea Decisions,” October 12, 1993, reprinted in Federal Sentencing Reporter, supra note. 267.
[292] Holder, “Memorandum to all Federal Prosecutors, Department Policy on Charging and Sentencing,” May 19, 2010, quoting from United States Attorneys’ Manual, 9-27.300.
[294] Attorney General Eric Holder, “Remarks at the Annual Meeting of the American Bar Association's House of Delegates,” August 12, 2013, http://www.justice.gov/iso/opa/ag/speeches/2013/ag-speech-130812.html (accessed November 1, 2013).
[295] Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” http://www.popehat.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/holder-mandatory-drug-minimums-memo.pdf, p. 3. Mandatory minimum sentences for drug offenders are only triggered if the charging document identifies the applicable specific drug quantity. There are various offenses with which drug offenders could be charged that do not carry mandatory sentences, most notably offenses that do not specify the quantity of drugs. Holder nonetheless instructed prosecutors to “be candid with the court, probation, and the public as to the full extent of the defendant’s culpability, including the quantity of drugs involved in the offense and the quantity attributable to the defendant’s role in the offense…”
[296] Paul J. Hofer, Policy Analyst, Federal Public and Community Defenders, “Memorandum Regarding
Estimate of Sentencing Effects of Holder Memo on Drug Mandatory Minimums,” September 9, 2013, revised September 17, 2013, http://www.fd.org/docs/latest-news/memo-on-holder-memo-impact-final.pdf?sfvrsn=2 (accessed November 1, 2013).
[297] “[I]n cases involving the applicability of Title 21 mandatory minimum sentences based on drug type and quantity, prosecutors should decline to charge the quantity necessary to trigger a mandatory minimum sentence if the defendant meets each of the following criteria: [1] The defendant’s relevant conduct does not involve the use of violence, the credible threat of violence, the possession of a weapon, the trafficking of drugs to or with minors, or the death or serious bodily injury of any person; [2] The defendant is not an organizer, leader, manager or supervisor of others within a criminal organization; [3] The defendant does not have significant ties to large-scale drug trafficking organizations, gangs, or cartels, and [4] The defendant does not have a significant criminal history. A significant criminal history will normally be evidenced by three or more criminal history points but may involve fewer or greater depending on the nature of any prior convictions.” Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” August 12, 2013,
[298] Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” http://www.popehat.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/holder-mandatory-drug-minimums-memo.pdf, p. 2. “However, in cases involving the applicability of Title 21 mandatory minimum sentences based on drug type and quantity, prosecutors should decline to charge the quantity necessary to trigger a mandatory minimum sentence if the defendant meets each of the following criteria: [1] The defendant’s relevant conduct does not involve the use of violence, the credible threat of violence, the possession of a weapon, the trafficking of drugs to or with minors, or the death or serious bodily injury of any person; [2] The defendant is not an organizer, leader, manager or supervisor of others within a criminal organization; [3] The defendant does not have significant ties to large-scale drug trafficking organizations, gangs, or cartels, and [4] The defendant does not have a significant criminal history. A significant criminal history will normally be evidenced by three or more criminal history points but may involve fewer or greater depending on the nature of any prior convictions.” Ibid.
[299] Ibid., p. 3.
[300] United States v. Kupa , No. 11-CR-345, 2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922, 125 (E.D.N.Y. 2013).
[301] Ibid. at 126.
[302] Holder, “Memorandum to the United States Attorneys and Assistant Attorney General for the Criminal Division: Department Policy on Charging Mandatory Minimum Sentences and Recidivist Enhancements in Certain Drug Cases,” http://www.popehat.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/holder-mandatory-drug-minimums-memo.pdf.
[303] Ashcroft, “Memo Regarding Policy on Charging of Criminal Defendants,” September 22, 2003, http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/2003/September/03_ag_516.htm. The memorandum does not say what prosecutors should do if there are two possible §924(c) counts.
[304] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former US Attorney (name withheld), April 25, 2013.
[305] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Robert Lund, assistant US attorney for the District of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, March 25, 2013.
[306]Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Tampa, Florida, May 29, 2013.
[307] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Judge Thelton Henderson, senior district judge, Northern District of California, San Francisco, California, June 11, 2013.
[308] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Scott Lassar, former US Attorney, Chicago, Illinois, April 6, 2013.
[309] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 1, 2013.
[310] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with Mary A. Mills, federal public defender, Tampa, Florida, June 3, 2013.
[311] Human Rights Watch interview with Stephen R. Sady, federal public defender, Portland, Oregon, May 9, 2013.
[312] Human Rights Watch interview with Deirdre von Dornum, federal public defender, Brooklyn, New York, April 15, 2013.
[313] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 13, 2013.
[314] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 1, 2013.
[315] Rachel Barkow, NYU law professor, quoted in Richard A. Oppel, “Sentencing Shift Gives New leverage to Prosecutors,” The New York Times, September 25, 2011, http://www.nytimes.com/2011/09/26/us/tough-sentences-help-prosecutors-push-for-plea-bargains.html?pagewanted=all (accessed October 8, 2013).
[316] See also Schulhofer and Nagel, “Plea Negotiations under the Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Guideline Circumvention and its Dynamics in the Post-Mistretta Period,” Northwestern University Law Review (Even prosecutors committed to drug enforcement and stringent sentencing of drug dealers sometimes view the guidelines sentences for [low-level] defendants as unnecessarily long and overly severe and will use their plea bargaining discretion to lessen sentence length.).
[317] As Justice Kennedy has pointed out, the sentence that would follow from conviction on the charges in the indictment is like “the sticker price for cars.” Neither the salesman (prosecutor) nor the consumer (defendant) expect the full price to be paid. Negotiation is expected. Lafler v. Cooper, 132 S. Ct. 1376, 1388 (2012).
[318] Human Rights Watch interviews with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, March 28, 2013 and May 16, 2013.
[319] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with assistant US attorney (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 13, 2013. He said that some prosecutors tell themselves defendants who do not plead should get higher sentences because the failure to plead indicates an absence of contrition— and hence is a predictor of recidivism. In his opinion, that argument is little more than rationalization for business as usual.
[320] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former US Attorney (name withheld), Utah, April 25, 2013.
[321] Human Rights Watch telephone interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), Los Angeles, California, June 19, 2013.
[322] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 22, 2013.
[323] Once a threat is made, it has to be carried out because “plea bargaining is what academics call a ‘repeat-play’ game; the same lawyers negotiate pleas again and again. A prosecutor who becomes known as a pushover will be taken advantage of, not once but many times.” United States v. Kupa, No. 11-CR-345,2013 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 146922, 59 (E.D.N.Y. 2013)(citing William J. Stuntz, The Collapse of American Criminal Justice (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2011), p. 258)).
[324] Human Rights Watch interview with former federal prosecutor (name withheld), New York, New York, April 1, 2013.
[325]United States v. Doutre, United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts, No. 1:08-cr-10215-PBS, Transcript of Sentencing, July 6, 2010, p. 4.
[326] See Methodology section. Our ability to shed light on the prevalence and impact of plea bargaining practices is limited by the lack of publicly accessible relevant data. We do not have data indicating how many defendants who pled guilty entered into plea agreements with the government. We do not have data on how many defendants who did enter into plea agreements benefitted from prosecutorial decisions to permit pleas to lesser included charges, to dismiss charges, to agree to guidelines sentencing factors that will reduce the sentence, or to refrain from filing additional charges. Finally, we do not have data that quantifies how often prosecutors file such superseding charges.
[327] Measuring the trial penalty is challenging because cases that plead guilty may differ from cases that go to trial in relevant ways other than the method of conviction. Some of these differences can be detected in the available data, but others are unmeasured. On the other hand, as discussed previously, some differences among cases, such as the amount of drug alleged by the government, whether a firearm enhancement under §924(c) was or wasn’t charged, and whether enhancements for prior convictions are applied, reflect prosecutorial charging decisions influenced by whether a defendant has been willing to plea or went to trial.
[328] Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm (accessed October 7, 2013). The magnitude of the difference between sentences imposed after guilty pleas compared to after trial in federal cases has remained relatively constant. In 2003, the average sentence for all federal defendants in cases resolved by plea was 54.7 months compared to 153.7 months for those resolved by trial, i.e., sentences after trial were roughly three times longer. Bureau of Justice Statistics, “Compendium of Federal Justice Statistics, 2003”, http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/cfjs03.pdf (accessed November 1, 2013), Table 5.3.
[329] Judges may reduce sentences below the range calculated under sentencing guidelines, although they may not reduce them below an applicable mandatory minimum. Interestingly, judges are more likely on their own to reduce sentences for those who go to trial than those who plead. Among those who went to trial 31.2 percent received judicially sponsored below guidelines sentences compared to 18.8 percent of defendants who pled guilty. It seems likely that judges give downward departures more frequently in cases that go to trial because those defendants do not benefit from government motions for downward departures; judges believe that absent departures, the sentences would be too severe. It is also possible that judges depart more frequently on their own in cases that go to trial because they are aware that many of these defendants have already been penalized for their refusal to plead through the prosecutors’ charging and plea bargaining decisions. Nevertheless, defendants who go to trial are still at a sentencing disadvantage despite their greater likelihood of receiving a departure initiated by the judge.
[330] The United States Sentencing Commission gathered data on a sample group of cases for 13,935 drug defendants from three fiscal years (FY 2006, 2008, and 2009) to determine eligibility for an §851 enhancement because of prior qualifying convictions and to determine in how many of the cases the enhancement was applied. At the request of Federal District Judge Mark Bennett, the Sentencing Commission provided him with the number and percentage of defendants in the sample who were eligible for the §851 penalty enhancement for each of the 94 federal districts and the number and percentage of the eligible defendants against whom the §851 was applied. It also provided aggregate data on the sentences received by the defendants depending on whether they pled and whether the enhancement was applied. Judge Bennett kindly provided the data to Human Rights Watch.
[331] We have no way of knowing how many of those who pled could have been charged with more than one §924(c) count or had additional §924(c) counts dismissed as part of the plea agreement.
[332] Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm.
[333] Out of a total of 984 defendants convicted of one or more §924(c) counts, 288 received a §5k1.1 sentence departure for substantial assistance, all but two of whom pled guilty. Human Rights Watch analysis of United States Sentencing Commission Fiscal Year 2012 Individual Data Files, http://www.ussc.gov/Research_and_Statistics/Datafiles/index.cfm.
[334] William J. Stuntz, The Collapse of American Criminal Justice (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2011), p. 58.
[335] For overview of plea bargaining in other countries, see Stephen C. Thaman, ed., World Plea Bargaining: Consensual Procedures and the Avoidance of the Full Criminal Trial (Durham: Carolina Academic Press, 2010); Laurie Levenson, “Peeking Behind the Plea Bargaining Process,” Loyola of Los Angeles Law Review, vol. 46 (December 2012), pp. 21-27.
[336] Observers have noted that the prevalence of coercive plea bargaining in the United States has negated in practice many of the gains in defendants’ substantive and procedural criminal justice rights since the 1960s. Stephen C. Thaman, “A Typology of Consensual Criminal Procedures: An Historical and Comparative Perspective on the Theory and Practice of Avoiding the Full Criminal Trial,” in World Plea Bargaining: Consensual Procedures and the Avoidance of the Full Criminal Trial, ed. Stephen C. Thaman (Durham: Carolina Academic Press, 2010), p. 327.
[337] Brief of the Office of the California State Federal public defender, the California Federal public defenders Association, and the California Attorneys for Criminal Justice as Amici Curiae in Support of the Respondent, Bordenkircher v. Hayes, 434 U.S. 357 (1978) at 3.
[338] Ibid. at 364.
[339] Justice William Brennan argued that the plea of a defendant “gripped by fear” is “‘not voluntary but … the product of duress as much so as choice reflecting physical constraint.’” in North Carolina v. Alford, 400 U.S. 25, 29 (1970) (Brennan, J., dissenting). In that case the defendant argued that his plea to second-degree murder was impermissibly coerced by his fear of a possible death sentence should he not plead. The majority disagreed.
[340]Bordenkircher v. Hayes, 434 U.S. 357, 363 (1978). See also United States v. Goodwin, 457 U.S. 368 (1982) (prosecutor’s decision to file additional charges against defendant after defendant refused to plead guilty does not give rise to presumption of vindictive prosecution).
[341]United States v. Andrews, 633 F.2d 449, 456 (6th Cir. 1980).
[342]United States v. Kent, 633 F.3d 920, 927 (9th Cir. 2011) (no vindictive prosecution where prosecutor filed §851 information enhancing sentence of defendant who was willing to plead guilty but not to cooperate with government).
[343] United States v. Hall , United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee, Case No. 3:07-cr-51, Report and Recommendation, December 20, 2007, p. 7; For similar rulings see, e.g., Irick v. United States, United States District Court for the Middle District of Georgia, Case Nos. 3:06-CR-32 and 3:09-CV-47, Transcript of 2255 Hearing, July 22, 2009. Looney v. United States, United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas, Case No. 7:09-CV-172, Report and Recommendation, August 28, 2012. United States v. Saltzman, 537 F.3d 353 (5th Cir. 2008).
[344] International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), adopted December 16, 1966, G.A. Res. 2200A (XXI), 21 U.N.
GAOR Supp. (No. 16) at 52, U.N. Doc. A/6316 (1966), 999 U.N.T.S. 171, entered into force March 23, 1976, ratified by the
United States on June 8, 1992, art. 14, par. 3(g).
[345] Manfred Nowak, U.N. Covenant on Civil and Political Rights: CCPR Commentary (Kehl: N.P. Engel, 1993), p. 265.
[346] See UN Human Rights Committee, General Comment 32, Article 14, par. 41, Compilation of General
Comments and General Recommendations Adopted by Human Rights Treaty Bodies, UN Doc. U.N. Doc. CCPR/C/GC/32 (2007); The cases in which the Human Rights Committee has considered the question have usually involved allegations of torture or physical abuse, e.g. , Singarasa v. Sri Lanka (2004); Deolall v. Guyana (2005); Kurbonov v. Tajikistan(2006); Uteeva v. Uzbekistan (2007).
[347]Allen v. United Kingdom, European Court of Human Rights 702 (2002).
[348] Karsten Altenhain, “Absprachen in German Criminal Trials,” in World Plea Bargaining: Consensual Procedures and the Avoidance of the Full Criminal Trial, ed. Stephen C. Thaman (Durham: Carolina Academic Press, 2010), pp.169-70. The sentencing parameters for guilt is the range within which a sentence can be considered as appropriate and within which the judge can choose an actual sentence. Ibid., p. 170, fn. 49.See also, Jenia Iontcheva Turner, “Judicial Participation in Plea Negotations: A Comparative View,” American Journal of Comparative Law, vol. 54(2006), p. 232 (the Federal Supreme Court has held that the defendant cannot be pressured to enter a plea bargain through threats of a higher sentence).
[349] Jenia Iontcheva Turner, “Judicial Participation in Plea Negotiations: A Comparative View,” American Journal of Comparative Law, p. 235.
[350] Information on the case of LaShonda Hall obtained from court documents filed United States v. Hall, United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee, Case No. 3:07-cr-00051, which are available on PACER.
[351] Harmelin v. Michigan , 501 U.S. 957 (1991).
[352]United States v. Looney, 532 F. 3d 392, 397 (5th Cir. 2008). There are numerous examples of courts refusing to find long drug sentences unconstitutional. E.g., United States v. Natacha Jihad Pizarro-Campos, 506 Fed. Appx. 947 (11th Cir. 2013)(10-year sentence for methamphetamine distribution not grossly disproportionate; in view of precedent; in addition, offense threatened grave harm to society because of detrimental effect that methamphetamine has on users and because of the crimes of violence associated with its distribution and sale. (United States v. Kelsor, 665 F.3d 684, 701 (6th Cir. 2011) (mandatory life sentence without parole for third felony drug conviction is not “grossly disproportionate” to the crime).
[353]United States v. Bernall, 417 Fed. Appx. 865 (11th Cir. 2011). Bernall was also sentenced to a consecutive 60 months after his life sentence for a § 924(c) violation.
[354] For other contexts in which Human Rights Watch has discussed the need for proportionate and parsimonious sentences in the United States, see, Human Rights Watch, Old Behind Bars: The Aging Prison Population in the United States, January 2012, http://www.hrw.org/sites/default/files/reports/usprisons0112webwcover_0.pdf; Human Rights Watch, Cruel and Usual: Disproportionate Sentences for New York Drug Offenders, Vol. 9, No. 2 (B), May 1997, http://www.hrw.org/reports/1997/usny/; Jamie Fellner (Human Rights Watch), “The Human Rights Paradigm: The Foundation for a Criminal Justice System We Can Be Proud Of,” commentary, The Sentencing Project: 25 Experts Envision the Next 25 Years of Reform, March 21, 2012, http://www.hrw.org/news/2012/03/21/human-rights-paradigm-foundation-criminal-justice-system-we-can-be-proud; Human Rights Watch, The Answer is No: Too Little Compassionate Release in US Federal Prisons, November 2012, http://www.hrw.org/sites/default/files/reports/us1112ForUploadSm.pdf.
[355] The prohibition of what are variously described as cruel, unusual, inhuman, or degrading punishments found in many national constitutions as well as in international and regional human rights treaties is the primary basis for prohibitions of grossly disproportionate sentences. Dirk van Zyl Smit and Andrew Ashworth, “Disproportionate Sentences as Human Right Violations,” The Modern Law Review, vol. 67 no. 4 (July 2004), p. 543. Article 7 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights provides that “No one shall be subjected to torture or to cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment.” The European Court of Human Rights has recognized that disproportionately severe sentences can be incompatible with the prohibition on inhuman punishment in Article 3 of the European Convention on Human Rights. For a discussion of proportionality in US constitutional jurisprudence addressing the length of sentences, see Richard S. Frase, “Excessive Prison Sentences, Punishment Goals, and the Eighth Amendment: ‘Proportionality’ Relative to What?” Minnesota Law Review, vol. 89 (February 2005), p. 571.